Abstract
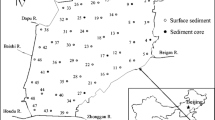
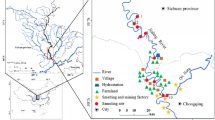
The concentrations, sources, and risks of heavy metals (Fe, Al, Mn, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, W, Pb, and Tl) in sediments in five river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake region were studied. The concentrations of the heavy metals varied spatially, with most of the highest concentrations in the Raohe river-lake ecosystem (RH). All heavy metals except As, Cd, W, and Tl were enriched in sediments possessing high total organic carbon contents or in finer sediments. Based on enrichment factors and statistical methods, it was found that Cd in sediments in the Xiushui (XS), Ganjiang (GJ), Xinjiang (XJ) river-lake ecosystems, and RH; Mn in the XS, GJ, and RH; and W in the XS and GJ were greatly affected by anthropogenic inputs. Moreover, the origins of Cu, Zn, and As require more attention due to the high concentrations found. The high enrichment factor of Cd in the sediments indicated that this metal might cause significant pollution in the environment. The results of the modified potential ecological risk index revealed that the XS, GJ, RH, and XJ were at considerable ecological risk, while the sediments in the Fuhe river-lake ecosystem (FH) were at moderate ecological risk, with Cd contributing the highest proportion of risk. The hazard score fundamentally validated the modified potential ecological risk analysis and revealed a mean toxicity of 57.80% to the benthic organisms in the RH.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad NI, Noh MFM, Mahiyuddin WRW, Jaafar H, Isha I, Azmi WNFW, Veloo Y, Hairi MH (2015) Mercury levels of marine fish commonly consumed in Peninsular Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3672–3686
Ahmed MK, Baki MA, Islam MS, Kundu GK, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Sarkar SK, Hossain MM (2015) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in tropical fish and shellfish collected from the river Buriganga, Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:15880–15890
Alves RI, Sampaio CF, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Segura-Muñoz SI (2014) Metal concentrations in surface water and sediments from Pardo River, Brazil: human health risks. Environ Res 133:149–155
Amin B, Ismail A, Arshad A, Yap CK, Kamarudin MS (2009) Anthropogenic impacts on heavy metal concentrations in the coastal sediments of Dumai, Indonesia. Environ Monit Assess 148:291–305
Brady JP, Ayoko GA, Martens WN, Goonetilleke A (2015) Development of a hybrid pollution index for heavy metals in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Monit Assess 187:1–14
Cai Y, Zhang W, Zhou M, Jiang H, Xu D, An S, Leng X (2015) Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the inflow rivers of Taihu Basin. Clean Soil Air Water 43:1582–1591
Calmano W, Hong J, Förstner U (1993) Binding and mobilization of heavy metals in contaminated sediments affected by pH and redox potential. Water Sci Technol 28(8–9):223–235
Cao QQ, Song Y, Zhang YR, Wang RQ, Liu J (2015) Risk analysis on heavy metal contamination in sediments of rivers flowing into Nansi Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–9
Chen H, Chen R, Teng Y, Wu J (2016) Contamination characteristics, ecological risk and source identification of trace metals in sediments of the Le'an River (China). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:85–92
Cheng HX, Li M, Zhao CD, Yang K, Li K, Peng M, Yang ZF, Liu F, Liu YH, Bai RR et al (2015) Concentrations of toxic metals and ecological risk assessment for sediments of major freshwater lakes in China. J Geochem Explor 57:15–26
CNMN (Nonferrous metal net of China) (2014) Asia's largest open pit copper mine: Dexing copper mine http://www.cnmn.com.cn/ShowNews1.aspx?id=294433. Accessed 26 February 2017
Duodu GO, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA (2016) Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 34:526. doi:10.1007/s00343-015-4240-5
Feng CH, Zhao S, Wang DX, Niu JF, Shen ZY (2014) Sedimentary records of metal speciation in the Yangtze Estuary: role of hydrological events. Chemosphere 107:415–422
Frémion F, Courtin-Nomade A, Bordas F, Lenain JF, Jugé P, Kestens T, Mourier B (2016) Impact of sediments resuspension on metal solubilization and water quality during recurrent reservoir sluicing management. Sci Total Environ 562:201–215
Gao X, Chen CTA (2012) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res 46:1901–1911
Gati G, Pop C, Brudaşcă F, Gurzău AE, Spînu M (2016) The ecological risk of heavy metals in sediment from the Danube Delta. Ecotoxicology 25:688–696
Gong XF, Chen CL, Zhou WB, Jian MF, Zhang ZH (2006) Assessment on heavy metal pollution in the sediment of Poyang Lake. Environ Sci 27:732–736 (in Chinese)
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hillbricht-Ilkowska A (1999) Shallow lakes in lowland river systems: role in transport and transformations of nutrients and in biological diversity. Hydrobiologia 408:349–358
Hu CH, Zhou P, Huang P, Du J, Zhou WB (2012) Behavior characteristics of dissolved heavy metals and health risks assessment from Poyang Lake Basin, China. J Agric Environ Sci 31(5):1009–1014
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Islam MK (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol Indic 48:282–291
Jamshidi S, Bastami KD (2016) Metal contamination and its ecological risk assessment in the surface sediments of Anzali wetland, Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.08.049
Ji Y, Zhang J, Li R, Pan B, Zhang L, Chen X (2015) Distribution and partitioning of heavy metals in sediments of the Xinjiang River in Poyang Lake Region, China. Environ Prog Sustain 34:713–723
Jian MF, You H, Ni CY (2006) Characteristics of heavy metal contaminant status and migration in Rao River of Lake Poyang. J Lake Sci 18:127–224 (in Chinese)
Jiang F, Qi SH, Liao FQ, Zhang XX, Wang D, Zhu JX, Xiong MY (2015) Hydrological and sediment effects from sand mining in Poyang Lake during 2001-2010. Acta Geograph Sin 70:837–845 (in Chinese)
Jiang X, Xiong Z, Liu H, Liu G, Liu W (2017) Distribution, source identification, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in wetland soils of a river–reservoir system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(1):436–444
Kim HT, Kim JG (2016) Uptake of cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc from sediments by an aquatic macrophyte and by terrestrial arthropods in a freshwater wetland ecosystem. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 71:198–209
Kwon YT, Lee CW, Ahn BY (2001) Sedimentation pattern and sediments bioavailability in a wastewater discharging area by sequential metal analysis. Microchem J 68:135–141
Lee S, Moon JW, Moon HS (2003) Heavy metals in the bed and suspended sediments of Anyang river, Korea: implications for water quality. Environ Geochem Health 25:433–452
Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Risk assessment and seasonal variations of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Upper Han River, China. J Hazard Mater 181:1051–1058
Li M, Wu JC, Li LQ (2008) Absorption and accumulation of heavy metals by plants in Poyang Lake wetland. J Agric Environ Sci 27(6):2413–2418
Li L, Cui J, Liu J, Gao J, Bai Y, Shi X (2016) Extensive study of potential harmful elements (Ag, As, Hg, Sb, and Se) in surface sediments of the Bohai Sea, China: Sources and environmental risks. Environ Pollut. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.034
Ling CH, Long J, Jiang YL, Hong YJ, Xu CQ, Wang PL (2015) Geochemical characteristics and palaeoclimate significance of the Quaternary laterite of Tutan section in Poyang Lake region, northern Jiangxi Province. J Palaeogeogr 17:699–708
Lu YZ (2006) Characteristics of distribution and transport of heavy metals in multi-phase system of natural waters. Doctor’s Thesis. Jilin University, Jilin, China
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
McPhedran KN, Grgicak-Mannion A, Paterson G, Briggs T, Ciborowski JJ, Haffner GD, Drouillard KG (2016) Assessment of hazard metrics for predicting field benthic invertebrate toxicity in the Detroit River, Ontario. Integr Environ Asses, Canada http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ieam.1785/epdf
Möller S, Einax JW (2013) Metals in sediments—spatial investigation of Saale River applying chemometric tools. Microchem J 110:233–238
Mwanamoki PM, Devarajan N, Thevenon F, Birane N, De Alencastro LF, Grandjean D et al (2014) Trace metals and persistent organic pollutants in sediments from river-reservoir systems in Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC): spatial distribution and potential ecotoxicological effects. Chemosphere 111:485–492
Mwanamoki PM, Devarajan N, Niane B, Ngelinkoto P, Thevenon F, Nlandu JW et al (2015) Trace metal distributions in the sediments from river-reservoir systems: case of the Congo River and Lake ma Vallée, Kinshasa (Democratic Republic of Congo). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(1):586–597
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of Soil Analysis. American Society of Agronomy, Wisconsin, pp 539–579
Pandey M, Pandey AK, Mishra A, Tripathi BD (2015) Application of chemometric analysis and self organizing map-artificial neural network as source receptor modeling for metal speciation in river sediment. Environ Pollut 204:64–73
Price NB, Brand T, Pates JM, Mowbray S, Theocharis A, Civitarese G, Miserocchi S, Heussner S, Lindsay F (1999) Horizontal distributions of biogenic and lithogenic elements of suspended particulate matter in the Mediterranean Sea. Prog Oceanogr 44:191–218
Ren TX, Wu ZH, Qiang RS (1998) Screening approach and fellow-up technology for regional geochemical anomalies. Geological publishing hourse, Beijing, pp 1–137 (in Chinese)
Rifaat AE (2005) Major controls of some metals distribution in sediments off the Nile Delta, Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Res 31:16–28
Sakan SM, Đorđević DS, Manojlović DD, Predrag PS (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J Envion Manag 90(11):3382–3390
Sundaramanickam A, Shanmugam N, Cholan S, Kumaresan S, Madeswaran P, Balasubramanian T (2016) Spatial variability of heavy metals in estuarine, mangrove and coastal ecosystems along Parangipettai, southeast coast of India. Environ Pollut 218:186–195
Suresh B, Ravishankar GA (2004) Phytoremediation—a novel and promising approach for environmental clean-up. Crit Rev Biotechnol 24:97–124
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39:611–627
Teng Y, Li J, Wu J, Lu S, Wang Y, Chen H (2015) Environmental distribution and associated human health risk due to trace elements and organic compounds in soil in Jiangxi province, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:406–416
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Varol M (2013) Dissolved heavy metal concentrations of the Kralkızı, Dicle and batman dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. Chemosphere 93(6):954–962
Wang SR (2014) Ecological security of Poyang Lake. Science Press, Beijing, pp 46–125 (in Chinese)
Wang L, Wang YP, Xu CY, An ZY (2012) Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Yangtze River. Environ Sci 33(8):2599–2606 (in Chinese)
Wei F, Chen J, Wu Y (1990) Background element values in soils of China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 329–493 (in Chinese)
Wei X, Han L, Gao B, Zhou HLJ, Wan X (2016) Distribution, bioavailability, and potential risk assessment of the metals in tributary sediments of three gorges reservoir: the impact of water impoundment. Ecol Indic 61:667–675
Xie X, Ren T, Sun H (2012) Geochemical atlas of China. Geological publishing hourse, Beijing, pp 1–121 (in Chinese)
Xie ZL, Jiang YH, Zhang HZ, Wang D, Qi SH, Du ZB, Zhang H (2016) Assessing heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in Poyang Lake area, China. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–15
Xu ZQ, Ni SJ, Tuo XG, Zhang CJ (2008) Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ Sci Technol 31:112–115 (in Chinese)
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river basin. Environ Pollut 159:2575–2585
Yi YJ, Sun J, Tang CH, Zhang SH (2016) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment in the upper reach of the Yangtze River. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:11002–11013
Yu Y, Wang H, Li Q, Wang B, Yan Z, Ding A (2016) Exposure risk of rural residents to copper in the Le’an River Basin, Jiangxi Province, China. Sci Total Environ 548:402–407
Yuan GL, Liu C, Chen L, Yang Z (2011) Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang lake in China. J Hazard Mater 185:336–345
Yuan GL, Sun TH, Han P, Li J, Lang XX (2014) Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China. J Geochem Explor 136:40–47
Zahra A, Hashmi MZ, Malik RN, Ahmed Z (2014) Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah—feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake reservoir, Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 470:925–933
Zeng XX, Liu YG, You SH, Tan XF ZGM, Hu XJ, Hu X, Huang L, Li F (2015) Spatial distribution, health risk assessment and statistical source identification of the trace elements in surface water from the Xiangjiang River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:9400–9412
Zhang H, Shan B (2008) Historical records of heavy metal accumulation in sediments and the relationship with agricultural intensification in the Yangtze–Huaihe region, China. Sci Total Environ 399:113–120
Zhang H, Wang ZF, Zhang YL, Hu ZJ (2012) The effects of the Qinghai–Tibet railway on heavy metals enrichment in soils. Sci Total Environ 439:240–248
Zhang C, Yu ZG, Zeng GM, Jiang M, Yang ZZ, Cui F, Zhu M, Shen L, Hu L (2014a) Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ Int 73:270–281
Zhang WL, Du Y, Zhai MM, Shang Q (2014b) Cadmium exposure and its health effects: a 19-year follow-up study of a polluted area in China. Sci Total Environ 470:224–228
Zhang ZY, Abuduwaili J, Jiang FQ (2015a) Heavy metal contamination, sources, and pollution assessment of surface water in the Tianshan Mountains of China. Environ Monit Assess 187:1–13
Zhang H, Wang ZF, Zhang YL, Ding MJ, Li LH (2015b) Identification of traffic-related metals and the effects of different environments on their enrichment in roadside soils along the Qinghai–Tibet highway. Sci Total Environ 521:160–172
Zhang H, Jiang YH, Yang T, Wang M, Shi GX, Ding MJ (2016) Heavy metal concentrations and risk assessment of sediments and surface water of the Gan River, China. Pol J Environ Stud 25:1529–1540
Zhao QG, Huang GQ, Qian HY (2007) Ecological environment and sustainable development of Poyang Lake. Acta Pedol Sin 44:318–326 (in Chinese)
Zohra BS, Habib A (2016) Assessment of heavy metal contamination levels and toxicity in sediments and fishes from the Mediterranean Sea (southern coast of Sfax, Tunisia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:13954. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-6534-3
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank three anonymous referees for their helpful comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41401587), the Science and Technology Research Project of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (grant no. GJJ160276), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20171BAB213023), and the Collaborative Innovation Center for Major Ecological Security Issues of Jiangxi Province and Monitoring Implementation (grant no. JXS-EW-00). The authors are grateful to Ms. LING Chunyuan and Ms. XU Xiaoling for their suggestions on the revised manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 195 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Jiang, Y., Ding, M. et al. Level, source identification, and risk analysis of heavy metal in surface sediments from river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 21902–21916 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9855-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9855-y