Abstract
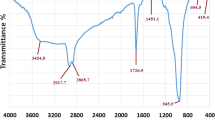
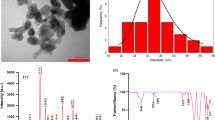
The cytotoxicity of nanoparticles (NPs) and their properties are important issues in nanotechnology research. Particularly, NPs affect the metabolism of microorganisms due to NP interactions with some biomolecules. In order to assess the mechanisms underlying NPs toxicity, we studied the damage caused by copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) on Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 24213 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27833. Spherical CuO-NPs characterized by their diameter (13 ± 3 nm) were synthesized with a maximum of 254 nm. These NPs reduced cell viability, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 500 and 700 ppm for Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, respectively. Surfactant was added to reduce the NP agglomeration, but it did not present any effect. The mechanism of CuO-NPs as antimicrobial agent was assessed by analyzing solubilized Cu2+, quantifying DNA release in the culture media, and measuring intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). CuO-NPs induced severe damage on cells as revealed by confocal optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Our results indicated that CuO-NPs interacted with bacteria, triggering an intracellular signaling network which produced oxidative stress, leading to ROS generation. Finally, we concluded that CuO-NPs exhibited higher antibacterial activity on Gram-negative bacteria than on Gram-positive ones.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anaya MN, Faghihzadeh F, Ganji N, Bothun G, Craver VO (2016) Comparative study between chemostat and batch reactors to quantify membrane permeability changes on bacteria exposed to silver nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 565:841–848
Applerot G, Lellouche J, Lipovsky A, Nitzan Y, Lubart R, Gedanken A, Banin E (2012a) Understanding the antibacterial mechanism of CuO nanoparticles: revealing the route of induced oxidative stress. Biomed Mater. doi:10.1002/smll.201200772
Applerot G, Lellouche J, Lipovsky A, Nitzan Y, Lubart R, Gedanken A, Banin E (2012b) Understanding the antibacterial mechanism of CuO nanoparticles: revealing the route of induced oxidative stress. Small 8(21):3326–3337. doi:10.1002/smll.201200772
Askarinezhad A, Morsali A (2008) Synthesis and characterization of CdCO3 and CdO nanoparticles by using a sonochemical method. Mater Lett 62:478–482
Aysaa NH, Salmanb HD (2016) Antibacterial activity of modified zinc oxide nanoparticles against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa isolates of burn infections. World Sci News 33:1–14
Azam A, Ahmed AS, Oves M, Khan M, Memic A (2012) Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of CuO nanoparticles against Gram-positive and -negative bacterial strains. Int J Nanomedicine 7:3527–3535
Baek YW, An YJ (2011) Microbial toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO, NiO, ZnO, and Sb2O3) to Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Total Environ 409:1603–1608
Batrakova EV, Kabonov AV (2008) Pluronic block copolymers: evolution of drug delivery concept from inert Nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. Control Release 130(2):98–106
Bijanzadeh AR, Vakili MR, Khordad R (2012) Astudy of the surface plasmon absorption band for nanoparticles. Int J Phys Sci 7(12):1943–1948
Blinova I, Ivask A, Heinlaan M, Mortimer M, Kahru A (2010) Ecotoxicity of nanoparticles of CuO and ZnO in natural water. Environ Pollut 158:41–47
Bogoslovskaja OA, Rakhmetova AA, Ovsyannikova MN, Olkhovskaya IP, Gluschenko NN (2014) Antimicrobial effect of copper nanoparticles with differing dispersion and phase composition. Nanotechnol Russia 9(1):82–86
Bondarenko O, Ivask A, Käkinen A, Kahru A (2012) Sub-toxic effects of CuO nanoparticles on bacteria: kinetics, role of cu ions and possible mechanisms of action. Environ Pollut 169:81–89
Bondarenko O, Juganson K, Ivask A, Kasemets K, Mortimer M, Kahru A (2013) Toxicity of ag, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles to selected environmentally relevant test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: a critical review. Arch Toxicol 87:1181–1200
Brayner R (2008) The toxicological impact of nanoparticles. Nano Today 3:48–55
Chang Y, Zhang M, Xia L, Zhang J, Xin G (2012) The toxic effects and mechanisms of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles. Materials 5:2850–2871
Chávez-Calderón A, Paraguay-Delgado F, Orrantia-Borunda E, Luna-Velazco A (2016) Size effect of SnO2 nanoparticles on bacteria toxicity and their membrane damage. Chemosphere 165:33–40
Chen PP, Mwakwari SC, Oyelere AK (2008) Gold nanoparticles: from nanomedicine to nanosensing. Review. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 1:45–65
Choi O, Hu Z (2009) Role of reactive oxygen species in determining nitrification inhibition bymetallic/oxide nanoparticles. J Environ Eng 135(12):1365–1370
Christy AJ, Nehru LC, Umadevi M (2013) A novel combustion method to prepare CuOnanorods and its antimicrobial and photocatalytic activities. Powder Technol 235:783–786
Concha-Guerrero SI, Souza-Brito EM, Piñón-Castillo HA, Tarango-Rivero SH, Caretta CA, Luna-Velazco A, Duran R, Orrantia-Borunda E (2014) Effect of CuO nanoparticles over isolated bacterial strains from agricultural soil. J Nanomater 2014:1–13
Cronholm P, Karlsson HL, Hedberg J, Lowe T, Winnberg L, Elihn K, Odnevall WI, Möller L (2013) Intracellular uptake and toxicity of ag- and CuOnanoparticles– a comparison between nanoparticles and their corresponding metal ion. Small 9:970–982
Cui Y, Zhao Y, Tian Y, Zhang W, Lu X, Jiang X (2012) The molecular mechanism of action of bactericidal gold nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Biomaterials 33(7):2327–2333
Dasari TP, Pathakoti P, Hwang H (2013) Determination of the mechanism of photoinduced toxicity of selected metal oxide nanoparticles (ZnO, CuO, Co3O4 and TiO2) to E. coli bacteria. J Environ Sci 25(5):882–888
De Berardis B, Civitelli G, Condello M, Lista P, Pozzi R, Arancia G, Meschini S (2010) Exposure to ZnO nanoparticles induces oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 246:116–127
Dimkpa CO, Calder A, Britt DW, McLean JE, Anderson AJ (2011) Responses of a soil bacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphisO6 to commercial metal oxide nanoparticles compared with responses tometal ions. Environ Pollut 159(7):1749–1756
Dutta RK, Nenavathu BP, Gangishetty MK, Reddy AVR (2012) Studies on antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles by ROS induced lipid peroxidation. Colloid Surf 94:143–150
Ebrahimnia-Bajestan E, Niazmand H, Duangthongsuk W, Wongwises S (2011) Numerical investigation of effective parameters in convective heat transfer of nanofluids flowing under a laminar flow regime. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54(19–20):4376–4388
Elsaesser A, Howard C (2012) Toxicology of nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:129–137
Fahmy B, Cormier SA (2009) Copper oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in airway epithelial cells. Toxicol In Vitro 23:1365–1371
Garcia-Saucedo C, Field JA, Otero-Gonzalez L, Sierra-Alvarez R (2011) Low toxicity of HfO2, SiO2, Al2O3 and CeO2 nanoparticles to the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Hazard Mater 192(3):1572–1579. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.081
Giannousi K, Hatzivassiliou E, Mourdikoudis S, Vourlias G, Pantazaki A, Dendrinou-Samara C (2016) Synthesis and biological evaluation of PEGylated CuO nanoparticles. J Inorg Biochem 164:82–90
Guo Z, Ng HW, Yee GL, Hahn HT (2009) Differential scanning calorimetry investigation on vinyl ester resin curing process for polymer nanocomposite fabrication. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9(5):3278–3285
Gupta P, Ramrakhiani M (2009) Influence of the particle size on the optical properties of CdSe nanoparticles. Open Nanosci J 3:15–19
Handy RD, Kammer FVD, Lead JR, Hassellov M, Owen R, Crane M (2008) Theecotoxicity and chemistry of manufactured nanoparticles. Ecotoxicology 17:287–314
Hou J, Wang X, Hayat T, Wang X (2017) Ecotoxicological effects and mechanism of CuO nanoparticles to individual organisms. Environ Pollut 221:209–217. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.066
Ivanov IE, Kintz EN, Porter LA, Goldberg JB, Burnham NA, Camesano TA (2011) Relating the physical properties of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa lipopolysaccharides to virulence by atomic force microscopy. J Bacteriol 193(5):1259–1266. doi:10.1128/JB.01308-10
Ivask A, Kurvet I, Kasemets K, Blinova I, Aruoja V, Suppi S, Vija H, Kakinen K, Titma T, Heinlaan M, Visnapuu M, Koller D, Kisand V, Kahru A (2014) Size-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles to bacteria, yeast, algae, crustaceans and mammalian cells in vitro. PLoS One 9(7):e102108. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102108
Jain TK, Morales MA, Sahoo SK, Leslie-Pelecky DL, Labhasetwar V (2005) Iron oxide nanoparticles for sustained delivery of anticancer agents. Mol Pharm 2(3):194–205. doi:10.1021/mp0500014
Javed R, Ahmed M, Haq I u, Nisa S, Zia M (2017) PVP and PEG doped CuO nanoparticles are more biologically active: antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic and cytotoxic perspective. Mater Sci Eng C 79:108–115. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.006
Jesuvathy Sornalatha D, Bhuvaneswari S, Murugesan S, Murugakoothan P (2015) Solochemical synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanostructures with different morphologies and their antibacterial activity. Optik 126(1):63–67
Ji Z, Jin X, George S, Xia T, Meng H, Wang X, Suarez E, Zhang H, Hoek EM, Godwin H, Nel A, Zink JI (2010) Dispersion and stability optimization of TiO2 nanoparticles in cell culture media. Environ Sci Technol 44(19):7309–7314
Joh DY, Kinder J, Herman LH, Ju SY, Segal MA, Johnson JN, Chan KL, Park J (2011) Single-walled carbon nanotubes as excitonic optical wires. Nat Nanotechol 6:51–56
Joost U, Juganson K, Visnapuu M, Mortimer M, Kahru A, Nommiste E, Joost U, Kisand V, Ivask A (2015) Photocatalytic antibacterial activity of nano-TiO2 (anatase)-based thin films: effects on Escherichia coli cells and fatty acids. J Photochem Photobiol B 142:178–185
Junqua M, Biolley JP, Pie S, Kanoun M, Duran R, Goulas P (2000) In vivo occurrence of carbonyl residues in Phaseolus vulgaris proteins as a direct consequence of a chronic ozone stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 38(11):853–861
Kang EB, Sharker SMd, In I, Park SY (2016) Pluronic mimicking fluorescent carbon nanoparticles conjugated with doxorubicin via acid-cleavable linkage for tumor-targeted drug delivery and bioimaging. J Ind Eng Chem 43:150-157
Karlsson HL, Cronholm P, Gustafsson J, Moller L (2008) Copper oxide nanoparticles are highly toxic: a comparison between metal oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1726–1732
Karlsson HL, Cronholm P, Hedberg Y, Tornberg M, Battice LD, Svedhem S, Wallinder IO (2013) Cell membrane damage and protein interaction induced by copper containing nanoparticles—importance of the metal release process. Toxicology 313:59–69
Kashmiri ZN, Mankar SA (2014) Free radicals and oxidative stress in bacteria. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 3(9):34–40
Kida T, Oka T, Nagano M (2007) Synthesis and application of stable copper oxide nanoparticle suspensions for Nanoparticulate film fabrication. J Am Ceram Soc 90(1):107–110
Kurzhals S, Gal N, Zirbs R, Reimhult E (2017) Aggregation of thermoresponsive core-shell nanoparticles: influence of particle concentration, dispersant molecular weight and grafting. J Colloid Interface Sci 500:321–332
Laha D, Pramanik A, Laskar A, Jana M, Pramanik P, Karmakar P (2014) Shape dependent bactericidal activity of copper oxide nanoparticle mediated by DNA and membrane damage. Mater Res Bull 59:185–191
Lanje AS, Sharma SJ, Pode RB, Ningthoujam RS (2010) Synthesis and optical characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles. Adv Appl Sci Res 1(2):36–40
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Van der Elst L, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108:2064–2110
Li Y, Liang J, Tao Z, Chen J (2007) CuO particles and plates: synthesis and gas-sensor application. Mater Res Bull 43:2380–2385
Ma R, Levard C, Marinakos SM, Cheng Y, Liu J et al (2012) Size-controlled dissolution of organic-coated silver nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 46:752–759
Ma H, Wallis LK, Diamond S, Li S, Canas-Carrell J, Parra A (2014) Impact of solar UV radiation on toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles through photocatalytic reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and photo-induced dissolution. Environ Pollut 193:165–172
Mahapatra O, Bhagat M, Gopalakrishnan C, Arunachalam KD (2008) Ultrafine dispersed CuO nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. J Exp Nanosci 3(3):185–193
Maldonado J, Solé A, Puyen ZM, Esteve I (2011) Selection of bioindicators to detect lead pollution in Ebro delta microbial mats, using high-resolution microscopic techniques. Aquat Toxicol 104(1–2):135–144
Margaritelis NV, Cobley JN, Paschalis V, Veskoukis AS, Theodorou AA, Kyparos A, Nikolaidis MG (2016) Going retro: oxidative stress biomarkers in modern redox biology. Free Radic Biol Med 98:2–12
Midander K, Cronholm P, Karlsson HL, Elihn K, Möller L, Leygraf C, Wallinder IO (2009) Surface characteristics, copper release, and toxicity of nano- and micrometer-sized copper and copper(II) oxide particles: a cross-disciplinary study. Small 5:389–399
Moritz M, Geszke M (2013) Thenewest achievements in synthesis, immobilization and practical applications of antibacterial nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 228:596–613
Nateche F, Martin A, Baraka S, Palomino JC, Khaled S, Portaels F (2009) Application of the resazurinmicrotitre assay for detection of multidrug resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis in Algiers. J Med Microbiol 55:857–860
Otero-Gonzalez L, Garcia-Saucedo C, Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2013) Toxicity of TiO(2), ZrO(2), Fe(0), Fe(2)O(3), and Mn(2)O(3) nanoparticles to the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chemosphere 93(6):1201–1206. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.075
Pisanic TR, Jin S, Shubayev VI (2009) Nanotoxicity: from in vivo and in vitro models to health risks. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., London, pp 397–425
Quinteros MA, Aristizábal VC, Dalmasso PR, Paraje MG, Páez PL (2016) Oxidative stress generation of silver nanoparticles in three bacterial genera and its relationship with the antimicrobial activity. Toxicol in Vitro 36:216–223
Raffi M, Mehrwan S, Bhatti TM et al (2010) Investigations into the antibacterial behavior of copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 60(1):75–80
Raghupathi KR, Koodali RT, Manna AC (2011) Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 27:4020–4028
Rehman S, Mumtaz A, Hasanain SK (2011) Size effects on the magnetic and optical properties of CuO nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 13:2497–2507
Ren G, Hu D, Cheng EW, Vargas-Reus MA, Reip P, Allaker RP (2009) Characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33:587–590
Rispoli F, Angelov A, Badia D, Kumar A, Seal S, Shah V (2010) Understanding the toxicity of aggregated zero valent copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. J Hazard Mater 180:212–216
Rodrigues EC, Morales MA, de Medeiros SN, Suguihiro NM, Baggio-Saitovitch EM (2016) Pluronic® coated sterically stabilized magnetite nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications. J Magn Magn Mater 416:434–440. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.05.033
Sager TM, Porter DW, Robinson VA, Lindsley WG, Schwegler-Berry DE, Castranova V (2009) Improved method to disperse nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo investigation of toxicity. Nanotoxicology 1(2):118–129. doi:10.1080/17435390701381596
Sau TK, Rogach AL, Jackel F, Klar TA, Feldmann J (2010) Properties and applications of colloidal nonspherical noble metal nanoparticles. Adv Mater 22(16):1805–1825
Simon T, Boca S, Biro D, Baldeck P, Astilean S, (2013) Gold–Pluronic core–shell nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 15.
Song W, Zhang J, Guo J, Zhang J, Ding F, Li L, Sun Z (2010) Role of the dissolved zinc ion and reactive oxygen species in cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 199:389–397
Sonia S, Jayasudha R, Jayram ND, Kumar PS, Mangalaraj D, Prabagaran SR (2016) Synthesis of hierarchical CuO nanostructures: biocompatibleantibacterial agents for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Curr Appl Phys 16:914–921
Suttiponparnit K, Jiang J, Sahu M, Suvachittanont S, Charinpanitkul T, Biswas P (2010) Role of surface area, primary particles size, and crystal phase on titanium dioxide nanoparticle dispersion properties. Res Lett 6:27
Thomasson SA, Thomasson JR (2011) A comparison of CPD (critical point drying) and HMDS (Hexamethyldisilazane) in the preparation of Corallorhiza spp. rhizomes and associated mycorrhizae for SEM (scanning electron microscopy). Trans Kans Acad Sci 114(2):129–134
Toduka Y, Toyooka T, Ibuki Y (2012) Flow cytometric evaluation of nanoparticles using side-scattered light and reactive oxygen species—mediated fluorescence—correlation with genotoxicity. Environ Sci Technol 46:7629–7636
Vatankhah C, Saki M, Jafargholineja S (2015) Theoretical and experimental investigation of quantum confinement effect on the blue shift in semiconductor quantum dots. Orient J Chem 31(2):907–912
Wang Z, Li J, Zhao J, Xing B (2011) Toxicity and internalization of CuO nanoparticles to prokaryotic alga Microcystisaeruginosa as affected by dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 45(14):6032–6040. doi:10.1021/es2010573
Wang, Z, von dem Bussche, A, Kabadi, PK, Kane, AB, Hurt, RH (2013) Biological and environmental transformations of copper-based nanomaterials. ACS Nano 7, 8715-8727
Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Mädler L, Gilbert B, Shi H, Yeh JI, Zink JI, Nel AE (2008) Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano 2:2121–2134
Yan L, Zheng YB, Zhao F, Li S, Gao X, Xu B, Weiss PS, Zhao Y (2012) Chemistry and physics of a single atomic layer: strategies and challenges for functionalization of graphene and graphene-based materials. Chem Soc Rev 41:97–114
Yang H, Liu C, Yang DF, Zhang HS, Xi Z (2009) Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials: the role of particle size, shape and composition. J Appl Toxicol 29:69–78
Zhang DX, Gutterman DD (2007) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species-mediated signaling in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H2023–H2031
Zhang Q, Zhang K, Xu D, Yang G, Huang H, Nie F, Liu C, Yang S (2014) CuO nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, growth mechanisms, fundamental properties, and applications. Prog Mater Sci 60:208–337
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CONACyT-ConsejoNacional de Ciencia y Tecnología No. 175089 and ECOS NORD 263456. All authors contributed, read, and approved the final manuscript. The authors have declared no conflict of interest. The authors thank W. Antunez-Flores and Ochoa-Gamboa R.A. for technical support in electronic microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
(DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulloa-Ogaz, A.L., Piñón-Castillo, H.A., Muñoz-Castellanos, L.N. et al. Oxidative damage to Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27833 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 24213 induced by CuO-NPs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 22048–22060 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9718-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9718-6