Abstract
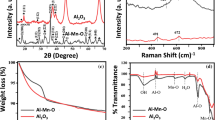
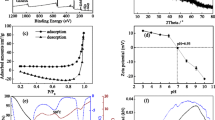
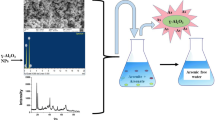
In order to remove arsenic (As) from contaminated water, granular Mn-oxide-doped Al oxide (GMAO) was fabricated using the compression method with the addition of organic binder. The analysis results of XRD, SEM, and BET indicated that GMAO was microporous with a large specific surface area of 54.26 m2/g, and it was formed through the aggregation of massive Al/Mn oxide nanoparticles with an amorphous pattern. EDX, mapping, FTIR, and XPS results showed the uniform distribution of Al/Mn elements and numerous hydroxyl groups on the adsorbent surface. Compression tests indicated a satisfactory mechanical strength of GMAO. Batch adsorption results showed that As(V) adsorption achieved equilibrium faster than As(III), whereas the maximum adsorption capacity of As(III) estimated from the Langmuir isotherm at 25 °C (48.52 mg/g) was greater than that of As(V) (37.94 mg/g). The As removal efficiency could be maintained in a wide pH range of 3~8. The presence of phosphate posed a significant adverse effect on As adsorption due to the competition mechanisms. In contrast, Ca2+ and Mg2+ could favor As adsorption via cation-bridge involvement. A regeneration method was developed by using sodium hydroxide solution for As elution from saturated adsorbents, which permitted GMAO to keep over 75% of its As adsorption capacity even after five adsorption–regeneration cycles. Column experiments showed that the breakthrough volumes for the treatment of As(III)-spiked and As(V)-spiked water (As concentration = 100 μg/L) were 2224 and 1952, respectively. Overall, GMAO is a potential adsorbent for effectively removing As from As-contaminated groundwater in filter application.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai Y, Elzinga EJ, Sparks DL (2001) X-ray absorption spectroscopic investigation of arsenite and arsenate adsorption at the aluminum oxide–water interface. J Colloid Interface Sci 235(1):80–88
Arco-Lazaro E, Agudo I, Clemente R, Bernal MP (2016) Arsenic(V) adsorption-desorption in agricultural and mine soils: effects of organic matter addition and phosphate competition. Environ Pollut 216:71–79
Basu T, Ghosh UC (2011) Influence of groundwater occurring ions on the kinetics of As (III) adsorption reaction with synthetic nanostructured Fe(III)–Cr(III) mixed oxide. Desalination 266:25–32
Belhachemi M, Addoun F (2011) Comparative adsorption isotherms and modeling of methylene blue onto activated carbons. Appl Water Sci 1:111–117
Brunauer S, Deming LS, Deming WE, Teller E (1940) On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of gases. J Am Chem Soc 62(7):1723–1732
Casas N, Schell J, Pini R, Mazzotti M (2012) Fixed bed adsorption of CO2/H2 mixtures on activated carbon: experiments and modeling. Adsorption 18:143–161
Chang FF, Qu JH, Liu HJ, Liu RP, Zhao X (2009) Fe–Mn binary oxide incorporated into diatomite as an adsorbent for arsenite removal: preparation and evaluation. J Colloid Interface Sci 338(2):353–358
Chen L, Wang TJ, Wu HX, Jin Y, Zhang Y, Dou XM (2011) Optimization of a Fe–Al–Ce nano-adsorbent granulation process that used spray coating in a fluidized bed for fluoride removal from drinking water. Powder Technol 206(3):291–296
Chen ASC, Sorg TJ, Wang LL (2015) Regeneration of iron-based adsorptive media used for removing arsenic from groundwater. Water Res 77:85–97
Çiftçi TD, Henden E (2015) Nickel/nickel boride nanoparticles coated resin: a novel adsorbent for arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) removal. Powder Technol 269:470–480
Dou XM, Zhang YS, Wang HJ, Wang TJ, Wang YL (2011) Performance of granular zirconium-iron oxide in the removal of fluoride from drinking water. Water Res 45:3571–3578
Dou XM, Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2013) Arsenate adsorption on three types of granular schwertmannite. Water Res 47(9):2938–2948
Driehaus W, Seith R, Jekel M (1995) Oxidation of arsenate(III) with manganese oxides in water treatment. Water Res 29(1):297–305
Dutta D, Thakur D, Bahadur D (2015) SnO2 quantum dots decorated silica nanoparticles for fast removal of cationic dye (methylene blue) from wastewater. Chem Eng J 281:482–490
Fletcher AJ, Thomas KM, Rosseinsky MJ (2005) Flexibility in metal-organic framework materials: impact on sorption properties. J Solid State Chem 178(8):2491–2510
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10
Freundlich HMF (1906) Ünber die adsorption in lösungen. Z Phys Chem (Leipzig) 19(57A):385–470
Gimbert F, Crini NM, Renault F, Badot PM, Crini G (2008) Adsorption isotherm models for dye removal by cationized starch-based material in a single component system: error analysis. J Hazard Mater 157:34–46
Guan X, Ma J, Dong H, Jiang L (2009) Removal of arsenic from water: effect of calcium ions on As(III) removal in the KMnO4–Fe(II) process. Water Res 43(20):5119–5128
Gupta K, Ghosh UC (2009) Arsenic removal using hydrous nanostructure iron(III)–titanium(IV) binary mixed oxide from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):884–892
Han CY, Pu HP, Li HY, Deng L, Huang S, He SF, Luo YM (2013) The optimization of As(V) removal over mesoporous alumina by using response surface methodology and adsorption mechanism. J Hazard Mater 254–255:301–309
Ho YS, Mckay G (1998a) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70:115–124
Ho YS, Mckay G (1998b) Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. J Environ Sci Health B Process Saf Environ Prot 76(B):184–185
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Hong HJ, Park IS, Ryu T, Ryu J, Kim BG, Chung KS (2013) Granulation of Li1.33Mn1.67O4(LMO) through the use of cross-linked chitosan for the effective recovery of Li+ from seawater. Chem Eng J 234:16–22
Hu X, Ding ZH, Zimmerman AR, Wang SS, Gao B (2015) Batch and column sorption of arsenic onto iron-impregnated biochar synthesized through hydrolysis. Water Res 68:206–216
Hughes MF (2002) Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicol Lett 133(1):1–16
Imyim A, Sirithaweesit T, Ruangpornvisuti V (2016) Arsenite and arsenate removal from wastewater using cationic polymer-modified waste tyre rubber. J Environ Manag 166:574–578
Jadhav SV, Bringas E, Yadav GD, Rathod VK, Ortiz I, Marathe KV (2015) Arsenic and fluoride contaminated groundwaters: a review of current technologies for contaminants removal. J Environ Manag 162(1):306–325
Jang JH, Dempsey BA (2008) Coadsorption of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) onto hydrous ferric oxide: effects on abiotic oxidation of arsenic(III), extraction efficiency, and model accuracy. Environ Sci Technol 42:2893–2898
Kanematsu M, Young TM, Fukushi K, Green PG, Darby JL (2013) Arsenic(III, V) adsorption on a goethite-based adsorbent in the presence of major co-existing ions: modeling competitive adsorption consistent with spectroscopic and molecular evidence. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 106:404–428
Kang L, Zhang M, Liu ZH, Ooi K (2007) IR spectra of manganese oxides with either layered or tunnel structures. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 67:864–869
Kumar E, Bhatnagar A, Hogland W, Marques M, Sillanpää M (2014) Interaction of anionic pollutants with Al-based adsorbents in aqueous media—a review. Chem Eng J 241:443–456
Kumar PS, Flores RQ, Sjöstedt C, Önnby L (2016) Arsenic adsorption by iron–aluminium hydroxide coated onto macroporous supports: insights from X-ray absorption spectroscopy and comparison with granular ferric hydroxides. J Hazard Mater 302:166–174
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Lata S, Samadder SR (2016) Removal of arsenic from water using nano adsorbents and challenges: a review. J Environ Manag 166:387–406
Lenoble V, Laclautre C, Serpaud B, Deluchat V, Bollinger JC (2004) As(V) retention and As(III) simultaneous oxidation and removal on a MnO2-loaded polystyrene resin. Sci Total Environ 326:197–207
Li Z, Deng S, Yu G, Huang J, Lim VC (2010) As(V) and As(III) removal from water by a Ce–Ti oxide adsorbent: behavior and mechanism. Chem Eng J 161:106–113
Li X, He K, Pan BC, Zhang SJ, Lu L, Zhang WM (2012a) Efficient As(III) removal by macroporous anion exchanger-supported Fe–Mn binary oxide: behavior and mechanism. Chem Eng J 193–194:131–138
Li Y, Liu JR, Jia SY, Guo JW, Zhuo J, Na P (2012b) TiO2 pillared montmorillonite as a photoactive adsorbent of arsenic under UV irradiation. Chem Eng J 191:66–74
Li WY, Liu J, Chen H, Deng Y, Zhang B, Wang Z, Zhang X, Hong S (2013) Application of oxalic acid cross-linking activated alumina/chitosan biocomposites in defluoridation from aqueous solution. Investigation of adsorption mechanism. Chem Eng J 225:865–872
Liu T, Wu K, Xue W, Ma C (2015) Characteristics and mechanisms of arsenate adsorption onto manganese oxide-doped aluminum oxide. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 34(4):1009–1018
Ma Y, Zheng YM, Chen JP (2011) A zirconium based nanoparticle for significantly enhanced adsorption of arsenate: synthesis, characterization and performance. J Colloid Interface Sci 354:785–792
Mandal BK, Suzuki KT (2002) Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta 58(1):201–235
Mangwandi C, Suhaimi SNA, Liu JT, Dhenge RM, Albadarin AB (2016) Design, production and characterisation of granular adsorbent material for arsenic removal from contaminated wastewater. Chem Eng Res Des 110:70–81
Masue Y, Loeppert RH, Kramer TA (2007) Arsenate and arsenite adsorption and desorption behavior on coprecipitated aluminum: iron hydroxides. Environ Sci Technol 41:837–842
Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142(1–2):1–53
Ntim SA, Mitra S (2012) Adsorption of arsenic on multiwall carbon nanotube-zirconia nanohybrid for potential drinking water purification. J Colloid Interf Sci 375:154–159
Ociński D, Jacukowicz-Sobala I, Mazur P, Raczyk J, Kociołek-Balawejder E (2016) Water treatment residuals containing iron and manganese oxides for arsenic removal from water—characterization of physicochemical properties and adsorption studies. Chem Eng J 294:210–221
Peng B, Song TT, Wang T, Chai LY, Yang WC, Li XR, Li CF, Wang HY (2016) Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@Cu(OH)2 composites and their arsenic adsorption application. Chem Eng J 299:15–22
Qi JY, Zhang GS, Li HN (2015) Efficient removal of arsenic from water using a granular adsorbent: Fe–Mn binary oxide impregnated chitosan bead. Bioresour Technol 193:243–249
Rahman MS (2007) The prospect of natural additives in enhanced oil recovery and water purification operations. M.A.Sc. thesis, Dalhousie University, Canada
Ranđelović MS, Zarubica AR, Purenović MM (2012) New composite materials in the technology for drinking water purification from ionic and colloidal pollutants. In: Hu N (ed) Composites and their applications. InTech, Rijeka, pp 273–300
Ren Z, Zhang G, Chen JP (2011) Adsorptive removal of arsenic from water by an iron–zirconium binary oxide adsorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 358:230–237
Ringot D, Lerzy B, Chaplain K, Bonhoure JP, Auclair E, Laron-delle Y (2007) In vitro biosorption of ochratoxin A on the yeast industry by-products: comparison of isotherm models. Bioresour Technol 98:1812–1821
Roy E, Patra S, Madhuri R, Sharma PK (2016) Europium doped magnetic graphene oxide-MWCNT nanohybrid for estimation and removal of arsenate and arsenite from real water samples. Chem Eng J 299:244–254
Samarghandi MR, Hadi M, Moayedi S, Askari FB (2009) Two parameter isotherms of methyl orange sorption by pinecone derived activated carbon. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 6(4):285–294
Santhosh C, Velmurugan V, Jacob G, Jeong SK, Grace AN, Bhatnagar A (2016) Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: a review. Chem Eng J 306(15):1116–1137
Sigdel A, Park J, Kwak H, Park PK (2016) Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto hydrous iron oxide-impregnated alginate beads. J Ind Eng Chem 35:277–286
Sips R (1948) On the structure of a catalyst surface. J Chem Phys 16:490–495
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of source, behaviors and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17(5):517–568
Sparks DL (1989) Kinetics of soil chemical processes. Academic, New York
Stachowicz M, Hiemstra T, van Riemsdijk WH (2008) Multi-competitive interaction of As(III) and As(V) oxyanions with Ca2+, Mg2+, PO4 3−, and CO3 2− ions on goethite. J Colloid Interface Sci 320(2):400–414
Tan XF, Liu YG, Gu YL, Xu Y, Zeng GM, Hu XJ, Liu SB, Wang X, Liu SM, Li J (2016) Biochar-based nano-composites for the decontamination of wastewater: a review. Bioresour Technol 212:318–333
Ulmanu M, Marañón E, Fernández Y, Castrillón L, Anger I, Dumitriu D (2003) Removal of copper and cadmium ions from diluted aqueous solutions by low cost and waste material adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut 142:357–373
Umpleby RJ, Baxter S, Rampey AM, Shimizu KD (2004) Characterization of the heterogeneous binding site affinity distributions in molecularly imprinted polymers. J Chromatogr B 804(1):141–149
Uppal H, Hemlata, Tawale J, Singh N (2016) Zinc peroxide functionalized synthetic graphite: an economical and efficient adsorbent for adsorption of arsenic(III) and(V). J Environ Chem Eng 4:2964–2975
Wang J, Xu WH, Chen L, Huang XJ, Liu JH (2014) Preparation and evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles impregnated chitosan beads for arsenic removal from water. Chem Eng J 251:25–34
Wang LL, Han C, Nadagouda MN, Dionysiou DD (2016) An innovative zinc oxide-coated zeolite adsorbent for removal of humic acid. J Hazard Mater 313:283–290
Weber WJ Jr, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89(2):31–60
Wen ZP, Zhang YL, Guo S, Chen R (2017) Facile template-free fabrication of iron manganese bimetal oxides nanospheres with excellent capability for heavy metals removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 486:211–218
World Health Organization (2008) Guidelines for drinking water quality, vol Volume 1, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva, p 306
Wu K, Liu T, Xue W, Wang XC (2012) Arsenic(III) oxidation/adsorption behaviors on a new bimetal adsorbent of Mn-oxide-doped Al oxide. Chem Eng J 192:343–349
Yin H, Feng XH, Qiu GH, Tan WF, Liu F (2011) Characterization of Co-doped birnessites and application for removal of lead and arsenite. J Hazard Mater 188(1–3):341–349
Yoon Y, Park WK, Hwang TM, Yoon DH, Yang WS, Kang JW (2016) Comparative evaluation of magnetite–graphene oxide andmagnetite-reduced graphene oxide composite for As(III) and As(V) removal. J Hazard Mater 304:196–204
Zhang Y, Yang M, Dou XM, He H, Wang DS (2005) Arsenate adsorption on an Fe–Ce bimetal oxide adsorbent: role of surface properties. Environ Sci Technol 39(18):7246–7253
Zhang GS, Qu JH, Liu HJ, Liu RP, Wu RC (2007) Preparation and evaluation of a novel Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent for effective arsenite removal. Water Res 41(9):1921–1928
Zhang Y, Dou XM, Zhao B, Yang M, Takayama T, Kato S (2010) Removal of arsenic by a granular Fe–Ce oxide adsorbent: fabrication conditions and performance. Chem Eng J 162(1):164–170
Zhang GS, Khorshed A, Chen JP (2013a) Simultaneous removal of arsenate and arsenite by a nanostructured zirconium–manganese binary hydrous oxide: behavior and mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 397:137–143
Zhang G, Ren Z, Zhang X, Chen J (2013b) Nanostructured iron(III)-copper(II) binary oxide: a novel adsorbent for enhanced arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. Water Res 47(12):4022–4031
Zhang W, Fu J, Zhang GS, Zhang XW (2014) Enhanced arsenate removal by novel Fe–La composite (hydr)oxides synthesized via coprecipitation. Chem Eng J 251:69–79
Zhao K, Guo HM, Zhou XQ (2014) Adsorption and heterogeneous oxidation of arsenite on modified granular natural siderite: characterization and behaviors. Appl Geochem 48:184–192
Zhu NY, Yan TM, Qiao J, Cao HL (2016) Adsorption of arsenic, phosphorus and chromium by bismuth impregnated biochar: adsorption mechanism and depleted adsorbent utilization. Chemosphere 164:32–40
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51578440/51208415), Program for Innovative Research Team (PIRT) in Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2013KCT-13), Key Laboratory Project of Education Department of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 14JS042), the Research Fund of Tianjin Key Laboratory of Aquatic Science and Technology (Grant No. TJKLAST-ZD-2016-08), and Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (Grant No. 2013ZX07310-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Zhang, J., Chang, B. et al. Removal of arsenic(III,V) by a granular Mn-oxide-doped Al oxide adsorbent: surface characterization and performance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 18505–18519 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9465-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9465-8