Abstract
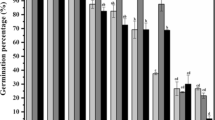
Plants have immense potential for their use in the minimization of emerging environmental pollution issues. Under simulated laboratory conditions, this work investigated the growth and biochemical responses of 14-day-old cotton burdock (Arctium tomentosum Mill.) seedlings to the body burdens of multi-metals including Pb, Cu, Ni, and Zn (1.0 μM–10 mM). Biochemical traits (superoxide generation, lipid peroxidation, content of total peroxides), growth traits (axial organs growth, dry weight accumulation, leaf area), and also metal body burdens varied with types and concentrations of metals. Results indicated a significant tolerance of A. tomentosum to multi-metals that can be implicated for its potential role in the metal phytoremediation programs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881
Anjum NA, Singh HP, Khan MI, Masood A, Per T et al (2015b) Too much is bad—an appraisal of phytotoxicity of elevated plant-beneficial heavy metal ions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3361–3382
Anjum NA, Sofo A, Scopa A, Roychoudhury A, Gill SS, Iqbal M, Lukatkin AS et al (2015c) Lipids and proteins—major targets of oxidative modifications in abiotic stressed plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4099–4121
Anjum NA, Ahamd I, Rodrigues SM, Henriques B, Cruz N, Coelho C, Pacheco M, Duarte AC, Pereira E (2013) Eriophorum angustifolium and Lolium perenne metabolic adaptations to metals- and metalloids-induced anomalies in the vicinity of a chemical industrial complex. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:568–581
Anjum NA, Duarte AC, Pereira E, Ahmad I (2015a) Juncus maritimus root-biochemical assessment for its mercury-stabilization potential in Ria de Aveiro coastal lagoon (Portugal). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2231–2238
Anjum NA, Israr M, Duarte AC, Pereira ME, Ahmad I (2014) Halimione portulacoides (L.) physiological/biochemical characterization for its adaptive responses to environmental mercury exposure. Environ Res 131:39–49
Anjum NA, Pereira ME, Ahmad I, Duarte AC, Umar S, Khan NA (2012) Phytotechnologies: remediation of environmental contaminants. CRC Press/Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Baderna D, Lomazzi E, Pogliaghi A, Ciaccia G, Lodi M, Benfenati E (2015) Acute phytotoxicity of seven metals alone and in mixture: are Italian soil threshold concentrations suitable for plant protection? Environ Res 140:102–111
Bashmakov DI (2015) Edaphotypes of Arctium tomentosum Mill. (Asteraceae, Magnoliópsida) from ecotopes with different anthropogenic loads. Povolzhskiy J Ecol 2:123–133 [English abstract]
Bashmakov DI, Lukatkin AS, Anjum NA, Ahmad I, Pereira E (2015) Evaluation of zinc accumulation, allocation, and tolerance in Zea mays L. seedlings: implication for zinc phytoextraction. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(20):15443–15448
Bashmakov DI, Lukatkin AS, Prasad MNV (2006) Temperate weeds in Russia: sentinels for monitoring trace element pollution and possible application in phytoremediation. In: Prasad MNV, Sajwan KS, Naidu R (eds) Trace elements in the environment: biogeochemistry, biotechnology, and bioremediation. CRC Press/Taylor & Fransis, Boca Raton, pp. 439–450
Bi Y, Tugume AK, Valkonen JPT (2012) Small-RNA deep sequencing reveals Arctium tomentosum as a natural host of Alstroemeria virus X and a new putative Emaravirus. PLoS One 7(8):e42758
Ernst WHO (2006) Evolution of metal tolerance in higher plants. For Snow Landsc Res 80(3):251–274
Flora of North America (2006) http://efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=200023154. Accessed 2 Feb 2015
Gajewska E, Sklodowska M (2007) Effect of nickel on ROS content and antioxidative enzyme activities in wheat leaves. Biometals 20:27–36
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(12):909–930
Hu N, Zheng J, Ding D, Li G, Yin J, Chen X et al (2013) Screening of native hyperaccumulators at the Huayuan river contaminated by heavy metals. Biorem J 17(1):21–29
Kandziora-Ciupa M, Ciepał R, Nadgórska-Socha A, Barczyk G (2016) Accumulation of heavy metals and antioxidant responses in Pinus sylvestris L. needles in polluted and non-polluted sites. Ecotoxicology 25:970–981
Kopittke PM, Blamey FP, Asher CJ, Menzies NW (2010) Trace metal phytotoxicity in solution culture: review. J Exp Bot 61(4):945–954
Kralova L, Száková J, Kubík Š, Tlustoš P, Balík J (2010) The variability of arsenic and other risk element uptake by individual plant species growing on contaminated soil. Soil Sediment Contam 19(5):617–634
Lukatkin AS (2002) Contribution of oxidative stress to the development of cold-induced damage to leaves of chilling-sensitive plants: 1. Reactive oxygen species formation during plant chilling. Russ J Plant Physiol 49(5):622–627
Lukatkin AS, Golovanova VS (1988) Rate of lipid peroxidation in chilled leaves of heat-loving plants. Soviet Plant Physiol 35:610–616
Maestri E, Marmiroli M, Visioli G, Marmiroli N (2010) Metal tolerance and hyperaccumulation: costs and trade-offs between traits and environment. Environ Exp Bot 68:1–13
Maisto G, Manzo S, De Nicola F, Carotenuto R, Rocco A, Alfani A (2011) Assessment of the effects of Cr, Cu, Ni and Pb soil contamination by ecotoxicological tests. J Environ Monit 13:3049–3056
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trend Plant Sci 7:405–410
Nadgórska-Socha A, Kandziora-Ciupa M, Ciepał R, Walasek K (2011) Effects of Zn, Cd, Pb on physiological response of Silene vulgaris plants from selected populations. Polish J Environ Stud 20:599–604
Pošćić F, Fellet G, Vischi M, Casolo V, Schat H, Marchiol L (2015) Variation in heavy metal accumulation and genetic diversity at a regional scale among metallicolous and non-metallicolous populations of the facultative metallophyte Biscutella laevigata subsp. Laevigata Intl J Phytorem 17(5):464–475
Prasad MNV, Freitas HM (2003) Metal hyperaccumulation in plants—biodiversity prospecting for phytoremediation technology. Electron J Biotechnol 6(3). http://www.ejbiotechnology.info/content/vol6/issue3/full/6
Prasad SM, Dwivedi R, Zeeshan M (2005) Growth photosynthetic electron transport, and antioxidant responses of young soybean seedlings to simultaneous exposure of nickel and UV-B stress. Photosynthetica 43:177–185
Sagisaka S (1976) The occurrence of peroxide in a perennial plant, Populus gelrica. Plant Physiol 57:308–309
Shah FUR, Ahmad N, Masood KR, Peralta-Videa JR, Ahmad FUD (2010) Heavy metal toxicity in plants. In: Ashraf M, Ozturk M, Ahmad MSA (eds) Plant adaptation and phytoremediation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 71–97
White PJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity in plants. In: Shabala S (ed) Plant stress physiology. CAB International, Wallingford, pp. 210–237
Wilkins DS (1978) The measurement of tolerance to edaphic factors by means of root growth. New Phytol 80:623–633
Acknowledgements
WEQH, ANK, DIB, and ASL thank the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia for financing their present research through project number 6.783.2014K. NAA (SFRH/BPD/84671/2012) and EP are grateful to the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) and the Aveiro University Research Institute/Centre for Environmental and Marine Studies (CESAM) (UID/AMB/50017/2013) for partial financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AL Harbawee, W.E.Q., Kluchagina, A.N., Anjum, N.A. et al. Evaluation of cotton burdock (Arctium tomentosum Mill.) responses to multi-metal exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 5431–5438 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8244-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8244-2