Abstract
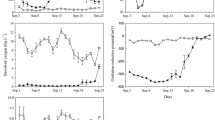
Phosphorus stored in lake sediments is an inner nutrient source and can be released into overlying water to exacerbate algal blooms. A simulated microcosm of Dianchi Lake was built to investigate phosphorus release from sediments to overlying water and its effect on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. The sediments of Dianchi Lake had a total phosphorus (TP) content of 1.7–1.8 mg g−1 with Ca bound phosphorus (Ca-P, 50–54 %) and organic phosphorus (Org-P, 28–32 %) as the main fractions. The sediments released 8 % of TP into the overlying water with Fe/Al bound phosphorus (Fe/Al-P, 26 %) and Org-P (65 %) being the main fractions released. The phosphorus concentration of the overlying water increased from 0.14–0.16 to 0.28–0.33 mg L−1. The biomass density of M. aeruginosa was positively correlated (R 2 = 0.825) with the concentration of orthophosphate, which was the predominant bioavailable phosphorus fraction for algal growth. Org-P can be partly utilized by M. aeruginosa but will not cause a bloom. A good understanding of the geochemical cycles of phosphorus is needed for regulating phosphorus release from sediments and thereby reducing the risk of cyanobacterial blooms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrieux-Loyer F, Aminot A (2001) Phosphorus forms related to sediment grain size and geochemical characteristics in French coastal areas. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 52:617–629
Cai T, Park SY, Li Y (2013) Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: status and prospects. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev 19:360–369
Christophoridis C, Fytianos K (2006) Conditions affecting the release of phosphorus from surface lake sediments. J Environ Qual 35:1181–1192
Chuai X, Ding W, Chen X, Wang X, Miao A, Xi B, He L, Yang L (2011) Phosphorus release from cyanobacterial blooms in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Ecol Eng 37:842–849
Deng D-G, Xie P, Zhou Q, Yang H, Guo L-G (2007) Studies on temporal and spatial variations of phytoplankton in Lake Chaohu. J Integr Plant Biol 49:409–418
Dittrich M, Chesnyuk A, Gudimov A, McCulloch J, Quazi S, Young J, Winter J, Stainsby E, Arhonditsis G (2013) Phosphorus retention in a mesotrophic lake under transient loading conditions: insights from a sediment phosphorus binding form study. Water Res 47:1433–1447
Du H, Yang L, Wu J, Xiao L, Wang X, Jiang L (2012) Simultaneous removal of phosphorus and nitrogen in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor with transgenic bacteria expressing polyphosphate kinase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:265–272
Gao L, Zhou J, Yang H, Chen J (2005) Phosphorus fractions in sediment profiles and their potential contributions to eutrophication in Dianchi Lake. Environ Geol 48:835–844
Hong H-S, Wang H-L, Huang B-Q (1995) The availability of dissolved organic phosphorus compounds to marine phytoplankton. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 13:169–176
Jansson M (1993) Uptake, exchange and excretion of orthophosphate in phosphate‐starved Scenedesmus quadricauda and Pseudomonas K7. Limnol Oceanogr 38:1162–1178
Jansson M, Berggren M, Laudon H, Jonsson A (2012) Bioavailable phosphorus in humic headwater streams in boreal Sweden. Limnol Oceanogr 57:1161–1170
Jin X, Wang S, Pang Y, Wu FC (2006) Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake. China Environ Pollut 139:288–295
Kim L-H, Choi E, Gil K-I, Stenstrom MK (2004) Phosphorus release rates from sediments and pollutant characteristics in Han River, Seoul. Korea Sci Total Environ 321:115–125
Lewis WM, Wurtsbaugh WA, Paerl HW (2011) Rationale for control of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus to reduce eutrophication of inland waters. Environ Sci Technol 45:10300–10305
Liu G, Fan C, Zhong J, Zhang L, Ding S, Yan S, Han S (2010) Using hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) modified clays to clean the Microcystis aeruginosa blooms in Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 9:413–418
Lu R (2000) Methods of soil and agro-chemical analysis. China Agricultural Scientech Press, Beijing
Pan G, Zhang M-M, Chen H, Zou H, Yan H (2006) Removal of cyanobacterial blooms in Taihu Lake using local soils. I. Equilibrium and kinetic screening on the flocculation of Microcystis aeruginosa using commercially available clays and minerals. Environ Pollut 141:195–200
Parsons TR, Strickland JDH (1963) Discussion of spectrophotometric determination of marine-plant pigments, with revised equations for ascertaining chlorophylls and carotenoids. J Mar Res 21:155–163
Qiu S, McComb A (1994) Effects of oxygen concentration on phosphorus release from reflooded air-dried wetland sediments. Mar Freshwater Res 45:1319–1328
Renuka N, Sood A, Prasanna R, Ahluwalia AS (2015) Phycoremediation of wastewaters: a synergistic approach using microalgae for bioremediation and biomass generation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1443–1460
Smith VH, Schindler DW (2009) Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends Ecol Evol 24:201–207
Wang S, Jin X, Zhao H, Wu F (2006) Phosphorus fractions and its release in the sediments from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River area in China. Colloids Surf, A 273:109–116
Wei F-S, Qi W, Sun Z, Huang Y, Shen Y (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis method. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 211–284
Wu Y, Hu Z, Yang L (2010) Hierarchical eco-restoration: a systematical approach to removal of COD and dissolved nutrients from an intensive agricultural area. Environ Pollut 158:3123–3129
Wu M, Huang S, Wen W, Sun X, Tang X, Scholz M (2011) Nutrient distribution within and release from the contaminated sediment of Haihe River. J Environ Sci 23:1086–1094
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin B, Zhu G, Gaoa G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol Oceanogr 55:420–432
Zan F, Huo S, Xi B, Li Q, Liao H, Zhang J (2011) Phosphorus distribution in the sediments of a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 62:1643–1653
Zeng S, Yuan X, Shi X, Qiu Y (2010) Effect of inoculum/substrate ratio on methane yield and orthophosphate release from anaerobic digestion of Microcystis spp. J Hazard Mater 178:89–93
Zhang T, Wang X, Jin X (2007) Variations of alkaline phosphatase activity and P fractions in sediments of a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Environ Pollut 150:288–294
Zhao S, Pan W-b, Ma C (2012) Stimulation and inhibition effects of algae-lytic products from Bacillus cereus strain L7 on Anabaena flos-aquae. J Appl Phycol 24:1015–1021
Zhou Q, Gibson CE, Zhu Y (2001) Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in sediments of three contrasting lakes in China and the UK. Chemosphere 42:221–225
Zhou Y, Song C, Cao X, Li J, Chen G, Xia Z, Jiang P (2008) Phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase activity in sediments of a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Taihu). Hydrobiologia 599:119–125
Zhu Y, Wu F, He Z, Guo J, Qu X, Xie F, Giesy JP, Liao H, Guo F (2013) Characterization of organic phosphorus in lake sediments by sequential fractionation and enzymatic hydrolysis. Environ Sci Technol 47:7679–7687
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41422111), the State Key Development Program for Basic Research of China (2015CB158200), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province China (BK20150066). The authors would like to thank Dr. Clare Morrison from School of Environment, Griffith University, Australia, for polishing the language of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Luo, X., Zhang, N. et al. Phosphorus released from sediment of Dianchi Lake and its effect on growth of Microcystis aeruginosa . Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 16321–16328 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6816-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6816-9