Abstract
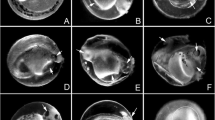
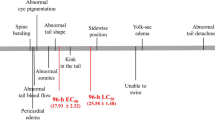
Organophosphate compounds (OP) are widely used throughout the world for pest control. 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCP) is a primary metabolite of two OP compounds namely CP and triclopyr. This study is carried out to know whether a metabolite of parent compound is doing well or harm to biota. The potential effect of TCP was evaluated on development as destabilization of any events transpiring during embryogenesis could be deleterious. To determine this, 4-hpf zebrafish embryos were exposed to five concentrations of TCP (200, 400, 600, 800, 1000 μg/L) or 99.5 % acetone (solvent control). Different early life-stage parameters were observed at four different developmental stages, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hpf. TCP-treated embryo/larvae showed increased mortality, delay in hatching time and decrease in percentage of hatched embryos. Reduction in heartbeat rate, blood flow and body and eye pigmentation was noticed in a dose-dependent manner. Pericardial and yolk sac edema were most severe malformations caused by TCP. Along with this crooked spine/notochord, tail deformation was noticed in hatched and unhatched embryos. The malformations observed provide a good starting point for examination of the molecular mechanisms that are affected during development by TCP. Results gain significance as TCP, which is a breakdown product, appears to be more toxic during development compared to parent compound, CP (our earlier publication).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adgate JL, Barr DB, Clayton CW, Eberly LE, Freeman NC, Lioy PJ, Needham LL, Pellizzari ED, Quackenboss JJ, Roy A, Sexton K (2001) Measurement of children’s exposure to pesticides: analysis of urinary metabolite levels in a probability-based sample. Environ Heath Prespect 10(6):583–589. doi:10.1289/ehp.01109583
Bakke JE, Price CE (1976) Matabolism of O, O-dimethyl-O-(3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl) phosphorothioate in sheep and rats and of 3,5,6- tri-chloro-2-pyridinol in sheep. J Environ Sci Health B 11:9–22
Barron MG, Plakas SM, Wilga PC (1991) Chlorpyrifos pharmacokinetics and metabolism following intravascular and dietary administration in channel catfish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 108:474–482
Bicker W, Lammerhofer M, Genser D, Kiss H, Lindner W (2005) A case study of acute human chlorpyrifos poisoning: novel aspects on metabolism and toxicokinetics derived from liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of urine samples. Toxicol Lett 159:235–251. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.05.013
Chemotti DC, Davis SN, Cook LW, Willoughby IR, Paradise CJ, Lom B (2006) The pesticide malathion disrupts and zebrafish embryogenesis: an investigative laboratory exercise in developmental toxicology. Bioscience 32:4–18
Cheng T, Bodden RM, Puhl RJ, Bauriedel WR (1989) Absorption, distribution, and metabolism of [14C] chlorpyrifos applied dermally to goats. J Agric Food Chem 37:1108–1111
Christiansen HE, Lang MR, Pace JM, Parichy DM (2009) Critical early roles for col27a1a and col27a1b in zebrafish notochord morphogenesis, vertebral mineralization and post-embryonic axial growth. PLoS One 4(12):e8481. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008481, 1–10
Cocker J, Mason HJ, Garfitt SJ, Jones K (2002) Biological monitoring of exposure to organophosphate pesticides. Toxicol Lett 134:97–103. doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00168-6
Coelho S, Olivera R, Preira S, Musso C, Domingues I, Bhujel RC, Soares AM, Noguira AJ (2011) Assessing lethal and sub-lethal effects of trichlorfon on different trophic levels. Aquat Toxicol 103(3–4):191–8. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.03.003
Davis DE (1977) Occupational and environmental pesticide exposure study in south Florida. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Report No. EPA-600/1-77-019
Dishberger HJ, Mc Kellar RL, Pennington JY, Rice JR (1977) Determination of residues of chlorpyrifos, its oxygen analogue, and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol in tissues of cattle fed chlorpyrifos. J Agric Food Chem 25:1325–1329
Eddins D, Cerutti D, Williams P, Linney E, Levin ED (2010) Zebrafish provide a sensitive model of persisting neurobehavioral effects of developmental chlorpyrifos exposure: comparison with nicotine and pilocarpine effects and relationship to dopamine deficits. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32:99–108. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2009.02.005
Fraysee B, Mons R, Garric J (2006) Development of a zebrafish 4-day embryo-larval bioassay to assess toxicity of chemicals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:253–267. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.10.015
Glickman NS, Yelon D (2002) Cardiac development in zebrafish: coordination of form and function. Semin Cell Dev Biol 13:507–513. doi:10.1016/S1084-9521(02)00104-0
Goetz AK, Dix DJ (2009) Toxicogenomic effects common to triazole antifungals and conserved between rats and humans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:80–89. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.04.016
Haendel MA, Tilton F, Bailey GS, Tanguay RL (2004) Developmental toxicity of the dithiocarbamate pesticide sodium metam in zebrafish. Toxicol Sci 81(2):399–400. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfh202
Hallare A, Nagel K, Kohler HR, Triebskorn R (2006) Comparitive embryotoxocity and proteotoxicity of three carrier solvents to zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:378–388. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.07.006
Hanley TR, Carney EW, Johnson EM (2000) Developmental toxicity studies in rats and rabbits with 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol, the major metabolite of chlorpyrifos. Toxicol Sci 53(1):100–108
Hou J (2008) The effect of retinoic acid deficiency on the embryonic cardiac development of zebrafish. PhD dissertation, Fudan University
Ivey MC, Palmer JS (1979) Chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol: residues in body tissues of swine treated with chlorpyrifos for hog louse and itch mite control. J Econ Entomol 72:837–838
Ivey MC, Palmer JS (1981) Chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol: residues in body tissues of sheep treated with chlorpyrifos for sheep ked control. J Econ Entomol 74:136–137
Johenson JA, Geen GH (1990) Sublethal and acute toxicity of ethylene glycol butyl ether ester formulation of triclopyr to juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19(4):610–616. doi:10.1007/BF01059083
Kim KH, Antkiewicz DS, Yan L, Eliceiri KW, Heideman W, Peterson RE, Lee Y (2007) Lrrc10 is required for early heart development and function in zebrafish. Dev Biol 308(2):494–506. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.06.005
Kimmel CB, Ballared WW, Kimmel SR, Ullman B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203:253–310. doi:10.1002/aja.1002030302
Kodde IF, Stok J, Smolenski RT, Jong JW (2007) Metabolic and genetic regulation of cardiac energy substrate preference. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 146(1):26–39. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.09.014
Lyons PJ, Sapio MR, Fricker LD (2013) Zebrafish cytosolic carboxypeptidases 1 and 5 are essential for embryonic development. J Biol Chem 288:30454–30462. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.497933
Madsen JD, Owens CS, Getsinger KD (1998) Evaluation of four herbicides for management of American frogbit (Limnobium spongia). Aquat Plant Manag 36:148–150
Marino T, Gilles M, Rick D et al (1999) Evaluation of the toxicity of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCP) to the early life stages of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum. Lab Project Number: 991173. Unpublished study prepared by The Dow Chemical Co. 56p
Mc Grath P, Li CQ (2008) Zebrafish: a predictive model for assessing drug-induced toxicity. Drug Discov Today 13:394–401. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2008.03.002
Mc Kellar RL, Dishberger HJ, Rice JR, Craig LF, Pennington JY (1976) Residues of chlorpyrifos, its oxygen analogue, and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyrid inol in milk and cream from cows fed chlorpyrifos. J Agri Food Chem 24:283--286
Nelson LS, Getsinger KD (2000) Herbicide evaluation for control of wild taro. Aquat Plant Manag 38:70–72
Nolan RJ, Rick DL, Freshour NL, Saunders JH (1984) Chlorpyrifos: pharmacokinetics in human volunteers. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 73:8–15
Nusslein-Volhard C (2015) Research group: colour pattern formation. Html:http://www.eb.tuebingen.mpg.de/research/emeriti/researchgroupcolourpatternformation. Max Planck Campus Tubingen
Petty DG, Getsinger KD, Woodburn KB (2003) A review of the aquatic environmental fate of triclopyr and its major metabolites. J Aquat Plant Manag 41:69–75
Racke KD (1993) Environmental fate of chlorpyrifos. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 131:1–150. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-4362-5-1
Raldua D, Andre M, Babin PJ (2008) Clofibrate and gemfibrozil induce an embryonic malabsorption syndrome in zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 228:301–314. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2007.11.016
Roberts T, Hutson D, Jewess PW, Lee PH, Nichloos JR, Plimmer (Eds.) (1999) Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals, Part 2: Insecticides and fungicides. R Soc Chem Camb Pestic Sci 55. http://www.rsc.org/metpath
Selderslaghs IW, Hooyberghs J, Coen WD, Witters HE (2010) Locomotor activity in zebrafish embryos: a new method to asses developmental neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32(4):460--71. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2010.03.002
Servizi JA, Gordon RW, Martens DW (1987) Acute toxicity of Garlon 4 and roundup herbicides to salmon, Daphnia, and trout. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 39:15–22. doi:10.1007/BF01691783
Shi X, Yongbing D, Lam KS (2008) Developmental toxicity and alteration of gene expression in zebrafish embryos exposed to PFOS. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 230(1):23–32. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2008.01.043
Sisman T (2010) Dichlorvos-induced developmental toxicity in zebrafish. Toxicol Ind Health 26(9):567–573. doi:10.1177/0748233710373089
Sreedevi B, Suvarchala G, Philip GH (2014) Morphological and physiological abnormalities during development in zebrafish due to chlorpyrifos. Indian J Sci Res 5(2):1–8
Wan MT, Moul DL, Watts RG (1987) Acute toxicity to juvenile Pacific salmonids of garlon 3A, garlon 4, triclopyr ester, and their transformation products: 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-methoxypyridine. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 39(4):721–728
Westerfield M (1995) The zebrafish book. University of Oregon Press, Eugene
Wiegand MD (1996) Composition, accumulation and utilization of yolk lipids in teleost fish. Rev Fish Biol Fish 6:259–286
Willaert A, Sandeep K, Bet LC, Paul JC, Seth DC, Joseph GHL, Elaine CD, Sruti S, Michael T, Anne DP, Zsolt U (2012) GLUT10 is required for the development of the cardiovascular system and the notochord and connects mitochondrial function to TGF-β signaling. Hum Mol Genet 21(6):1248–1259. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr555
Wilson NK, Chuang JC, Lyu C, Menton R, Morgon MK (2003) Aggregate exposure of nine preschool children to persistent organic pollutants at day care and at home. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 13(1):187–202
Worting CR, Hance RJ (1991) (Eds.), 9th ed, The pesticide manual, a world compendium, The British Crop Protection Council, Fernham. Book mark:http://trove.nla.gov.au/version/46254630
Yong T, Xiayang X, Steven W, Meera S, David JK, Jeff SM, John KC (2011) Loss of zebrafish lgi1b leads to hydrocephalus and sensitization to pentylenetetrazol induced seizure-like behavior. PLoS One 6(9):e24596. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024596, 1–10
Zhou S, Dong Q, Li S, Guo J, Wang X, Zhu G (2009) Developmental toxicity of cartap on zebrafish embryos. Aquat Toxicol 95:339–346. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.10.006
Acknowledgments
One of the authors G. Suvarchala is grateful to Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, for the financial support through Inspire Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Henner Hollert
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suvarchala, G., Philip, G.H. Toxicity of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol tested at multiple stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio) development. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 15515–15523 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6684-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6684-3