Abstract
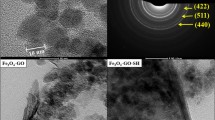
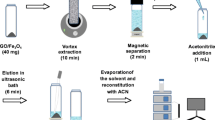
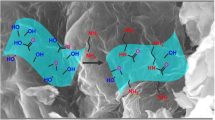
New-generation adsorbent, Fe3O4@SiO2/GO, was developed by modification of graphene oxide (GO) with silica-coated (SiO2) magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4). The synthesized adsorbent was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometry, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and field emission scanning electron microscopy. The developed adsorbent was used for the removal and simultaneous preconcentration of As(III) and As(V) from environmental waters prior to ICP-MS analysis. Fe3O4@SiO2/GO provided high adsorption capacities, i.e., 7.51 and 11.46 mg g−1 for As(III) and As(V), respectively, at pH 4.0. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic were investigated for As(III) and As(V) adsorption. Preconcentration of As(III) and As(V) were studied using magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) method at pH 9.0 as the adsorbent showed selective adsorption for As(III) only in pH range 7–10. MSPE using Fe3O4@SiO2/GO was developed with good linearities (0.05–2.0 ng mL−1) and high coefficient of determination (R 2 = 0.9992 and 0.9985) for As(III) and As(V), respectively. The limits of detection (LODs) (3× SD/m, n = 3) obtained were 7.9 pg mL−1 for As(III) and 28.0 pg mL−1 for As(V). The LOD obtained is 357–1265× lower than the WHO maximum permissible limit of 10.0 ng mL−1. The developed MSPE method showed good relative recoveries (72.55–109.71 %) and good RSDs (0.1–4.3 %, n = 3) for spring water, lake, river, and tap water samples. The new-generation adsorbent can be used for the removal and simultaneous preconcentration of As(III) and As(V) from water samples successfully. The adsorbent removal for As(III) is better than As(V).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolmohammad-Zadeh H, Talleb Z (2014) Speciation of As(III)/As(V) in water samples by a magnetic solid phase extraction based on Fe3O4/Mg–Al layered double hydroxide nano-hybrid followed by chemiluminescence detection. Talanta 128:147–155. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2014.04.070
Akin I, Arslan G, Tor A, Ersoz M, Cengeloglu Y (2012) Arsenic(V) removal from underground water by magnetic nanoparticles synthesized from waste red mud. J Hazard Mater 235–236:62–68. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.06.024
Aktera KF, Chen Z, Smith L, Davey D, Naidu R (2005) Speciation of arsenic in ground water samples: A comparative study of CE-UV, HG-AAS and LC-ICP-MS. Talanta 68:406–415. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2005.09.011
Ali I (2012) New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem Rev 112:5073–5091. doi:10.1021/cr300133d
Ali I, Khan TA, Asim M (2011) Removal of arsenic from water by electrocoagulation and electrodialysis techniques. Sep Purif Rev 40:25–42. doi:10.1080/15422119.2011.542738
Ali I, Al-Othman ZA, Alwarthan A, Asim M, Khan TA (2014) Removal of arsenic species from water by batch and column operations on bagasse fly ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3218–3229. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-2235-3
Anthemidis AN, Martavaltzoglou EK (2006) Determination of arsenic(III) by flow injection solid phase extraction coupled with on-line hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry using a PTFE turnings-packed micro-column. Anal Chim Acta 573–574:413–418. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2005.12.055
Azam S, Mohammad A (2015) Magnetic Fe3O4@C nanoparticles modified with 1-(2-thiazolylazo)-2-naphthol as a novel solid-phase extraction sorbent for preconcentration of copper (II). Microchim Acta 182:257–264. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1327-1
Baby TT, Ramaprabhu S (2010) SiO2 coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle dispersed multiwalled carbon nanotubes based amperometric glucose biosensor. Talanta 80:2016–2022. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2009.11.010
Baig JA, Kazi TG, Shah AQ, Arain MB, Afridi HI, Kandhro GA, Khan S (2009) Optimization of cloud point extraction and solid phase extraction methods for speciation of arsenic in natural water using multivariate technique. Anal Chim Acta 651:57–63. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2009.07.065
Beker U, Cumbal L, Duranoglu D, Kucuk I, Sengupta A (2010) Preparation of Fe oxide nanoparticles for environmental applications: arsenic removal. Environ Geochem Health 32:291–296. doi:10.1007/s10653-010-9301-2
Bhatti AA, Kamboh MA, Solangi IB, Memon S (2013) Synthesis of calix[6]arene based XAD-4 material for the removal of reactive blue 19 from aqueous environments. J Appl Polym Sci 130:776–785. doi:10.1002/app.39214
Carabante I, Mouzon J, Kumpiene J, Gran M, Fredriksson A, Hedlund J (2014) Reutilization of porous sintered hematite bodies as effective adsorbents for arsenic(V) removal from water. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:12689–12696. doi:10.1021/ie500919d
Chandra V, Park J, Chun Y, Lee JW, Hwang IC, Kim KS (2010) Water-dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano 4:3979–3986. doi:10.1021/nn1008897
Chen G, Tuanwei C (2014) SPE speciation of inorganic arsenic in rice followed by hydride-generation atomic fluorescence spectrometric quantification. Talanta 119:202–206. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2013.11.016
Chen D, Huang C, He M, Hu B (2009a) Separation and preconcentration of inorganic arsenic species in natural water samples with 3-(2-aminoethylamino) propyltrimethoxysilane modified ordered mesoporous silica micro-column and their determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 164:1146–1151. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.022
Chen S, Zhan X, Lu D, Liu C, Zhu L (2009b) Speciation analysis of inorganic arsenic in natural water by carbon nanofibers separation and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry determination. Anal Chim Acta 634:192–196. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.12.018
Dreyer DR, Todd AD, Bielawski CW (2014) Harnessing the chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem Soc Rev 43:5288–5301. doi:10.1039/C4CS00060A
Elcik H, Cakmakci M, Sahinkaya E, Ozkaya B (2013) Arsenic removal from drinking water using low pressure membranes. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:9958–9964. doi:10.1021/ie401393p
Fang D, Ruizhi D, Kai Y, Xubiao L, Xinman T, Shenglian L, Lixia Y (2013) Determination of trace total inorganic arsenic by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry after solid phase extraction-preconcentration on aluminium hydroxide gel. Microchim Acta 180:509–515. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-0941-7
Feng L, Cao M, Ma X, Zhu Y, Hu C (2012) Superparamagnetic high-surface-area Fe3O4 nanoparticles as adsorbents for arsenic removal. J Hazard Mater 217–218:439–446. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.03.073
Franger S, Berthet P, Berthon J (2004) Electrochemical synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in alkaline aqueous solutions containing complexing agents. J Solid State Electrochem 8:218–223. doi:10.1007/s10008-003-0469-6
Habuda-Stanić M, Nujić M (2015) Arsenic removal by nanoparticles: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8094–8123. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4307-z
Han C, Li H., Pu H., Yu H., Deng L., Huang S., Luo Y. (2013), Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous alumina and their performances for removing arsenic(V), Chem. Eng. J. , 217 :1–9. doi 10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.087
Huang C, Xie W, Li X, Zhang J (2011) Speciation of inorganic arsenic in environmental waters using magnetic solid phase extraction and preconcentration followed by ICP-MS. Microchim Acta 173:165–172. doi:10.1007/s00604-010-0532-9
Hui C, Shen C, Tian J, Bao L, Ding H, Li C, Tian Y, Shi X, Gao HJ (2011) Core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles synthesized with well-dispersed hydrophilic Fe3O4 seeds. Nanoscale 3:701–705. doi:10.1039/C0NR00497A
Jacukowicz-Sobala I, Ociński D, Kociołek-Balawejder E (2013) Synthesis and evaluation of a novel hybrid polymer containing manganese and iron oxides as a sorbent for As(III) and As(V) removal. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:6453–6461. doi:10.1021/ie400478x
Jain C, Ali I (2000) Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res 34:4304–4312. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00182-2
Kamboh MA, Solangi IB, Sherazi STH, Memon S (2011) A highly efficient calix[4]arene based resin for the removal of azo dyes. Desalination 268:83–89. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.001
Kamboh M, Akoz E, Memon S, Yilmaz M (2013) Synthesis of amino-substituted p-tert-butylcalix [4]arene for the removal of Chicago Sky Blue and Tropaeolin 000 Azo Dyes from aqueous environment. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1–9. doi:10.1007/s11270-012-1424-x
Kumar S, Nair RR, Pillai PB, Gupta SN, Iyengar MAR, Sood AK (2014) Graphene oxide–MnFe2O4magnetic nanohybrids for efficient removal of lead and arsenic from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:17426–17436. doi:10.1021/am504826q
Laure IL, Tkachev SV, Buslaeva EY, Fatushina EV, Gubin SP (2013) The coordination chemistry of graphene oxide: Interactions with metal ions in water. Russ J Coord Chem 39:487–492. doi:10.1134/S1070328413070038
Li J, Zhang S, Chen C, Zhao G, Yang X, Li J, Wang X (2012) Removal of Cu(II) and fulvic acid by graphene oxide nanosheets decorated with Fe3O4nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:4991–5000. doi:10.1021/am301358b
Li Y, Du Q, Liu T, Sun J, Wang Y, Wu S, Wang Z, Xia Y, Xia L (2013) Methylene blue adsorption on graphene oxide/calcium alginate composites. Carbohydr Polym 95:501–507. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.094
Li ZJ, Lin W, LY Y, Xiao CL, Lei M, Zheng LR, Jing Z, Yang JH, Zhao YL, Zhu ZT, Chai ZF, Shi WQ (2015) Efficient removal of uranium from aqueous solution by zero-valentiron nanoparticle and its graphene composite. J Hazard Mater 290:26–33. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.028
Luo X, Wang C, Luo S, Dong R, Tu X, Zeng G (2012) Adsorption of As (III) and As (V) from water using magnetite Fe3O4-reduced graphite oxide–MnO2 nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 187:45–52. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.073
Luo X, Wang C, Wang L, Deng F, Luo S, Tu X, Au C (2013) Nanocomposites of graphene oxide-hydrated zirconium oxide for simultaneous removal of As(III) and As(V) from water. Chem Eng J220:98–106. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.017
Luo S, Xu X, Zhou G, Liu C, Tang Y, Liu Y (2014) Amino siloxane oligomer-linked graphene oxide as an efficient adsorbent for removal of Pb(II) from wastewater. J Hazard Mater 274:145–155. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.062
Morado Piñeiro A, Moreda-Piñeiro J, Alonso-Rodríguez E, López-Mahía P, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, Prada-Rodríguez D (2013) Arsenic species determination in human scalp hair by pressurized hot water extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Talanta 105:422–428. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2012.10.070
Musil S, Pétursdóttir ÁH, Raab A, Gunnlaugsdóttir H, Krupp E, Jr Feldmann (2014) Speciation without chromatography using selective hydride generation: inorganic arsenic in rice and samples of marine origin. Anal Chem 86:993–999. doi:10.1021/ac403438c
Oh J, Jun HL, Ja CK, Hyouk RC, Youngkwan L, Taesung K, Nguyen DL, Jae DN (2010) Graphene oxide porous paper from amine-functionalized poly(glycidyl methacrylate)/graphene oxide core-shell microspheres. J Mater Chem 20:9200–9204. doi:10.1039/C0JM00107D
Pan YF, Chiou C, Lin TF (2010) Adsorption of arsenic(V) by iron-oxide-coated diatomite (IOCD). Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:1401–1410. doi:10.1007/s11356-010-0325-z
Prabakar SJR, Narayanan SS (2006) Surface modification of amine-functionalised graphite for preparation of cobalt hexacyanoferrate (CoHCF)-modified electrode: an amperometric sensor for determination of butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA). Anal Bioanal Chem 386:2107–2115. doi:10.1007/s00216-006-0854-y
Rashidi F, Sarabi RS, Ghasemi Z, Seif A (2010) Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies for the removal of lead (II) and copper (II) ions from aqueous solutions by nanocrystalline. Superlattice Microst 48:577–591. doi:10.1016/j.spmi.2010.09.011
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Milani Hosseini M-R, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S (2006) Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1116:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.03.007
Sanghavi BJ, Gadhari NS, Kalambate PK, Karna SP, Srivastava AK (2015) Potentiometric stripping analysis of arsenic using a graphene paste electrode modified with a thiacrown ether and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:1473–1481. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1470-3
Shamsipur M, Fattahi N, Assadi Y, Sadeghi M, Sharafi K (2014) Speciation of As(III) and As(V) in water samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after solid phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on the solidification of floating organic drop. Talanta 130:26–32. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2014.06.049
Shengsen W, Bin G, Andrew RZ, Yuncong L, Lena M, Willie GH, Kati WM (2015) Removal of arsenic by magnetic biochar prepared from pinewood and natural hematite. Bioresour Technol 175:391–395. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.104
Shipley HJ, Yean S, Kan AT, Tomson MB (2009) Adsorption of arsenic to magnetite nanoparticles: effect of particle concentration, pH, ionic strength, and temperature. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:509–515. doi:10.1897/08-155.1
Shubhda S, Kiran J, Singh VN, Sukhvir S, Vijayan N, Nita D, Govind G, Senguttuvan TD (2012) Faster response of NO2 sensing in graphene–WO3 nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 23:205501. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/23/20/205501
Simeonidis K, Gkinis T, Tresintsi S, Martinez-Boubeta C, Vourlias G, Tsiaoussis I, Angelakeris M (2011) Magnetic separation of hematite-coated Fe3O4 particles used as arsenic adsorbents. Chem Eng J 168:1008–1015. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.074
Sitko R, Zawisza B, Malicka E (2013) Graphene as a new sorbent in analytical chemistry. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 51:33–43. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2013.05.011
Song P, Yang Z, Xu H, Huang J, Yang X, Wang L (2014) Investigation of influencing factors and mechanism of antimony and arsenic removal by electrocoagulation using Fe-Al electrodes. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:12911–12919. doi:10.1021/ie501727a
Sun B, Zhai H, Zhang LB, Zhang CX, Wu XS (2014) Removal of trace arsenic based on biomimetic separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:396–403. doi:10.1021/ie503033r
Tang Y, Huang F, Zhao W, Liu Z, Wan D (2012) Synthesis of graphene-supported Li4Ti5O12 nanosheets for high rate battery application. J Mater Chem 22:11257–11260. doi:10.1039/C2JM30624G
Voice TC, Flores del Pino LV, Hazezov I, Long DT (2011) Field deployable method for arsenic speciation in water. Phys Chem Earth 36:436–441. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2010.03.027
Wan Ibrahim WA, Veloo KV, Sanagi MM (2012) Novel sol–gel hybrid methyltrimethoxysilane–tetraethoxysilane as solid phase extraction sorbent for organophosphorus pesticides. J Chromatogr A 1229:55–62. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.01.022
Wan Ibrahim WA, Rashidi Nodeh H, Hassan YAE, Sanagi MM (2015) Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on modified ferum oxides for enrichment, preconcentration, and isolation of pesticides and selected pollutants. Crit Rev Anal Chem 45:270–287. doi:10.1080/10408347.2014.938148
Wang X, Dou W (2012) Preparation of graphite oxide (GO) and the thermal stability of silicone rubber/GO nanocomposites. Thermochim Acta 529:25–28. doi:10.1016/j.tca.2011.11.016
Wang Y, Gao S, Zang X, Li J, Ma J (2012a) Graphene-based solid-phase extraction combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry for a sensitive determination of trace amounts of lead in environmental water and vegetable samples. Anal Chim Acta 716:112–118. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2011.12.007
Wang Y, Wang L, Tian T, Hu X, Yang C, Xu Q (2012b) Automated solid-phase extraction hyphenated to voltammetry for the determination of quercetin using magnetic nanoparticles and sequential injection lab-on-valve approach. Analyst 137:2400–2405. doi:10.1039/C2AN35300H
Wang C, Luo H, Zhang Z, Wu Y, Zhang J, Chen S (2014) Removal of As (III) and As (V) from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero valent iron-reduced graphite oxide modified composites. J Hazard Mater 268:124–131. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.009
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: first addendum to third edition, vol 1, Recommendations. World Health Organization, Geneva
Xiu C, Shengnan W, Yongxin L, Gang W (2015) Sensing hydrogen peroxide using a glassy carbon electrode modified with in-situ electrodeposited platinum-gold bimetallic nanoclusters on a graphene surface. Microchim Acta 182:265–272. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1321-7
Yadollah Y, Mohammad F, Mahnaz A (2015) Magnetic silica nanomaterials for solid-phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of ultra-trace quantities of plasticizers. Microchim Acta 182:1491–1499. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1474-z
Yu C, Cai Q, Guo ZX, Yang Z, Khoo SB (2003) Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry study of the retention behavior of arsenic species on various solid phase extraction cartridges and its application in arsenic speciation. Spectrochim Acta B58:1335–1349. doi:10.1016/s0584-8547(03)00079-x
Yu X, Tong S, Ge M, Wu L, Zuo J, Cao C, Song W (2013) Synthesis and characterization of multi-amino-functionalized cellulose for arsenic adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 92:380–387. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.050
Zhang K, Dwivedi V, Chi C, Wu J (2010) Graphene oxide/ferric hydroxide composites for efficient arsenate removal from drinking water. J Hazard Mater 182:162–168. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.06.010
Zhang C, Ai L, Jiang J (2015) Graphene hybridized photoactive iron terephthalate with enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of Rhodamine B under visible light. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:153–163. doi:10.1021/ie504111y
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Ministry of Education (MOE) Malaysia for financial support through the Research Grants No. 10J43 and 04H22. H. R. Nodeh would like to thank UTM for the International Doctoral Fellowship (IDF) received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Santiago V. Luis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashidi Nodeh, H., Wan Ibrahim, W.A., Ali, I. et al. Development of magnetic graphene oxide adsorbent for the removal and preconcentration of As(III) and As(V) species from environmental water samples. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 9759–9773 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6137-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6137-z