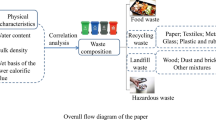
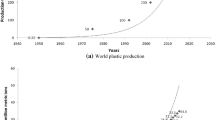
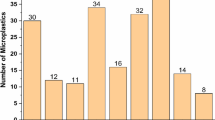
Abstract
The solid wastes generated during the production of chemicals are important sources of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and heavy metals. However, few studies have been conducted regarding long-term monitoring of the risks and states of PCBs and heavy metal pollution from these sources. Herein, we reported the concentrations and risks posed by these pollutants at a chemical solid waste storage site in Taizhou, China, based on data collected before (in 2006) and after clearing the solid waste (in 2013). We examined the concentrations of 24 PCBs, including ten dioxin-like-PCB (DL-PCB) congeners (PCB77, 105, 114, 118, 123, 126, 156, 167, 169, and 189). Our data showed that the mean ∑24PCB concentrations in the soil, water, and plant samples were 6902.90 ng/g, 1637.58 ng/L, and 33.95 ng/g, respectively, in 2013. Furthermore, Cr was the most prevalent contaminant. The hazard quotient (HQ) values showed that Pb posed the highest risk in the soil samples, followed by Hg. The results of the reporter gene assay showed that soil extracts from S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, and S9 exhibited potential estrogenic activities. A comparison of the data showed that the PCB pollution in some sites of this area was still serious. The data provided here are fundamentally useful for policy makers to regulate this type of storage site.

ᅟ





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bobovnikova T, Dibtseva A, Mitroshkov A, Pleskachevskaya G (1993) Ecological assessment of a region with PCB emissions using samples of soil, vegetation and breast milk: a case study. Sci Total Environ 139–140:357–364
China, GB15618-1995 Environmental quality standard for soils 3. 1. 1996
Council Regulation (2001) (EC) No 2375/2001 amending Commission Regulation (EC) No 466/2001 Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs OJ L321, 6. 12.
Garritano S, Pinto B, Calderisi M, Cirillo T, Amodio-Cocchieri R, Reali D (2006) Estrogen-like activity of seafood related to environmental chemical contaminants. Environ Heal 5:9
Gaudet C, Lingard S, Cureton P, Keenleyside K, Smith S, Raju G (1995) Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines for mercury. Water Air Soil Pollut 80:1149–1159
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Jiang Y, Wang X, Zhu K, Wu M, Sheng G, Fu J (2011) Polychlorinated biphenyls contamination in urban soil of Shanghai: level, compositional profiles and source identification. Chemosphere 83:767–773
Li Z, Kong S, Chen L, Bai Z, Ji Y, Liu J, Lu B, Han B, Wang Q (2011) Concentrations, spatial distributions and congener profiles of polychlorinated biphenyls in soils from a coastal city—Tianjin, China. Chemosphere 85:494–501
Muir DCG, Norstrom RJ, Simon M (1988) Organochlorine contaminants in arctic marine food chains: accumulation of specific polychlorinated biphenyls and chlordane-related compounds. Environ Sci Technol 22:1071–1079
Niu LL, Yang FC, Xu C, Yang H, Liu WP (2013) Status of metal accumulation in farmland soils across China: from distribution to risk assessment. Environ Pollut 176:55–62
Plíšková M, Vondráček J, Canton RF, Nera J, Kočan A, Petrík J, Trnovec T, Sanderson T, Van den Berg M, Machala M (2005) Impact of polychlorinated biphenyls contamination on estrogenic activity in human male serum. Environ Health Persp 113:1277–1284
Rhind SM (2002) Endocrine disrupting compounds and farm animals: their properties, actions and routes of exposure. Domest Anim Endocrin 23:179–187
Shen CF, Chen YX, Huang SB, Wang ZJ, Yu CN, Qiao M, Xu YP, Setty K, Zhang JY, Zhu YF, Lin Q (2009) Dioxin-like compounds in agricultural soils near e-waste recycling sites from Taizhou area, China: chemical and bioanalytical characterization. Environ Int 35:50–55
Singh A, Chandra S, Kumar GS, Chauhan LK, Kumar RS (2007) Mutagenicity of leachates from industrial solid wastes using Salmonella reverse mutation assay. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66:210–216
Tang XJ, Shen CF, Chen L, Xiao X, Wu JY, Khan ML, Dou CM, Chen YX (2010a) Inorganic and organic pollution in agricultural soil from an emerging e-waste recycling town in Taizhou area, China. J Soils Sediments 10:895–906
Tang XJ, Shen CF, Shi DZ, Cheema SA, Khan MI, Zhang CK, Chen YX (2010b) Heavy metal and persistent organic compound contamination in soil from Wenling: an emerging e-waste recycling city in Taizhou area, China. J Hazard Mater 173:653–660
Tanskanen P (2013) Management and recycling of electronic waste. Acta Mater 61:1001–1011
Toppari J, Larsen JC, Christiansen P, Giwercman A, Grandjean P, Guillette LJ, Jégou B, Jensen TK, Jouannet P, Keiding N, Leffers H, McLachlan JA, Meyer O, Müller J, Rajpert-DeMeyts E, Scheike T, Sharpe R, Sumpter J, Skakkebaek NE (1996) Male reproductive health and environmental xenoestrogens. Environ Health Persp 104(Suppl 4):741–803
USEPA (2009) Human health criteria table. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC. EPA 816-F-09-0004
Vanden Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization re-evaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93:223–241
Wang Y, Luo CL, Li J, Yin H, Li XD, Zhang G (2011) Characterization and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls in soils and vegetations near an electronic waste recycling site, South China. Chemosphere 85:344–350
WHO (1998) Assessment of the health risk of dioxins: re-evaluation of the tolerable daily intake (TDI), WHO European Centre for Environment and Health, International Programme on Chemical Safety, WHO Consultation
Wong MH, Wu SC, Deng WJ, Yu XZ, Luo Q, Leung AOW, Wong CS, Luksemburg WJ, Wong AS (2007) Export of toxic chemicals—a review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling. Environ Pollut 149:131–140
Wu JP, Luo XJ, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Chen SJ, Mai BX, Yang ZY (2008) Bioaccumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in wild aquatic species from an electronic waste (e-waste) recycling site in South China. Environ Int 34:1109–1113
Yang HY, Xue B, Jin LX, Zhou SS, Liu WP (2010) Polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Yueqing Bay, Xiangshan Bay, and Sanmen Bay in East China Sea. Chemosphere 83:137–143
Yang HY, Zhuo SS, Xue B, Zhang CL, Liu WP (2012) Distribution, historical trends and inventories of polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments from Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent East China Sea. Environ Pollut 169:20–26
Zhang Q, Lu MY, Wang C, Du J, Zhou PX, Zhao MR (2014a) Characterization of estrogen receptor α activities in polychlorinated biphenyls by in vitro dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. Environ Pollut 189:169–175
Zhang Q, Ye JJ, Chen JY, Xu HJ, Wang C, Zhao MR (2014b) Risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in soils of an abandoned e-waste site in China. Environ Pollut 185:258–265
Zhang Q, Lu MY, Dong XW, Wang C, Zhang CL, Liu WP, Zhao MR (2014c) Potential estrogenic effects of phosphorus-containing flame retardants. Environ Sci Technol 48:6995–7001
Zhao GF, Xu Y, Han GG, Ling B (2006) Biotransfer of persistent organic pollutants from a large site in China used for the disassembly of electronic and electrical waste. Environ Geochem Health 28:341–351
Zheng LK, Wu KS, Li Y, Qi ZL, Han D, Zhang B, Gu CW, Chen GJ, Liu JX, Chen SJ, Xu XJ, Huo X (2008) Blood lead and cadmium levels and relevant factors among children from an e-waste recycling town in China. Environ Res 108:15–20
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21307109, 21337005), the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (KF2013-19), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY14B070001), and Zhejiang Provincial Xinmiao Talent Plan (2015R403057).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roland Kallenborn
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 898 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhu, J., Ye, J. et al. Temporal trends and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in a solid waste site in Taizhou, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 438–446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5249-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5249-1