Abstract
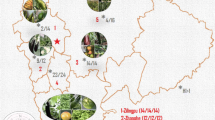
The contamination of phthalate esters (PAEs) has become a potential threat to the environment and human health because they could be easily released as plasticizers from the daily supply products, especially in polyethylene films. Concentration levels of total six PAEs, nominated as priority pollutants by the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), were investigated in soils and vegetables from four greenhouse areas in suburbs of Nanjing, East China. Total PAEs concentration ranged from 930 ± 840 to 2 450 ± 710 μg kg−1 (dry weight (DW)) in soil and from 790 ± 630 to 3 010 ± 2 130 μg kg−1 in vegetables. Higher concentrations of PAEs were found in soils except in Suo Shi (SS) area and in vegetables, especially in potherb mustard and purple tsai-tai samples. Risk assessment mainly based on the exposures of soil ingestion and daily vegetable intake indicated that bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in the samples from Gu Li (GL) and Hu Shu (HS) exhibited the highest hazard to children less than 6-year old. Therefore, the human health risk of the PAEs contamination in soils and vegetables should greatly be of a concern, especially for their environmental estrogen analog effects.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Al2O3 :
-
Alumina
- BB:
-
Benzyl benzoate
- BBP:
-
Butyl benzyl phthalate
- CLEA:
-
The Contaminated Land Exposure Assessment
- DEHP:
-
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
- DEP:
-
Diethyl phthalate
- DMP:
-
Dimethyl phthalate
- DnBP:
-
Di-n-butyl phthalate
- DnOP:
-
Di-n-octyl phthalate
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- H2SO4 :
-
Sulphuric acid
- IR:
-
Index of risk
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- MCRA:
-
Monte Carlo Risk Assessment
- Na2SO4 :
-
Anhydrous sodium sulfate
- ND:
-
Not detected
- PAEs:
-
Phthalate esters
- RfD:
-
Oral reference dose
- TDI:
-
Total daily intake
- USEPA:
-
US Environmental Protection Agency
References
CNWest (News of China West) (2012a) http://news.cnwest.com/content/2012-06/12/content_6651470.htm. (in Chinese)
CEC-CEDA (Chinese enterprise center - China Entrepreneur Department Association) information (2012b) http://info.cec-ceda.org.cn/hg/pages/20060526_14168_8_2.html. (in Chinese)
Aranda JM, O’connor GA, Eiceman GA (1989) Effects of sewage sludge on bis-(2-ethylexyl) phthalate uptake by plant. J Environ Qual 18:45–50
Balbuena P, Campbell J Jr, Clewell HJ III, Clewell RA (2013) Evaluation of a predictive in vitro leydig cell assay for anti-androgenicity of phthalate esters in the rat. Toxicol in Vitro 27:1711–1718
Bergé A, Cladière M, Gasperi J, Coursimault A, Tassin B, Moilleron R (2013) Meta-analysis of environmental contamination by phthalates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8057–8076
Cai QY, Mo CH, Wu QT, Zeng QY (2008) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in the soil-radish (Raphanus sativus) system with sewage sludge and compost application. Bioresour Technol 99:1830–1836
Cecinato A, Balducci C, Mastroianni D, Perilli M (2012) Sampling and analytical methods for assessing the levels of organic pollutants in the atmosphere: PAH, phthalates and psychotropic substances: a short review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1915–1926
Chai LY, Xin ZH, Cai J, Yu MX, Hu QH (2008) Determination of phthalate plasticizers in food. Food Sci Chin 29:362–365 (in Chinese)
Chai C, Cheng H, Ge W, Ma D, Shi Y (2014) Phthalic acid esters in soils from vegetable greenhouses in Shandong Peninsula, East China. PLoS One 9:e95701–e95709
Chen YX, Shen DS, Hu ZQ, Liu XL, Wu DL, Zhao DS, Zhang JY (1997) Degradation characters of PAEs in soil. Acta Sci Circumst 17:340–345 (in Chinese)
Chen YS, Luo YM, Zhang HB, Song J (2011) Preliminary study on PAEs pollution of greenhouse soils. Acta Pedol Sin 3:516–523 (in Chinese)
Cheng Z, Nie XP, Wang HS, Wong MH (2013) Risk assessments of human exposure to bioaccessible phthalate esters through market fish consumption. Environ Int 57–58:75–80
CSTEE (EU Scientific Committee on Toxicity, Ecotoxicity and the Environment) (1998) Phthalate migration from soft PVC toys and child-care articles. http://ec.europa.eu/health/archive/ph_risk/committees/sct/documents/out12_en.pdf.
Environmental Monitoring Center of China (1992) Test methods for evaluating solid waste. Chin Environ Sci Press, Beijing, pp 321–343
Fierens T, Van Holderbeke M, Willems H, De Henauw S, Sioen I (2012) Phthalates in Belgian cow’s milk and the role of feed and other contamination pathways at farm level. Food Chem Toxicol 50(8):2945–2953
Fierens T, Van Holderbeke M, Willems H, De Henauw S, Sioen I (2013) Transfer of eight phthalates through the milk chain—a case study. Environ Int 51:1–7
Fu XW, Du QZ (2011) Uptake of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate of vegetables from plastic film greenhouses. J Agric Food Chem 59:11585–11588
Guo Y, Wu Q, Kannan K (2011) Phthalate metabolites in urine from China, and implications for human exposures. Environ Int 37:893–898
He WS (2004) Soil problems and countermeasure in facility agriculture in China. Soils 3:235–242 (in Chinese)
Kato K, Nakaoka T, Ikeda H (1981) Contamination of phthalic acid esters in vegetables. Chem Abstr 95:60034K
Kirchman H, Tengsred A (1991) Organic pollutants in sewage sludge.2. Analysis of barley grains grown on sludge-fertilizer soil. Swed J Agric Res 21:115–119
Laturnus F, Grøn C (2007) Organic waste products in agriculture-monitoring the waste constituents phthalate esters in soil-crop system by gas chromatography and ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. J Environ Eng Landsc Manag XV:253–260
Li JC, Hu XF, Li WY, Xu WH (2010a) Study of heavy metals pollution analysis and control in protected vegetable base soil. Chin Agric Sci Bull 26:393–396 (in Chinese)
Li M, Cai QY, Zeng QY, Lv HX (2010b) Occurrence of phthalic acid esters in soils and vegetables from green food and organic vegetable fields. J Anhui Agric Sci 38:10189–10191 (in Chinese)
Liu LP, Bao HQ, Liu F, Zhang J, Shen HQ (2012a) Phthalates exposure of Chinese reproductive age couples and its effect on male semen quality, a primary study. Environ Int 42:78–83
Liu SJ, Fang CG, Li Q, Jiang N, Yang DP (2012b) Monitoring and analysis of residues of phthalate esters in food in Jilin province. Chin J Health Lab Technol 3:68–71 (in Chinese)
Liu H, Cui KY, Zeng F, Chen LX, Cheng YT, Li HR, Li SC, Zhou X, Zhu F, Ouyang GF, Luan TG, Zeng ZX (2014) Occurrence and distribution of phthalate esters in riverine sediments from the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Mar Pollut Bull 83:358–365. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.03.038#doilink
Lu RK (1999) Soil Science Society of China. Analysis methods of soil agricultural chemicals. Science and technology of China press, Beijing
Ma TT (2012b) Current pollution status, environmental risk assessment and bio-remediation of representative phthalate esters in farmland soil of typical facility agricultural regions. Dissertation, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Ma TT, Luo YM, Christie P, Teng Y, Liu WX (2012) Removal of phthalic esters in contaminated soil by different cropping systems: a field study. Eur J Soil Biol 50:76–82
Ma TT, Teng Y, Christie P, Luo YM, Chen YS, Ye M, Huang YJ (2013) A new procedure combining GC-MS with accelerated solvent extraction for the analysis of phthalic acid esters in contaminated soils. Front Environ Sci Eng 7:31–42
Masood F, Malik A (2013) Mutagenicity and genotoxicity assessment of industrial wastewaters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7386–7397
Mikula P, Svobodová Z, Smutná M (2005) Phthalates: toxicology and food safety—a review. Czech J Food Sci 23:217–223
Mo CH, Cai QY, Tang SR, Zeng QY, Wu QT (2009) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in vegetables from nine farms of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:181–189
New York Department of Environmental Conservation (1994) Determination of soil cleanup objectives and cleanup levels. New York.
Ni YW, Ou ZQ (2000) Preferential flow and contamination preferential migration in soil: a review. Soil Environ Sci 9:60–63
NMED (New Mexico Environment Department) (2009) Technical background document for development of soil screening levels.
Overcash MR, Weber JB, Miles ML (1982) Behavior of organic priority pollutants in the terrestrial system: di-n-butyl phthalate ester, toluene, and 2,4 dinitrophenol. Water Resources Research Institute of the University of North Carolina.
Pang JM, Duan YL, Chi BL, Fan XW (1995) Residual and toxic analysis of DEHP in soil and Chinese cabbage. Chin Environ Chem 14:239–242 (in Chinese)
Pei XQ, Song M, Guo M, Mo FF, Shen XY (2013) Concentration and risk assessment of phthalates present in indoor air from newly decorated apartments. Atmos Environ 68:17–23
Pradeep S, Benjamin S (2012) Mycelial fungi completely remediate di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, the hazardous plasticizer in PVC blood storage bag. J Hazard Mater. (235-236):69–77.
Romero-Franco M, Hernández-Ramírez RU, Calafat AM, Cebrián ME, Needham LL, Teitelbaum S, Wolff MS, López-Carrillo L (2011) Personal care product use and urinary levels of phthalate metabolites in Mexican women. Environ Int 37(5):867–871
Shen L, Xia B, Dai X (2013) Residues of persistent organic pollutants in frequently-consumed vegetables and assessment of human health risk based on consumption of vegetables in Huizhou, South China. Chemosphere 93:2254–2263
Shi W, Zhang FX, Hu GJ, Hao YQ, Zhang XW, Liu HL, Wei S, Wang XR, Giesy JP, Yu HX (2012) Thyroid hormone disrupting activities associated with phthalate esters in water sources from Yangtze River Delta. Environ Int 42:117–123
Sioen I, Fierens T, Van Holderbeke M, Geerts L, Bellemans M, De Maeyer M, Servaes K, Vanermen G, Boon PE, De Henauw S (2012) Phthalates dietary exposure and food sources for Belgian preschool children and adults. Environ Int 48:102–108
Tai YP, Mo CH, Wu XL, Li YW, Wang JY, Su QY, Huang PX (2011) Occurrence of quinolone antibiotics in soils from vegetable fields of Dongguan City. J Environ Sci 31:839–845
Teil MJ, Tlili K, Blanchard M, Chevreuil M, Alliot F, Labadie P (2012) Occurrence of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polychlorinated biphenyls, and phthalates in freshwater fish from the orge river (Ile-de France). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 63:101–113
USEPA (1996) Proposed guidelines for carcinogen risk assessment. Washington, DC, pp 17960–18011.
Wang LX, Kou LJ, Pan FY, Wang ML (2007) Determination of phthalates in vegetables by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with matrix solid phase dispersion. Chin J Anal Chem 35:1559–1564
Wolfe NL, Burns LA, Steen WC (1980) Use of linear free energy relationships and an evaluative model to assess the fate and transport of phthalate esters in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere 9:393–402
Wu R, Niu MF, Guo Y, Wang J, Zhao MQ, Shi Y, Liu ZY (2009) Survey and analysis of pesticide contamination in greenhouse. J Agro-Environ Sci 28:130–134
Wu XL, Liang RX, Dai QY, Jin DC, Wang YY, Chao WL (2010) Complete degradation of di-n-octyl phthalate by biochemical cooperation between Gordonia sp. strain JDC-2 and Arthrobacter sp. strain JDC-32 isolated from activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 176:262–268
Xu ZW, Cheng L, Shi J, Lu JG, Zhang WM, Zhao YL, Li FY, Chen MD (2014) Kinetic study of the removal of dimethyl phthalate from an aqueous solution using an anion exchange resin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:6571–6577
Yuan SY, Huang IC, Chang BV (2010) Biodegradation of dibutyl phthalate and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and microbial community changes in mangrove sediment. J Hazard Mater 184:826–831
Zhang LF, Dong L, Ren LJ, Shi SH, Zhou L, Zhang T, Huang YR (2012) Concentration and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in the surface water of the Yangtze River Delta, China. J Environ Sci 24:335–342
Zhang Q, Lu XM, Zhang XL, Sun YG, Zhu DM, Wang BL, Zhao RZ, Zhang ZD (2013) Levels of phthalate esters in settled house dust from urban dwellings with young children in Nanjing, China. Atmos Environ 69:258–264
Zhang Y, Tao Y, Sun GQ, Wang L (2014) Effects of di-n-butyl phthalate on the physiology and ultrastructure of cucumber seedling roots. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:6662–6670
Ziogou K, Kirk PWW, Lester JN (1989) Behavior of phthalic acid esters during batch anaerobic digestion of sludge. Water Res 23:743–748
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Environmental Protection Special Funds for Scientific Research on Public Welfare of China (201209030, 201109018 and 2010467016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Leif Kronberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, T.T., Wu, L.H., Chen, L. et al. Phthalate esters contamination in soils and vegetables of plastic film greenhouses of suburb Nanjing, China and the potential human health risk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 12018–12028 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4401-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4401-2