Abstract
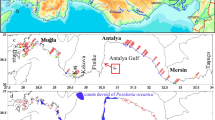
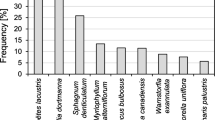
A survey of the epiphytic leaves of Posidonia oceanica was conducted along a depth transect at both the control station Attaya in the Kerkennah Islands and the disturbed Mahres station on the Sfax coast (Tunisia). Samples were collected by scuba divers at depths of 5, 10, 15, and 20 m in July 2008. We evaluated whether the pattern of spatial variability of the macroepiphyte assemblages of leaves of Posidonia oceanica differed in relation to anthropogenic interference. The results indicate that the decrease in shoot density and leaf length according to depth was low at Mahres. The biomass of epiphytic leaves and the percentage cover of epiphytic assemblages decreased with depth for both stations and heavily at Mahres, this decline being related to anthropogenic disturbance. This study shows that the highest values of epifauna and epiflora were detected at the disturbed station Mahres. Macroalgae assemblages decreased with depth at both stations and were dominated by Rhodophyta, whereas the percentage cover of the epifauna leaf that decreases according to depth was dominated by Hydrozoa and Bryozoa. Changes in epiphyte assemblages, epiphytic biomass, percentage cover, and species richness in proportion to Heterokontophyta, Rhodophyta, Cyanobacteria, Hydrozoa, Porifera, and Tunicata between the two stations constitute promising tools for detecting environmental disturbance.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcoverro T, Duarte CM, Romero J (1997) The influence of herbivores on Posidonia oceanica epiphytes. Aquat Bot 56:93–104
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol 26:32–46
Anderson MJ (2005) PERMANOVA: a FORTRAN computer program for permutational multivariate analysis of variance. Department of Statistics, University of Auckland, Auckland
APAL (2001) Zone sensible Bordj El Hassar-Kerkennah. Rapport Définitif COMETE Engineering 105 pp
Armitage AR, Frankovich TA, Fourqurean JW (2006) Variable responses within epiphytic and benthic microalgal communities to nutrient enrichment. Hydrobiologia 569:423–435
Balata D, Nesti U, Piazzi L, Cinelli F (2007) Patterns of spatial variability of seagrass epiphytes in the north-west Mediterranean Sea. Mar Biol 151:2025–2035
Balata D, Piazzi L, Nesti U, Bulleri F, Bertocci I (2010) Effects of enhanced loads of nutrients on epiphytes on leaves and rhizomes of Posidonia oceanica. J Sea Res 63:173–179
Ballesteros E (1987) Estructura i dinamica del poblament algal de les fulles de Posidonia oceanica (L.) delile als herbeis de Tossa de Mar (girona). Butlletí de la Institució Catalana Història Natural 54:13–30
Banni M, Dondero F, Jebali J, Guerbej H, Boussetta H, Viarengo A (2007) Assessment of heavy metal contamination using real-time PCR analysis of mussel metallothionein mt10 and mt20 expression: a validation along the Tunisian coast. Biomark 12:369–383
Bates WR (2005) Environmental factors affecting reproduction and development in ascidians and other protochordates. Can J Zool 83:51–61
Ben Brahim M, Hiroaki T, Hamza A (2007) Proceedings of the third Mediterranean symposium on marine vegetation, Marseille 300 pp
Ben Brahim M, Hamza A, Hannachi I, Rebai A, Jarboui O, Bouain A, Aleya L (2010) Variability in the structure of epiphytic assemblages of Posidonia oceanica in relation to human interferences in the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia. Mar Environ Res 70:411–421
Ben Brahim M, Hamza A, Ben Ismail S, Mabrouk L, Bouain A, Aleya L (2013) What factors drive seasonal variation of phytoplankton, protozoans and metazoans on leaves of Posidonia oceanica and in the water column along the coast of the Kerkennah Islands, Tunisia? Mar Pollut Bull 71:286–298
Ben Ismail S, Sammari C, Béranger K, Lellouch JM (2010) Atlas des données hydrologiques au large des côtes tunisiennes. 169 pp
Ben Ismail S, Sammari C, Gasparini GP, Béranger K, Brahim M, Aleya L (2012) Water masses exchanged through the Channel of Sicily: evidence for the presence of new water masses on the Tunisian side of the channel. Deep-Sea Res I 63:65–81
Borg JA, Attrill MJ, Rowden AA, Schembri PJ, Jones MB (2005) Architectural characteristics of two bed types of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica over different spatial scales. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 62:667–678
Brahim M, Atoui A, Sammari C, Aleya L (2014) Surface sediment dynamics along the eastern coast of Djerba Island (Gabes Gulf, Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci 92:45–54
Casola E, Scardi M, Mazzella L, Fresi E (1987) Structure of the epiphytic community of Posidonia oceanica leaves in a shallow meadow. PSZN Mar Ecol 8:285–286
Chouba L, Mzoughi-Aguir N (2006) Les métaux traces (Cd, Pb, Hg) et les hydrocarbures totaux dans les sédiments superficiels de la frange côtière du Golfe de Gabes. Bulletins de l’Institut Océanographique et de Pêche de Salammbô 33:93–100
Cifuentes M, Kamlah C, Thiel M, Lenz M, Wahl M (2007) Effects of temporal variability of disturbance on the succession in marine fouling communities in northern-central Chile. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 352:280–294
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Cosentino A, Giacobbe S (2008) Distribution and functional response of sublittoral soft bottom assemblages to sedimentary constraints. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 79:263–276
den Hartog C (1970) The seagrasses of the world. North Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam, London, 275 pp
Etienne L, Beltrando G (2013) Daoud A (2013) Human influences on environmental changes in the Kerkennah Archipelago (Tunisia) since the 60’s, 3rd international geography symposium GEOMED.. ISBN 978-605-62253-8-3
Fathallah S, Medhioub MN, Medhioub A, Kraiem MM (2011) Ruditapes decussatus embryo-larval toxicity bioassay for assessment of Tunisian coastal water contamination. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3:277–285
Ferrat L, Wyllie-Echeverria S, Rex GC, Pergent-Martini C, Pergent G, Zou J, Romeo M, Pasqualini V, Fernandez C (2012) Posidonia oceanica and Zostera marina as potential biomarkers of heavy metal contamination in coastal systems, ecological water quality—water treatment and reuse, Dr. Voudouris (Ed.) 676 pp
Gambi MC, Conti G, Bremec CS (1998) Polychaete distribution, diversity and seasonality related to seagrass cover shallow soft bottoms of the Tyrrhenian Sea (Italy). Sci Mar 62:1–17
Gera A, Pages JS, Romero J, Alcoverro T (2013) Combined effects of fragmentation and herbivory on Posidonia oceanica seagrass ecosystems. J Ecol 101:1053–1061
Ghannem N, Azri C, Serbaji MM, Yaich C (2011) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the coastal zone of “Sfax–Kerkennah” plateau, Tunisia. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 30:221–233
Giovannetti E, Montefalcone M, Morri C, Bianchi CN, Albertelli G (2010) Early warning response of Posidonia oceanica epiphyte community to environmental alterations (Ligurian Sea, NW Mediterranean). Mar Pollut Bull 60:1031–1039
Guidetti P (2001) Detecting environmental impacts on the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile: the use of reconstructive methods in combination with “beyond BACI” designs. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 260:27–39
Hattour A, Ben Mustapha K, El Abed A, Chaouch M (1998) L’écosystème du golfe de Gabès; dégradation de son couvert végétal et de sa pêcherie benthique. Bulletins de l’Institut Océanographique et de Pêche de Salammbô 25:5–40
Hattour MJ, Sammari C, Ben Nassrallah S (2010) Hydrodynamique du golfe de Gabès déduite à partir des observations de courants et de niveaux. Revue Paralia 12:1–3
Hauxwell J, Cebrián J, Valiela I (2003) Eelgrass Zostera marina loss in temperate estuaries: relationship to land-derived nitrogen loads and effect of light limitation imposed by algae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 247:59–73
Houda B, Dorra G, Chafai A, Emna A, Khaled M (2011) Impact of a mixed “industrial and domestic” wastewater effluent on the southern coastal sediments of Sfax (Tunisia) in the Mediterranean Sea. Int J Environ Res 5:691–704
Hughes RG, Garcia-Rubies A, Gili JM (1991) The growth and degeneration of the hydroid Sertularia perpusilla, an obligate epiphyte of leaves of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Hydrobiologia 216:211–214
Jebali J, Banni M, Alves de Almeida E, Boussetta H (2007) Oxidative DNA damage levels clams Ruditapes decussatus as pollution biomarkers of Tunisian marine environment. Environ Monit Assess 124:195–200
Kuffner IB, Paul VJ (2001) Effects of nitrate, phosphate and iron on the growth of macroalgae and benthic cyanobacteria from Cocos Lagoon, Guam. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 222:63–72
Lambert G (2005) Ecology and natural history of the protochordates. Can J Zool 83:34–50
Lemmens JWTJ, Clapin G, Lavery P, Cary J (1996) Filtering capacity of seagrass meadows and other habitats of Cockburn Sound, Western Australia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 143:187–200
Lepoint G, Havelange S, Gobert S, Bouquegneau JM (1999) Fauna vs flora contribution to the leaf epiphytes biomass in a Posidonia oceanica seagrass bed (Revellata Bay, Corsica). Hydrobiologia 394:63–67
Lepoint G, Nyssen F, Gobert S, Dauby P, Bouquegneau JM (2000) Relative impact of a seagrass bed and its adjacent epilithic algal community in consumer diets. Mar Biol 136:513–518
Libes M (1986) Productivity-irradiance relationship of Posidonia oceanica and its epiphytes. Aquat Bot 26:285–306
Littler MM, Littler DS (1999) Blade abandonment/proliferation: a novel mechanism for rapid epiphyte control in marine macrophytes. Ecology 80:1736–1746
Martínez-Crego B, Prado P, Alcoverro T, Romero J (2010) Composition of epiphytic leaf community of Posidonia oceanica as a tool for environmental biomonitoring. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 71:286–298
Mascaro O, Valdemarsen T, Holmer M, Perez M, Romero J (2009) Experimental manipulation of sediment organic content and water column aeration reduces Zostera marina (eelgrass) growth and survival. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 373:26–34
Mayot N, Boudouresque CF, Charbonnel E (2006) Change over time of shoot density of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica at its depth limit. Biologia Marina Mediterranea 13:250–254
Mazzella L, Buia MC, Gambi MC, Lorenti M, Russo GF, Scipione MB, Zupo V (1992) Plant–animal trophic relationships in the Posidonia oceanica ecosystem of Mediterranean Sea: a review. In: John DM, Hawkins SJ, Price JH (eds) Plant–animal interactions in the marine benthos. Clarendon Press, Oxford, Systematic association special volume, pp 165–187
Mccarthy JF, Shugart LR (1990) Biomarkers of environmental contamination. Lewis Publishers, Florida, 457 p
Meinesz A, Lefevre JR, Astier JM (1991) Impact of coastal development on the infralittoral zone along the southern Mediterranean shore of continental France. Mar Pollut Bull 23:343–347
Missaoui H, Jabeur C, Gobert B, Jarboui O, El Abed A (2000) Analyse typologique de la flottille chalutière du Golfe de Gabès (Sud Est de Tunisie). Bulletin de l’Institut Natational des Sciences et Technologies de la Mer de Salammbô 27:15–26
Moncreiff CA, Sullivan MJ, Daehnick AE (1992) Primary production dynamics in seagrass beds of Mississippi Sound: the contributions of seagrass, epiphytic algae, sand microflora, and phytoplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 87:161–171
Nesti U, Piazzi L, Balata D (2008) Variability in the structure of epiphytic assemblages of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica in relation to depth. Mar Ecol. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0485.2008.00275.x
Oueslati A (1994) Les côtes de la Tunisie. Recherches sur leur évolution au Quaternaire
Pergent G, Romero J, Pergent-Martini C, Mateo MA, Boudouresque CF (1994) Primary production, stocks and fluxes in the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 106:139–146
Pergent G, Pergent-Martini C, Boudouresque CF (1995) Utilisation de l'herbier à Posidonia oceanica comme indicateur biologique de la qualité du milieu littoral en Méditerranée: état des connaissances. Mésogée 54:3–27
Pergent-Martini C, Leoni V, Pasqualini V, Ardizzone GD, Balestri E, Bedini R, Belluscio A, Belsher T, Borg J, Boudouresque CF, Boumaza S, Bouquegneau JM, Buia MC, Calvo S, Cebrian J, Charbonnel E, Cinelli F, Cossu A, DiMaida G, Dural B, Francour P, Gobert S, Lepoint G, Meinesz A, Molenaar H, Mansour HM, Panayotidis P, Peirano A, Pergent G, Piazzi L, Pirrotta M, Relini G, Romero J, Sanchez-Lizaso JL, Semroud R, Shembri P, Shili A, Tomasello A, Velimirov B (2005) Descriptors of Posidonia oceanica meadows: use and application. Ecol Indic 5:213–230
Perry CT, Beavington-Penney SJ (2005) Epiphytic calcium carbonate production and facies development within sub-tropical seagrass beds, Inhaca Island, Mozambique. Sediment Geol 174:161–176
Rabaoui L, Balti R, El Zrelli R, Tlig-Zouari S (2013) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the gulf of Gabes (Tunisia) using four mollusc species. Mediterranean Marine Science 15:45–58
Romero J (1988) Epífitos de las hojas de Posidonia oceanica: variaciones estacionales y batimétricas de biomasa en la pradera de las islas Medes (Girona). Acta Oecol 9:19–25
Smaoui-Damak W, Hamza-Chaffaia A, Bebianno MJ, Amiard JC (2004) Variation of metallothioneins in gills of the clam Ruditapes decussatus from the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia). Comparative Biochem and Physiol Part C 139:181–188
SMAPIII Projet (2006–2008) Stratégies de gestion intégrée des zones côtières pour les régions du Kroumirie et Mogods et les municipalités de Sfax. Ministère de l’intérieur et du développement local, Tunis, 146p
Tsirika A, Skoufas G, Haritonidis S (2007) Seasonal and bathymetric variations of epiphytic macroflora on Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile leaves in the National Marine Park of Zakynthos (Greece). Mar Ecol 28:146–153
Underwood AJ (1992) Beyond BACI: the detection of environmental impacts on populations in the real, but variable, world. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 161:145–178
Valdivia N, Heidemann A, Thiel M, Molis M, Wahl M (2005) Effects of disturbance on the diversity of hard-bottom macrobenthic communities on the coast of Chile. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 299:45–54
Waycott M, Duarte CM, Carruthers TJB, Orth RJ, Dennison WC, Olyarnik S, Calladine A, Fourqurean JW, Heck KL Jr, Hughes RA, Kendrick GA, Kenworthy WJ, Short FT, Williams SL (2009) Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:12377–12381
Wear GJ, Sullivan MJ, Moore AD, Millie DF (1999) Effects of water-column enrichment on the production dynamics of three seagrass species and their epiphytic algae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 179:201–213
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported by the JICA (Japan International Cooperation Agency) and ESREB project (Étude des Stocks et des Ressources Exploitables des Bivalves) in Tunisia. It was conducted as part of a collaborative project between the Université de Franche-Comté, Laboratoire de Chrono-Environnement, UMR CNRS 6249 and the INSTM (Institut National des Sciences et Technologies de la Mer) and the Faculty of Sciences of Sfax (Tunisia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brahim, M.B., Mabrouk, L., Hamza, A. et al. Bathymetric variation of epiphytic assemblages on Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile leaves in relation to anthropogenic disturbance in the southeastern Mediterranean. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 13588–13601 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3315-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3315-8