Abstract
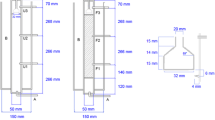
Sequential upflow anaerobic filter (UAF)/air lift (ALR) reactors were employed to investigate the effects of hydraulic retention time (HRT) and nitrobenzene (NB) concentration on treatment of NB-containing wastewater. The results showed that NB was effectively reduced to aniline (AN) with glucose as co-substrate in the UAF reactor. The AN and the remaining intermediates after the UAF reactor were then efficiently degraded in the ALR reactor. A removal efficiency of 100% and 96% was obtained for NB and chemical oxygen demand (COD), respectively, using sequential UAF/ALR reactors with an HRT of 8–72 h in the UAF reactor and 2–18 h in the ALR reactor. The corresponding optimal influent NB concentration varied between 100 and 400 mg l−1 to achieve the optimal NB and COD removal. The NB removal efficiency decreased to 90% and to 97% if the HRT in the UAF reactor decreased from 8 to 2 h and the influent NB concentration increased from 400 to 800 mg l−1, respectively. The results showed that sequential UAF/ALR system can be operated at low HRTs and high NB concentrations without significantly affecting the removal efficiency of NB in the reactor system. The UAF/ALR system can provide an effective yet low cost method for treatment of NB-containing industrial wastewater.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn JH, Forster CF (2000) A comparison of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic upflow filters. Bioresour Technol 73:201–205
Anderson GK, Yang G (1992) Determination of bicarbonate and total volatile acid concentration in anaerobic digesters using a simple titration. Water Environ Res 64:53–59
Aziz MA, Ng WJ, Zhou XJ (1994) Acidogenic–aerobic treatment of a wastewater containing nitrobenzene. Bioresour Technol 48:37–42
Behling E, Diaz A, Colina G, Herrera M, Gutierrez E, Chacin E (1997) Domestic wastewater treatment using a UASB reactor. Bioresour Technol 61:239–245
De MA, O’Connor OA, Kosson DS (1994) Metabolism of aniline under different anaerobic electron-accepting and nutritional conditions. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:233–239
Dickel O, Haug W, Knackmuss HJ (1993) Biodegradation of nitrobenzene by a sequential anaerobic–aerobic process. Biodegradation 4:187–194
Haigler BE, Spain JC (1991) Biotransformation of nitrobenzene by bacteria containing toluene degradative pathways. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3156–3162
Hallas LE, Alexander M (1983) Microbial transformation of nitroaromatic compounds in sewage effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:1234–1241
Han W, Yue QY, Wu SQ, Zhao YQ, Gao BY, Li Q, Wang Y (2013) Application and advantages of novel clay ceramic particles (CCPs) in an up-flow anaerobic bio-filter (UAF) for wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 137:171–178
Jin B, Yu Q, Yan XQ, Leeuwen J (2001) Characterization and improvement of oxygen transfer in pilot plant external air-lift bioreactor for mycelial biomass production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:265–272
Jin B, Yin PH, Lant P (2006) Hydrodynamics and mass transfer coefficient in three-phase air-lift reactors containing activated sludge. Chem Eng Process 45:608–617
Kahng HY, Kukor JJ, Oh KH (2000) Characterization of strain HY99, a novel microorganism capable of aerobic and anaerobic degradation of aniline. FEMS Microbiol Lett 190:215–221
Karim K, Gupta SK (2001) Biotransformation of nitrophenols in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactors. Bioresour Technol 80:179–186
Kocadagistan B, Kocadagistan E, Topcu N, Demircioglu N (2005) Wastewater treatment with combined upflow anaerobic fixed-bed and suspended aerobic reactor equipped with a membrane unit. Process Biochem 40:177–182
Kuscu ÖS, Sponza DT (2009a) Effects of nitrobenzene concentration and hydraulic retention time on the treatment of nitrobenzene in sequential anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR)/continuously stirred tank reactor (CSTR) system. Bioresour Technol 100:2162–2170
Kuscu ÖS, Sponza DT (2009b) Effect of increasing nitrobenzene loading rates on the performance of anaerobic migrating blanket reactor and sequential anaerobic migrating blanket reactor/completely stirred tank reactor system. J Hazard Mater 168:390–399
Li HL, Cheng Y, Wang HF, Sun HF, Liu YF, Liu KX, Peng SX (2003) Inhibition of nitrobenzene-induced DNA and hemoglobin adductions by dietary constituents. Appl Radiat Isot 58:291–298
Liu XY, Wang BJ, Jiang CY, Zhao KX, Harold LD, Liu SJ (2007) Simultaneous biodegradation of nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds in a sequencing batch bioreactor. J Environ Sci 19:530–535
Majumder PS, Gupta SK (2003) Hybrid reactor for priority pollutant nitrobenzene removal. Water Res 37:4331–4336
National Environmental Protection Agency (2002) Analyzing method for water and waste water. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Nishino SF, Spain JC (1993) Degradation of nitrobenzene by a Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2520–2525
Nishino SF, Spain JC (1995) Oxidative pathway for the biodegradation of nitrobenzene by Comamonas sp. strain JS765. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2308–2313
O’Neill FJ, Bromley-challenor KCA, Greenwood RJ, Knapp JS (2000) Bacterial growth on aniline: implications for the biotreatment of industrial wastewater. Water Res 34:4397–4409
Rajagopal R, Torrijos M, Kumar P, Mehrotra I (2013) Substrate removal kinetics in high-rate upflow anaerobic filters packed with low-density polyethylene media treating high-strength agro-food wastewaters. J Environ Manage 116:101–106
Razo-Flores E, Luijten M, Donlon B, Lettinga G, Field J (1997) Biodegradation of selected azo dye under methanogenic conditions. Water Sci Technol 36:65–72
Rubio FC, Garcia JL, Molina E, Chisti Y (2001) Axial inhomogeneities in steady-state dissolved oxygen in airlift bioreactors: predictive models. Chem Eng J 84:43–55
Schnell S, Bak F, Pfennig N (1989) Anaerobic degradation of aniline and dihydroxybenzenes by newly isolated sulfate-reducing bacteria and description of Desulfobacterium anilini. Arch Microbiol 152:556–563
Spain JC (1995) Biodegradation of nitroaromatic compounds. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:523–555
Speece RE (1996) Anaerobic biotechnology for industrial wastewater. Archae Press, Tennessee
Sponza DT (2001) Anaerobic granule formation and tetrachloethylene (TCE) removal in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reator. Enzyme Microb Technol 29:417–427
Sponza DT, Cıgal C (2009) Relationships between anaerobic consortia and removal efficiencies in an UASB reactor degrading 2,4 DCP. Desalination 245:1–18
Wang X, Jia XQ, Wen JP (2011) Transient CFD modeling of toluene waste gas biodegradation in a gas–liquid–solid three-phase airlift loop reactor by immobilized Pseudomonas putida. Chem Eng J 172:735–745
Wu JH, Yin WZ, Gu JJ, Li P, Wang XD, Yang B (2013) A biotic Fe–H2O system for nitrobenzene removal from groundwater. Chem Eng J 226:14–21
Young JC (1991) Factors affecting the design and performance of upflow anaerobic filters. Water Sci Technol 24:133–155
Young JC, McCarty PL (1969) The anaerobic filter for waste treatment. J Water Pollut Control Fed 41:R160–R173
Zhao DF, Liu CS, Zhang YB, Liu QY (2011) Biodegradation of nitrobenzene by aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR). Desalination 281:17–22
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (50708039, 21177089), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2012ZZ0047), Guangdong Provincial Natural Foundation for Science (05300188) and Guangzhou Elite Plan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Chen, G., Gu, J. et al. Effects of hydraulic retention time and nitrobenzene concentration on the performance of sequential upflow anaerobic filter and air lift reactors in treating nitrobenzene-containing wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 12800–12810 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3225-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3225-9