Abstract
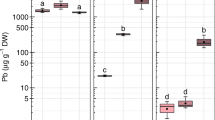
The selection and breeding of lead pollution-safe cultivars (Pb-PSCs) has been used to minimize the influx of Pb into the human food chain. We examined the growth response of 23 selected soybean cultivars to various lead concentrations and also assessed their tolerance to lead. Variations in uptake, enrichment, and translocation of lead among these cultivars were studied to screen out soybean Pb-PSCs. The results indicated that the seed Pb concentrations under three Pb treatments (500, 1,000, and 2,000 mg kg−1) varied significantly (P < 0.05), with average values of 0.20, 0.25, and 0.33 mg kg−1, respectively. Cultivars Shennong 6, Shennong 8, Tiefeng 29, Tiefeng 37, Ji 1005, Liaodou 15, and Suke 1 were found to fit the criteria for Pb-PSCs. The seeds of these seven cultivars were further assessed for interactions between Pb and other mineral nutrient elements such as Ca, Cu, Fe, Mg, Mn, and Zn. High lead concentration in soil was found to inhibit the uptake of Ca, Cu, Fe, Mg, and Zn. Furthermore, Mn accumulation was found to be enhanced in the seeds of all of the seven Pb-PSCs in response to high Pb concentration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aide M, Whitener K, Westhoff E, Kelley J (2008) Effectiveness of triple superphosphate amendments in alleviating soil lead accumulation in Missouri Alfisols. Soil Sediment Contam 17:630–642
Alloway BJ (1995) Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional, Chapman and Hall, Glasgow, 368
Azmat R, Haider S, Nasreen H, Aziz F, Riaz M (2009) A viable alternative mechanism in adapting the plants to heavy metal environment. Pak J Bot 41:2729–2738
Baker AJM, Whiting SN (2002) In search of the holy grail—a further step in understanding metal hyperaccumulation? New Phytol 155:1–7
Bose S, Bhattacharyya AK (2008) Heavy metal accumulation in wheat plant grown in soil amended with industrial sludge. Chemosphere 70:1264–1272
Carbonell G, Imperial RM, Torrijos M, Delgado M, Rodriguez JA (2011) Effects of municipal solid waste compost and mineral fertilizer amendments on soil properties and heavy metals distribution in maize plants (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 85:1614–1623
Carlson RW, Bazzaz FA, Stukel JJ, Wedding JB (1997) Physiological effects, wind re-entrainment and rainwash of lead aerosol particulates deposited on plant leaves. Environ Sci Technol 10:1139–1142
Chai SW, Wen YM, Zhang YL, Zhao JF (2006) Evaluation on the pollution of agricultural soil heavy metal in Guangzhou City. Res Environ Sci 19:138–142 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen HM, Zheng CR, Tu C, Shen ZG (2000) Chemical methods and phytoremediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals. Chemosphere 41:229–234
Chen Y, Shen Z, Li X (2004) The use of vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) in the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals. Appl Geochem 19:1553–1565
Cseh E, Fodor F, Varga A, Zaray G (2000) Effect of lead treatment on the distribution of essential elements in cucumber. J Plant Nutr 23:1095–1105
Dunbar KR, McLaughlin MJ, Reid RJ (2003) The uptake and partitioning of cadmium in two cultivars of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J Exp Bot 54:349–354
El Naggar AH, Osman MEH, Dyab MA, El-Mohsenawy EA (2001) Cobalt and lead toxicities on Calothria fusa and Nostoc muscorum. Egypt J Bot 39:183–208
Finster ME, Kimberly AG, Helen JB (2004) Lead levels of edibles grown in contaminated residential soils: a field survey. Sci Total Environ 320:245–257
Florin PJ, Van Beusichem ML (1993) Uptake and distribution of cadmium in maize inbred lines. Plant Soil 150:25–32
Geebelen W, Vangronsveld J, Adriano DC, Poucke LCV, Clijsters H (2002) Effect of Pb-EDTA and EDTA in oxidative stress reactions and mineral uptake in Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Plant 115:377–384
Grant CA, Clarke JM, Duguid S, Chaney RL (2008) Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation. Sci Total Environ 390:301–310
Greger M, Lofstedt M (2004) Comparison of uptake and distribution of cadmium in different cultivars of bread and durum wheat. Crop Sci 44:501–507
Gu JG, Zhou QX, Wang X (2003) Reused path of heavy metal pollution in soils and its research advance. J Basic Sci Eng 11:143–151 (in Chinese)
Haussling M, Jorns CA, Lehmbecker G, Hecht-Bucholz C, Marschner H (1998) Ion and water uptake in relation to root development of Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst). J Plant Physiol 133:486–491
He B, Yang XE, Ni WZ, Wei YZ, Long XX, Ye ZQ (2002) Sedum alfredii: a new lead-accumulating ecotype. Acta Bot Sin 44:1365–1370
Kannan S, Keppel H (1976) Absorption and transport of Pb2+ in young pea seedlings. Z Naturforsch 31:393–396
Kastori R, Plesnicar M, Sakac Z, Pankovic D, Arsenijevic-Maksimovic I (1998) Effect of lead excess on sunflower growth and photosynthesis. J Plant Nutr 21:75–85
Kopittke PM, Asher CJ, Blamey FPC, Menzies NW (2007) Toxic effects of Pb2+ on the growth and mineral of signal grass (Brachiaria decumbens) and Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana). Plant Soil 300:127–136
Kurz H, Schulz R, Romheld V (1999) Selection of cultivars to reduce the concentration of cadmium and thallium in food and fodder plants. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 162:323–328
Lamhamdi M, Galiou OE, Bakrim A, Nóvoa-Munoz JC, Arias-Estévez M, Aarab A, Lafont R (2012) Effect of lead stress on mineral content and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and spinach (Spinacia oleracea) seedlings. Saudi J Biol Sci. http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.sjbs. Accessed 1 Sep 2012.
Lavado RS, Porcelli CA, Alvarez R (2001) Nutrient and heavy metal concentration and distribution in corn, soybean and wheat as affected by different tillage systems in the Argentine Pampas. Soil Tillage Res 62:55–60
Li YM, Chaney RL, Schneiter AA, Miller JF (1995) Genotype variation in kernel cadmium concentration in sunflower germplasm under varying soil conditions. Crop Sci 35:137–141
Li YM, Chaney RL, Schneiter AA, Miller JF, Elias EM, Hammond JJ (1997) Screening for low grain cadmium phenotypes in sunflower, durum wheat and flax. Euphytica 94:24–30
Liu ZT, Bi YL (2006) Yield rise and potential of Heilongjiang soybean production in the perspective of science and technology progress. Soybean Bull 80:1–3 (in Chinese)
Liu JG, Li KQ, Xu JK, Zhang ZJ, Ma TB, Lu XL, Yang JC, Zhu QS (2003) Lead toxicity, uptake, and translocation in different rice cultivars. Plant Sci 165:793–802
Liu JG, Qian M, Cai GL, Yang JC, Zhu QS (2007) Uptake and translocation of Cd in different rice cultivars and the relation with Cd accumulation in rice grain. J Hazard Mater 143:443–447
Liu WT, Zhou QX, Sun YB, Liu R (2009) Identification of Chinese cabbage genotypes with low cadmium accumulation for food safety. Environ Pollut 157:1961–1967
Liu WT, Zhou QX, Zhang YL, Wei SH (2010) Lead accumulation in different Chinese cabbage cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars. J Environ Manag 91:781–788
Lu RK (1999) Analytical methods of agricultural chemistry in soil. China Agricultural Scinetech, Beijing
Mccue P, Shetty K (2004) Health benefits of soy isoflavonoids and strategies for enhancement: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 44:361–367
Mclaughlin MJ, Williams GMJ, Mckay A (1994) Effect of cultivar on uptake of cadmium by potato tubers. Aust J Agric Res 45:1483–1495
Murakami M, Ae N (2009) Potential for phytoextraction of copper, lead, and zinc by rice (Oryza sativa L.), soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.), and maize (Zea mays L.). J Hazard Mater 162:1185–1192
Nan ZR, Zhao CY, Li JJ, Chen FH, Sun W (2002) Relations between soil properties and selected heavy metal concentrations in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 133:205–213
Needleman H (2004) Lead poisoning. Annu Rev Med 55:209–222
Nogales R, Lara FG, Benitez E, Soto J, Hervas D, Polo A (1997) Metal extractability and availability in a soil after heavy application either nickel or lead in different form. Water Air Soil Pollut 94:33–44
Päivöke AEA (2002) Soil lead alters phytase activity and mineral nutrient balance of Pisum sativum. Environ Exp Bot 48:61–73
Pugh RE, Dick DG, Fredeen AL (2002) Heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cd, Fe and Cu) contents of plant foliage near the Anvil Range lead/zinc mine, Faro. Yukon Territ Ecotoxicol Saf 55:273–279
Saygideger S (1997) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of lead in the green alga Spirogyra fluviatilis Hilse and Zygnema pectinatum (Zygnemataceae). Turk J Biol 21:343–352
Shentu JL, He ZL, Yang XE, Li TQ (2008) Accumulation properties of cadmium in a selected vegetable-rotation system of southeastern China. J Agric Food Chem 56:6382–6388
Sinha P, Dube BK, Srivastava P, Chatterjee C (2006) Alteration in uptake and translocation of essential nutrients in cabbage by excess lead. Chemosphere 65:651–656
Uveges JL, Corbett AL, Mal TK (2002) Effects of lead contamination on the growth of Lythrum salicaria. Environ Pollut 120:319–323
Wang JL, Fang W, Yang ZL, Zhu Y, Yu H (2007) Inter- and intraspecific variations of cadmium accumulation of 13 leafy vegetable species in a greenhouse experiment. J Agric Food Chem 55:9118–9123
Wang C, Lu J, Zhang SH, Wang PF, Hou J, Qian J (2011) Effect of Pb stress on nutrient uptake and secondary metabolism in submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1297–1303
Wei SH, Zhou QX (2004) Identification of weed species with hyperaccumulative characteristics of heavy metals. Prog Nat Sci 14:495–503
Wei SH, Zhou QX, Wang X (2005) Identification of weed plants excluding the absorption of heavy metals. Environ Int 31:829–834
Wei SH, Zhou QX, Mathews S (2008) A newly found cadmium accumulator—Taraxacum mongolicum. J Hazard Mater 159:544–547
Xin JL, Huang BF, Yang ZY, Yuan JG, Dai HW, Qiu Q (2010) Responses of different water spinach cultivars and their hybrid to Cd, Pb and Cd–Pb exposures. J Hazard Mater 175:468–476
Yu H, Wang JL, Fang W, Yuan JG, Yang ZY (2006) Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice. Sci Total Environ 370:302–309
Zeng FR, Mao Y, Cheng WD, Wu FB, Zhang GP (2008) Genotypic and environmental variation in chromium, cadmium and lead concentrations in rice. Environ Pollut 153:309–314
Zhang ZW, Watanabe T, Shimbo S, Higashikawa K, Ikeda M (1998) Lead and cadmium contents in cereals and pulses in north-eastern China. Sci Total Environ 220:137–145
Zhang GP, Fukami M, Sekimoto H (2000) Genotypic differences in the effects of cadmium on growth and nutrient compositions in wheat. J Plant Nutr 23:1337–1350
Zhou QX, Song YF (2004) Remediation of contaminated soils: principles and methods. Science, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhou QX, Wei SH, Zhang QR (2004) Ecological remediation. Chinese Environmental Science, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhou H, Zeng M, Zhou X, Liao BH, Liu J, Lei M, Zhong QY, Zeng H (2013) Assessment of heavy metal contamination and bioaccumulation in soybean plants from mining and smelting areas of southern Hunan Province, China. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:2719–2727
Zhu Y, Yu H, Wang JL, Fang W, Yuan JG, Yang ZY (2007) Heavy metal accumulations of 24 asparagus bean cultivars grown in soil contaminated with Cd alone and with multiple metals (Cd, Pb, and Zn). J Agric Food Chem 55:1045–1052
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China as key projects (No. 21037002 and No. U1133006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, Y., Sun, T. & Zhou, Q. Assessment of lead tolerance in 23 Chinese soybean cultivars and the effect of lead on their mineral ion complement. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 12909–12921 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3181-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3181-4