Abstract
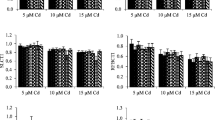
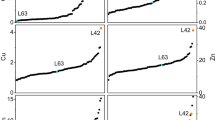
Genotypic variation in uptake and distribution of cadmium (Cd) was studied in 19 inbred lines of maize (Zea mays L.). The inbred lines were grown for 27 days on an in situ Cd-contaminated sandy soil or for 20 days on nutrient solution culture with 10 µg Cd L-1. The Cd concentrations in the shoots showed large genotypic variation, ranging from 0.9 to 9.9 µg g-1 dry wt. for the Cd-contaminated soil and from 2.5 to 56.9 µg g-1 dry wt. for the nutrient solution culture. The inbred lines showed a similar ranking for the Cd concentrations in the shoots for both growth media (r2=0.89). Two main groups of inbreds were distinguished: a group with low shoot, but high root Cd concentrations (shoot: 7.4±5.3 µg g-1 dry wt.; root: 206.0±71.2 µg g-1 dry wt.; ‘shoot Cd excluder’) and a group with similar shoot and root Cd concentrations (shoot: 54.2±3.4 µg g-1 dry wt.; root: 75.6±11.2 µg g-1 dry wt.; ‘non-shoot Cd excluder’). The classification of the maize inbred lines and the near equal whole-plant Cd uptake between the two groups demonstrates that internal distribution rather than uptake is causing the genotypic differences in shoot Cd concentration of maize inbred lines. Zinc (Zn), a micronutrient chemically related to Cd, showed an almost similar distribution pattern for all maize inbred lines. The discrepancy in the internal distribution between Cd and Zn emphasizes the specificity of the Cd distribution in maize inbred lines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano D C 1986 Trace Elements in the Terrestrial Environment. pp 106–155. Springer-Verlag, New York, Berlin, Heidelberg, Tokyo.
Bernard A and Lauwerys R 1984 Cadmium in human population. Experientia 40, 143–152.
Bogess S F, Willavize S and Koeppe D E 1978 Differential response of soybean varieties to soil cadmium. Agron. J. 70, 756–760.
Cataldo D A, Garland T R and Wildung R E 1983 Cadmium uptake kinetics in intact soybean plants. Plant Physiol. 73, 844–848.
Dabin P, Marafante E, Mousny J M and Myttenaere C 1978 Absorption, distribution and binding of cadmium and zinc in irrigated rice plants. Plant and Soil 50, 329–341.
Davis R D 1984 Cadmium — a complex environmental problem: Cadmium in sludges used as fertilizer. Experiientia 40, 117–126.
Florÿn P J, Nelemans J A and Van Beusichem M L 1991 Cadmium uptake by lettuce varieties. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 39, 103–114.
Girling C A and Peterson P J 1981 The significance of the cadmium species in uptake and metabolism of cadmium in crop plants. J. Plant Nutr. 3, 707–720.
Hinesly T D, Alexander D E, Ziegler E L and Barrett G L 1978 Zinc and cadmium accumulation by corn inbreds grown on sludge-amended soil. Agron. J. 70, 425–428.
Hinesly T D, Alexander D E, Redborg K E and Ziegler E L 1982 Differential accumulations of cadmium and zinc by corn hybrids grown on soil amended with sewage sludge. Agron. J. 74, 469–474.
Houba V J G, Uittenboogaard J and De Lange-Harmse A-M 1991 Chemical composition of various plant species (1980–1990). Report of the International Plant-analytical Exchange Program, Department of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, Wageningen Agricultural University, The Netherlands. 118 p.
John M K 1973 Cadmium uptake by eight food crops as influenced by various soil levels of cadmium. Environ. Pollut. 4, 7–15.
Marschner H 1983 General introduction to the mineral nutrition of plants.In Inorganic Plant Nutrition. Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, New Ser. Vol. 15B. Eds. A Läuchli and R L Bieleski. pp 5–60. Springer-Verlag, New York, Berlin, Heidelberg, Tokyo.
Turner M A 1973 Effect of cadmium treatment on cadmium and zinc uptake by selected vegetable species. J. Environ. Qual. 2, 118–119.
Wolterbeek H Th, Van der Meer A and De Bruin M 1988 The uptake and distribution of cadmium in tomato plants as affected by etylenediaminetetraacetic acid and 2,4-dinitrophenol. Environ. Pollut. 55, 301–315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Florijn, P.J., Van Beusichem, M.L. Uptake and distribution of cadmium in maize inbred lines. Plant Soil 150, 25–32 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00779172
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00779172