Abstract
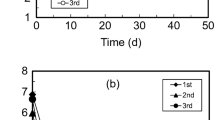
Bioremediation is widely used in organic pollutants disposal. However, very little has been known on its application in constructed wetlands contaminated with organochlorine pesticide, endosulfan in particular. To evaluate the effect of bioremediation on endosulfan removal and clarify the fate, bioaugmentation and biostimulation were studied in laboratory-scale vertical-flow constructed wetlands. After 20 days’ experiment, endosulfan isomers removal efficiencies were increased to 89.24–97.62 % through bioremediation. In bacteria bioaugmentation (E-in) and sucrose biostimulation (E-C), peak concentrations of endosulfan in sediment were reduced by 31.02–76.77 %, and plant absorption were 347.45–576.65 μg kg−1. By contrast, plant absorption in KH2PO4 biostimulation (E-P) was increased to 811.64 and 1,067.68 μg kg−1. Degradation process was probably promoted in E-in and E-C, while plant absorption was enhanced in E-P. Consequently, E-in and E-C were effective for endosulfan removal in constructed wetlands, while adding KH2PO4 had potential to cause air pollution. Additionally, combined bioremediation was not recommended.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Shanab RA, Ghanem K, Ghanem N, Al-Kolaibe A (2008) The role of bacteria on heavy-metal extraction and uptake by plants growing on multi-metal-contaminated soils. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:253–262
Baek SY, Choi SD, Chang YS (2011) Three-year atmospheric monitoring of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in Polar Regions and the South Pacific. Environ Sci Technol 45:4475–4482
Beolchini F, Rocchetti L, Regoli F, Dell’Anno A (2010) Bioremediation of marine sediments contaminated by hydrocarbons: experimental analysis and kinetic modeling. J Hazard Mater 182:403–407
Cheng S, Vidakovic-Cifrek Ž, Grosse W, Karrenbrock F (2002) Xenobiotics removal from polluted water by a multifunctional constructed wetland. Chemosphere 48:415–418
Collins C, Fryer M, Grosso A (2006) Plant uptake of non-ionic organic chemicals. Environ Sci Technol 40:45–52
Didier T, Philippe LG, Sonia H, Amar B, Claudia MC, Marielle DI, Jairo F (2012) Prospects of Miscanthus x giganteus for PAH phytoremediation: a microcosm study. Ind Crops Prod 36:276–281
Fan JL, Wang WG, Zhang B, Guo YY, Ngo HH, Guo WS, Wu HM (2013) Nitrogen removal in intermittently aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands: impact of influent COD/N ratios. Bioresour Technol 143:461–466
Farlane CM, Pfleeger T, Fletcher J (1990) Effect, uptake and disposition of nitrobenzene in several terrestrial plants. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:513–520
Fierer N, Jackso JA, Vilgalys R, Jackson RB (2005) Assessment of soil microbial community structure by use of taxon-specific quantitative PCR assays. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4117–4120
Filler DM, Van Stempvoort DR, Leigh MB (2009) Remediation of frozen ground contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons: feasibility and limits, in Permafrost soils. Heidelberg, Berlin, pp 279–301
Garcia-Blanco S, Venosa AD, Suidan MT, Lee K, Cobanli S, Haines JR (2007) Biostimulation for the treatment of an oil-contaminated coastal salt marsh. Biodegradation 18:1–15
Goswami S, Vig K, Singh DK (2009) Biodegradation of α and β endosulfan by Aspergillus sydoni. Chemosphere 75:883–888
Gregoire C, Elsaesser D, Huguenot D, Lange J, Lebeau T, Merli A, Mose R, Passe-port E, Payraudeau S, Schutz T, Schulz R, Tapia-Padilla G, Tournebize J, Trevisan M, Wanko A (2009) Mitigation of agricultural nonpoint-source pesticide pollution in artificial wetland ecosystems. Environ Chem Lett 7:205–231
Jia HL, Liu LY, Sun YQ, Sun B, Wang DG, Su YH, Kannan K, Li YF (2010) Monitoring and modeling endosulfan in Chinese surface soil. Environ Sci Technol 44:9279–9284
Kadlec RH (2000) The inadequacy of first-order treatment wetland models. Ecol Eng 15:105–119
Kalyani SS, Sharma J, Singh S, Dureja PL (2009) Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan-degrading microorganism from tropical acid soil. J Environ Sci Health B 44:663–672
Laabs V, Amelung W, Pinto AA, Wantzen M, da Silva CJ, Zech W (2002) Pesticides in surface water, sediment, and rainfall of the northeastern Pantanal basin, Brazil. J Environ Qual 31:1636–1648
Leonard AW, Hyne RV, Lim RP, Leigh KA, Le J, Beckett R (2001) Fate and toxicity of endosulfan in Namoi River water and bottom sediment. J Environ Qual 30:750–759
Miglioranza KSB, de Moreno JEA, Moreno VJ (2004) Organochlorine pesticides sequestered in the aquatic macrophyte Schoenoplectus californicus (C.A. Meyer) Soják from a shallow lake in Argentina. Water Res 38:1765–1772
Perfumo A, Banat IM, Marchant R, Vezzulli L (2007) Thermally enhanced approaches for bioremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 66:179–184
Prochaska CA, Zouboulis AI (2006) Removal of phosphates by pilot vertical-flow constructed wetlands using a mixture of sand and dolomite as substrate. Ecol Eng 26:293–303
Santos HF, Carmo FL, Paes JE, Rosado AS, Peixoto RS (2011) Bioremediation of mangroves impacted by petroleum. Water Air Soil Pollut 216:329–350
Semrany S, Favier L, Djelal H, Taha S, Amrane A (2012) Bioaugmentation: possible solution in the treatment of Bio-Refractory Organic Compounds (Bio-ROCs). Biochem Eng J 69:75–86
Silva MH, Beauvais SL (2010) Human health risk assessment of endosulfan. I: toxicology and hazard identification. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 56:4–17
Taccari M, Milanovic V, Comitini F, Casucci C, Ciani M (2012) Effects of biostimulation and bioaugmentation on diesel removal and bacterial community. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 66:39–46
UNEP/POPS/POPRC.6/13/Add.1 (2010) Report of the Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee on the work of its sixth meeting. Sixth meeting of Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee, Geneva, 11–15 October
Watanabe K, Yamamoto S, Hino S, Harayama S (1998) Population dynamics of phenol-degrading bacteria in activated sludge determined by gyrB-targeted quantitative PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1203–1209
Wu H, Zhang J, Li P, Zhang J, Xie H, Zhang B (2011a) Nutrient removal in constructed microcosm wetlands for treating polluted river water in northern China. Ecol Eng 37:560–568
Wu Z, Dong H, Zou L, Lu D, Liu Z (2011b) Enriched microbial community in bioaugmentation of petroleum-contaminated soil in the presence of wheat straw. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164:1071–1082
Wu SQ, Chang JJ, Dai Y, Wu ZB, Liang W (2013) Treatment performance and microorganism community structure of integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland plots for domestic wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3789–3798
Yu L, Peng D, Ren Y (2011) Protozoan predation on nitrification performance and microbial community during bioaugmentation. Bioresour Technol 102:10855–10860
Zhang A, Fang L, Wang J, Liu W, Yuan H, Jantunen L, Li YF (2012) Residues of currently and never used organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils from Zhejiang Province, China. J Agric Food Chem 60:2982–2988
Zhao CC, Xie HJ, Zhang J, Xu JT, Liang S (2013) Spatial distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and effect of soil characters: a case study of a pesticide producing factory. Chemosphere 90:2381–2387
Zuin VG, Yariwake JH, Bicchi C (2003) Fast supercritical fluid extraction and high-resolution gas chromatography with electron-capture and flame photometric detection for multiresidue screening of organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides in Brazil’s medicinal plants. J Chromatogr A 985:159–166
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support by the National Science Foundation of China (21007032), National Water Special Project (2012ZX07203-004), Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University (2012JC029), and Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Shandong province (JQ201216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Leif Kronberg
Congcong Zhao and HuiJun Xie equally contributed t this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Xie, H., Mu, Y. et al. Bioremediation of endosulfan in laboratory-scale constructed wetlands: effect of bioaugmentation and biostimulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 12827–12835 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3107-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3107-1