Abstract
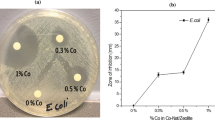
This paper investigates the potential of using the silver antibacterial properties combined with the metal ion exchange characteristics of silver-modified clinoptilolite to produce a treatment system capable of removing both contaminants from aqueous streams. The results have shown that silver-modified clinoptilolite is capable of completely eliminating Escherichia coli after 30-min contact time demonstrating its effectiveness as a disinfectant. Systems containing both E. coli and metals exhibited 100 % E. coli reduction after 15-min contact time and maximum metal adsorption removal efficiencies of 97, 98, and 99 % for Pb2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ respectively after 60 min; 0.182–0.266 mg/g of metal ions were adsorbed by the zeolites in the single- and mixed-metal-containing solutions. Nonmodified clinoptilolite showed no antibacterial properties. This study demonstrated that silver-modified clinoptilolite exhibited high disinfection and heavy metal removal efficiencies and consequently could provide an effective combined treatment system for the removal of E. coli and metals from contaminated water streams.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association, Maryland
Bandyopadhyaya R, Sivaiah MV, Shankar PA (2008) Technical note: silver-embedded granular activated carbon as an antibacterial medium for water purification. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:1177–1180
Bektas N, Kara S (2004) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by natural clinoptilolite: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Sep Purif Technol 39:189–200
Bognachikova N, Concepcion-Rosabal B, Petranovskii V, Avalos Boja M, Rodriguez-Fuentes G (2000) Microbicide effect of Ag-clinoptilolites, part 1: preparation and investigation of the structure of samples containing silver in different states, Complex Mediums. In: Proceedings of SPIE 4097, San Diego, CA, 30, June 2000: 322–329
Concepcion-Rosabal B, Rodriguez-Fuentes G, Bogdanchikova N, Bosch P, Avalos P, Lara VH (2005) Comparative study of natural and synthetic clinoptilolites containing silver in different states. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 86:249–255
Copcia VE, Luchian C, Dunca S, Bilba N, Hristodor CM (2011) Antibacterial activity of silver-modified natural clinoptilolite. J Mater Sci 46:7121–7128
De la Rosa GI, Olguin MT, Alcantara D (2008a) Antibacterial behaviour of silver-modified clinoptilolite-heulandite rich tuff on coliform microorganisms from wastewater in a column system. J Environ Manag 40:853–863
De la Rosa GI, Olguin MT, Alcantara D (2008b) Bactericides of coliform microorganisms from wastewater using silver-clinoptilolite rich tuffs. Appl Clay Sci 40:45–53
De la Rosa GI, Olguin MT, Alcantara D (2010) Silver-modified Mexican clinoptilolite-rich tuffs with various particle sizes as antimicrobial agents against Escherichia coli. J Mex Chem Soc 54:139–142
Erdem E, Karapinar N, Donat R (2004) The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:309–314
Feng QL, Wu J, Chen GQ, Cui FZ, Kim TN, Kim JO (2000) A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Biomed Mater Res 52:662–668
Gedik K, Imamoglu I (2008) Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions using clinoptilolite: influence of pretreatment and regeneration. J Hazard Mater 155:385–392
Guerra R, Lima E, Viniegra M, Guzman A, Lara V (2012) Growth of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhi inhibited by fractal silver nanoparticles supported on zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 147:267–273
Gunay A, Arslankaya E, Tosun I (2007) Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 146:362–371
Gupta SS, Bhattacharyya KG (2011) Kinetics of adsorption of metal ions on inorganic materials: a review. Adv Colloid Interface 162:39–58
Hrenovic J, Milenkovic J, Ivankovic T, Rajic N (2012) Antibacterial activity of heavy metal-loaded natural zeolite. J Hazard Mater 201–202:260–264
Inglezakis VJ, Loizidou MD, Grigoropoulou HP (2002) Equilibrium and Kinetic ion exchange studies of Pb2+, Cr3+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ on natural clinoptilolite. Water Res 36:2784–2792
Jung WK, Koo HC, Kim KW, Shim S (2008) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2171–2178
Krishnani KK, Zhang Y, Xiong L, Yan Y, Boopathy R, Mulchandani A (2012) Bactericidal and ammonia removal activity of silver ion-exchanged zeolite. Bioresource Technol 117:86–91
Kwakye-Awuah B, Williams C, Kenward MA, Radecka I (2008) Antimicrobial action and efficiency of silver loaded zeolite X. J Appl Microbiol 104:1516–1524
Lemire JA, Harrison JJ, Turner RJ (2013) Antimicrobial activity of metals: mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:371–384
Matsumara Y, Yoshikata K, Kunisaki S, Tsuchido T (2003) Mode of Bactericidal action of Silver Zeolite and its comparison with that of Silver Nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4278–4281
Mumpton FA, Ormsby AC (1976) Morphology of zeolites in sedimentary rocks by scanning electron microscopy. Clays Clay Mineral 24:1–23
Nies DH (1999) Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:730–750
Ouki S, Cheeseman C, Perry R (1993) Effects of conditioning and treatment of chabazite and clinoptilolite prior to lead and cadmium removal. Environ Sci Technol 27:1108–1116
Pathak Satya P, Gopal K (2012) Evaluation of bactericidal efficacy of silver ions on Escherichia coli for drinking water disinfection. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2285–2290
Record MT Jr, Courtenay ES, Cayley DS, Guttman HJ (1998) Responses of E. coli to osmotic stress: large changes in amounts of cytoplasmic solutes and water. Trends Biochem Sci 23:143–148
Rivera-Garza M, Olguin MT, Garcia-Sosa I, Alcantara D, Rodriguez-Fuentes G (2000) Silver supported on natural Mexican zeolite as an antibacterial material. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 29:431–444
Shameli K, Ahmad MB, Zargar M, Yunus WMZ, Ibrahim NA (2011a) Fabrication of silver nanoparticles doped in the zeolite framework and antibacterial activity. Int J Nanomedicine 6:331–341
Shameli K, Ahmad MB, Zargat M, Yunus WMZ, Rustaiyan A, Ibrahim NA (2011b) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in montmorillonite and their antibacterial behaviour. Int J Nanomedicine 6:581–590
Silvestry-Rodriguez N, Sicairos-Ruelas E, Gerba CP, Bright KR (2007) Silver as a disinfectant. Rev Environ Contam T 191:23–45
Spain A (2003) Implications of microbial heavy metal tolerance in the environment. Rev Undergrad Res 2:1–6
Sprynskyy M, Buszewski B, Terzyk AP, Namiesnik J (2006) Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 304:21–28
Sprynskyy M, Golembiewski R, Trykowski G, Buszewski B (2010) Heterogeneity and hierarchy of clinoptilolite porosity. J Phys Chem Solids 71:1269–1277
Top A, Ulku S (2004) Silver, zinc and copper exchange in an Na-clinoptilolite and resulting effect on antibacterial activity. Appl Clay Sci 27:13–19
Van Grieken R, Marugán J, Pablos C, Furones L, López A (2010) Comparison between the photocatalytic inactivation of Gram-positive E. faecalis and Gram-negative E. coli faecal contamination indicator microorganisms. Appl Catal B Environ 100:212–220
Wang S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 156:11–24
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure
(DOCX 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhigbe, L., Ouki, S., Saroj, D. et al. Silver-modified clinoptilolite for the removal of Escherichia coli and heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 10940–10948 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2888-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2888-6