Abstract
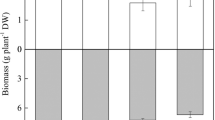
Experiments were conducted to assess the impact of citric acid (CA) and rhizosphere bacteria on metal uptake in Phragmites australis cultured in a spiked acid mine drainage (AMD) soil. Rhizosphere iron-oxidizing bacteria (Fe(II)OB) enhanced the formation of Fe plaque on roots, which decreased the uptake of Fe and Mn. CA inhibited the growth of Fe(II)OB, decreased the formation of metal plaque, raised the metal mobility in soil, and increased the accumulation of metals in all tissues of the reeds. The higher the CA dosage, the more metals accumulated into reeds. The total amount of metals in reeds increased from 7.8 ± 0.5 × 10−6 mol plant−1 (Mn), 1.4 ± 0.1 × 10−3 mol plant−1 (Fe), and 1.0 ± 0.1 × 10−4 mol plant−1 (Al) in spiked soil without CA to 22.2 ± 0.5 × 10−6 mol plant−1 (Mn), 3.5 ± 0.06 × 10−3 mol plant−1 (Fe), and 5.0 ± 0.2 × 10−4 mol plant−1 (Al) in soil added with 33.616 g C6H8O7·H2O for per kilogram soil. CA could be effective at enhancing the phytoremediation of metals from AMD-contaminated soil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. J Clean Prod 14:1139–1145
Baldantoni D, Ligrone R, Alfani A (2009) Macro- and trace-element concentrations in leaves and roots of Phragmites australis in a volcanic lake in Southern Italy. J Geochem Explor 101:166–174
Batty LC, Younger PL (2004) Growth of Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin ex. Steudel in mine water treatment wetlands: effects of metal and nutrient uptake. Environ Pollut 132:85–93
Batty LC, Baker AJM, Wheeler BD, Curtis CD (2000) The Effect of pH and plaque on the uptake of Cu and Mn in Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin ex. Steude. Ann Bot 86:647–653
Batty LC, Baker AJM, Wheeler BD (2002) Aluminum and phosphate uptake by Phragmites australis: the role of Fe, Mn and Al root plaque. Ann Bot 89:443–449
Bird SC (1987) The effect of hydrological factors on trace metal contamination in the river Tawe, South Wales. Environ Pollut 45:87–124
Bonanno G, Lo Giudice R (2009) Heavy metal bioaccumulation by the organs of Pharamites australis (common reed) and their potential use as contamination indicators. Ecol Indic 10:39–645
Chen H, Cutright TJ (2001) EDTA and HEDTA effects on Cd, Cr and Ni uptake by Hellianthus annuus. Chemosphere 45:21–28
Chen H, Cutright TJ (2002) The interactive effects of chelator, fertilizer and rhizobacteria for enhancing phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. J Soil Sediment 2:203–210
Chen YX, Lin Q, Luo YM, He YF, Zhen SJ, Yu YL, Tian GM, Wong MH (2003) The role of citric acid on the phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Chemosphere 50:807–811
Chen Y, Wang Y, Wu W, Lin Q, Xue S (2006) Impacts of chelate-assisted phytoremediation on microbial community composition in the rhizosphere of a copper accumulator and non-accumulator. Sci Total Environ 356:247–255
Crowder AA, Coltman DW (1993) Formation of manganese oxide plaque on rice roots in solution culture under varying pH and manganese (Mn2+) concentration conditions. J Plant Nutr 16:589–599
Cutright TJ, Senko J, Sivaram S, York M (2012) Evaluation of phytoextraction potential at an acid mine drainage (AMD) impacted site. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 21:970–984
de Souza MP, Huang CP, Chee N, Terry N (1999) Rhizosphere bacteria enhance the accumulation of selenium and mercury in wetland plants. Planta 209:259–263
Duarte B, Delgado M, Caçador I (2007) The role of citric acid in cadmium and nickel uptake and translocation, in Halimione portulacoides. Chemosphere 69:836–840
Duquène L, Vandenhove H, Tack F, Meers E, Baeten J, Wannijn J (2009) Enhanced phytoextraction of uranium and selected heavy metals by Indian mustard and ryegrass using biodegradable soil amendments. Sci Total Environ 407:1496–1505
Emerson D, Weiss JV, Megonigal JP (1999) Iron-oxidizing bacteria are associated with ferric hydroxide precipitates (Fe-Plaque) on the roots of wetland plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2758–2761
Ernst WHO (1995) Sampling of plant material for chemical analysis. Sci Total Environ 176:15–24
Garbisu C, Alkorta I (2001) Phytoextraction: a cost effective plant-based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Bioresour Technol 77:229–236
Greipsson S (1994) Effects of iron plaque on roots of rice on growth and metal concentration of seeds and plant tissues when cultivated in excess copper. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 25:2761–2769
Greipsson S, Crowder AA (1992) Amelioration of copper and nickel toxicity by iron plaque on roots of rice (Oryza sativa). Can J Bot 70:824–830
Hansel CM, Fendorf S (2001) Characterization of Fe plaque and associated metals on the roots of mine-waste impacted aquatic plants. Environ Sci Technol 35:3863–3868
Harrison AP Jr (1984) The acidophilic thiobacilli and other acidophilic bacteria that share their habitat. Annu Rev Microbiol 38:265–292
Herlihy AT, Kaufmann PR, Mitch ME, Brown DD (1990) Regional estimates of acid mine drainage impact on streams in the mid-Atlantic and Southeastern United States. Water Air Soil Pollut 50:91–107
Huang JW, Chen J, Berti WR, Cunningham SD (1997) Phytoremediation of lead contaminated soils-role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction. Environ Sci Technol 31:800–805
Johnson DB (1995) Selective solid media for isolating and enumerating acidophilic bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 23:205–218
Jones DL (1998) Organic acids in the rhizosphere- a critical review. Plant Soil 205:25–44
Jones DL, Darah PR, Kochian LV (1996) Critical evaluation of organic acid mediated iron dissolution in the rhizosphere and its potential role in root iron uptake. Plant Soil 180:57–66
Kapulnik Y, Okon Y (2002) Plant growth promotion by rhizosphere bacteria. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Beeckman T, Kafkafi U (eds) Plant Roots: the Hidden Half, 3rd edn. Marcel Dekker, NY, pp 869–885
Karathanasis AD, Johnson CM (2003) Metal removal potential by three aquatic plants in an acid mine drainage wetland. Mine Water Environ 22:22–30
Kim SH, Lee IS (2010) Comparison of the ability of organic acids and EDTA to enhance the phytoextraction of metals from a multi-metal contaminated soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:255–259
Kuffner M, Puschenreiter M, Wieshammer G, Gorfer M, Sessitsch A (2008) Rhizosphere bacteria affect growth and metal uptake of heavy metal accumulating willows. Plant Soil 304:35–44
Lasat MM (2002) Phytoextraction of toxic metals: a review of biological mechanisms. J Environ Qual 31:109–120
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Smith FA, Smith SE (2004) Do iron plaque and genotypes affect arsenate uptake and translocation by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture? J Exp Bot 55:1707–1713
Marchand EA, Silverstein J (2003) The role of enhanced heterotrophic bacterial growth on iron oxidation by acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Geomicrobiol J 20:231–244
Marques APGC, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2009) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils: phytoremediation as a potentially promising clean-up technology. Crit. Rev Environ Sci Technol 39:622–654
Mauricio GA, Peña CJJ, Maldonado VM (2010) Isolation and characterization of hexavalent chromium-reducing rhizospheric bacteria from a wetland. Int J Phytoremediation 12:317–334
Mendelssohn IA, Kleiss BA, Wakeley JS (1995) Factors controlling the formation of oxidized root channels- a review. Wetlands 15:37–46
Mihalík J, Tlustoš P, Szaková J (2010) Comparison of willow and sunflower for uranium phytoextraction induced by citric acid. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 285:279–285
Najeeb U, Xu L, Ali S, Jilani G, Gong HJ, Shen WQ, Zhou WJ (2009) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of manganese and plant growth by alleviating the ultrastructural damages in Juncus effusus L. J Hazard Mater 170:1156–1163
Nealson KH, Tebo BM, Rosson RA (1988) Occurrence and mechanisms of microbial oxidation of manganese. Adv Appl Microbiol 33:279–318
Neubauer SC, Toledo-Durán GE, Emerson D, Megonigal JP (2007) Returning to their roots: iron-oxidizing bacteria enhance short-term plaque formation in the wetland-plant rhizosphere. Geomicrobiol J 24:65–73
Otte ML, Rozema J, Koster L, Haarsma MS, Broekman RA (1989) Iron plaque in roots of Aster tripolium L.: interaction with zinc uptake. New Phytol 111:309–317
Otte ML, Dekkers MJ, Rozema J, Broekman RA (1991) Uptake of arsenic by Aster tripolium in relation to rhizosphere oxidation. Can J Bot 69:2670–2677
Pishchik VN, Provorov NA, Vorobyov NI, Chizevskaya EP, Safronova VI, Tuev AN, Kozhemyakov AP (2009) Interactions between plants and associated bacteria in soils contaminated with heavy metals. Microbiology 78:785–793
Quartacci MF, Baker AJM, Navari-Izzo F (2005) Nitrilotriacetate- and citric acid-assisted phytoextraction of cadmium by Indian mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czernj, Brassicaceae). Chemosphere 59:1249–1255
Römkens P, Bouwman L, Japenga J, Draaisma C (2002) Potentials and drawbacks of chelate-enhanced phytoremediation of soils. Environ Pollut 116:109–121
Sawidis T, Chettri MK, Zachariadisa GA, Stratis JA (1995) Heavy metals in aquatic plants and sediments from water systems in Macedonia, Greece. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 32:73–80
Scott A, Wild C (1991) Transformations and r-squared. Am Stat 45(2):127–128
Senko JM, Wanjugi P, Lucas M, Bruns MA, Burgos WD (2008) Characterization of Fe(II) oxidizing bacterial communities at two acidic Appalachian coal mine drainage impacted sites. ISME J 2:1134–1145
Sinhal VK, Srivastava A, Singh VP (2010) EDTA and citric acid mediated phytoextraction of Zn, Cu, Pb and Cd through marigold (Tagetes erecta). J Environ Biol 31:255–259
St-Cyr L, Campbell PGC (1996) Metal (Fe, Mn, Zn) in the root plaque of submerged aquatic plants collected in situ: relations with metal concentrations in adjacent sediments and in the root tissues. Biogeochemistry 33:45–76
Taylor GJ, Crowder AA (1983) Use of the DCB technique for extraction of hydrous iron oxides from roots of wetland plant. Am J Bot 70:1254–1257
Treeby M, Marschner H, Römheld V (1989) Mobilization and other micronutrient cations from a calcareous soil by plant borne, microbial and synthetic metal chelators. Plant Soil 114:217–226
Trolldenier G (1988) Visualization of oxidizing power of rice roots and of possible participation of bacteria in iron deposition. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenkd 151:117–121
Van der Welle MEW, Roelofs JGM, Op den Camp HJM, Lamers LPM (2007) Predicting metal uptake by wetland plants under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:686–694
Vardar F, Ünal M (2007) Aluminum toxicity and resistance in higher plants. Adv Mol Biol 1:1–12
Weiss JV, Emerson D, Backer SM, Megonigal JP (2003) Enumeration of Fe(II)-oxidizing and Fe(III)-reducing bacteria in the root zone of wetland plants: implications for a rhizosphere iron cycle. Biogeochemistry 64:77–96
White JC, Mattina MI, Lee WY, Eitzer BD, Iannucci-Berger W (2003) Role of organic acids in enhancing the desorption and uptake of weathered p, p0-DDE by Cucurbita pepo. Environ Pollut 124:71–80
Ye ZH, Baker AJM, Wong MH, Willis AJ (1997) Copper and nickel uptake, accumulation and tolerance in Typha latifolia with and without iron plaque on the root surface. New Phytol 136:481–488
Ye ZH, Baker AJM, Wong MH, Willis AJ (1998) Zinc, lead and cadmium accumulation and tolerance in Typha latifolia as affected by iron plaque on the root surface. Aquat Bot 61:55–67
Zhang X, Zhang F, Mao D (1998) Effect of iron plaque outside roots on nutrient uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.): zinc uptake by Fe-deficient rice. Plant Soil 202:33–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, L., Cutright, T.J. Remediation of acid mine drainage (AMD)-contaminated soil by Phragmites australis and rhizosphere bacteria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 7350–7360 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2642-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2642-0