Abstract
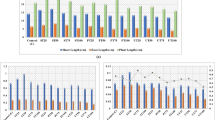
Walnut husk washing waters (WHWW), a by-product of walnut production, are indiscriminately used for irrigation without preliminary risk assessment. Basing on previous in vitro results on the toxicity of this by-product, we have followed the morphophysiological development of Zea mays, Lactuca sativa cv. Gentilina and L. sativa cv. Canasta under diluted and undiluted WHWW irrigation. Significant development alterations have been observed in root and shoot elongations for all crops as well as in total biomass and chlorophyll content. The genotoxic potential of WHWW has been concurrently verified; acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining evidenced chromatin modifications and DNA degradation and also was confirmed by DNA laddering. The DNA instability was also assessed through RAPD, thus suggesting the danger of the by-product of walnut processing and focusing the attention on the necessity of an efficient treatment of WHWWs. The findings obtained by PCA of agronomic and physiological traits suggested that establishing guidelines for the administration of WHWW for irrigation is of great importance, and it is necessary to supervise their use in agricultural soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas MH, Abdelhafez AA (2013) Role of EDTA in arsenic mobilization and its uptake by maize grown on an As-polluted soil. Chemosphere 90(2):588–594
Aras S, Cansaran D (2006) Isolation of DNA for sequence analysis from herbarium material of some lichen specimens. Turk J Bot 30:449–453
Atienzar FA, Conradi M, Evenden AJ, Jha AN, Depledge MH (1999) Qualitative assessment of genotoxicity using random amplified polymorphic DNA: comparison of genomic template stability with key fitness parameters in Daphnia magna exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2275–2282
Bartoli G, Papa S, Sagnella E, Fioretto A (2012) Heavy metal content in sediments along the Calore river: relationships with physical-chemical characteristics. J Env Manag 95:9–14
Baskic D, Popovic S, Pistic P, Arsenijevic N (2006) Analysis of cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in human leukocytes: fluorescence microscopy using V/propidium iodide versus acridine orange/ethidium bromide. Cell Biol Int 30:924–932
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Byczkowska A, Kunikowska A, Kazmierczak A (2013) Determination of ACC-induced cell-programmed death in roots of Vicia faba ssp. minor seedlings by acridine orange and ethidium bromide staining. Protoplasma 250:121–128
Cenkci S, Yildiz M, Cigerci IH, Bozdag A, Terzi H (2010) Evaluation of 2,4-D and Dicamba genotoxicity in bean seedlings using comet and RAPD assays. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1558–1564
Chapman KW, Lawless HT, Boor KJ (2001) Quantitative descriptive analysis and principal component analysis for sensory characterization of ultrapasteurized milk. J Dairy Sci 84:12–20
Ciniglia C, Pinto G, Sansone C, Pollio A (2010) Acridine orange/Ethidium bromide double staining test: a simple In-vitro assay to detect apoptosis induced by phenolic compounds in plant cells. Allelopathy J 26(2):301–308
Ciniglia C, Sansone C, Panzella L, Napolitano A, d’Ischia M (2012) Effects of walnut husk washing waters and their phenolic constituents on horticultural species. Environ Sci Pollut Res 8:3299–3306
Davis JC (2002) Statistics and data analysis in geology. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Dong Z, Saikumar P, Weinberg JM, Venkatachalam MA (1997) Internucleosomal DNA cleavage triggered by plasma membrane damage during necrotic cell death: involvement of serine but not cysteine proteases. Am J Pathol 151:1205–1213
Enan MR (2006) Application of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) to detect the genotoxic effect of heavy metals. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 43(3):147–154
FAOSTAT Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2010) Statistical databases. FAO, Rome
Fargasova A (2001) Phytotoxic effects of Cd, Zn, Pb, Cu and Fe on Sinapis alba L., seedlings and their accumulation in roots and shoots. Biol Plant 44(3):471–473
Fojtova M, Kovarik A (2000) Genotoxic effect of cadmium is associated with apoptotic changes in tobacco cells. Plant Cell Environ 5(23):531–537
Grant WF, Owens ET (2006) Zea mays assays of chemical/ radiation genotoxicity for the study of environmental mutagens. Mutat Res 613:17–64
He ZL, Yang XE, Stoffella PJ (2005) Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. J Trace Elem Med Biol 19(2–3):125–140
Jan N, Hussain M, Andrabi KI (2008) Programmed cell death or apoptosis: do animals and plants share anything in common. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 3:111–126
Kekec G, Sakcali MS, Uzonur I (2010) Assessment of genotoxic effects of boron on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by using RAPD analysis. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84(6):759–764
Kopittke PM, Blamey FPC, Asher CJ, Menzies NW (2010) Trace metal phytotoxicity in solution culture: a review. J Exp Bot 61:945–954
Körpe DA, Aras S (2011) Evaluation of copper-induced stress on eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) seedlings at the molecular and population levels by use of various biomarkers. Mutat Res 719:29–34
Koukalova B, Kovarik A, Fajkus J, Siroky J (1997) Chromatin fragmentation associated with apoptotic changes in tobacco cells exposed to cold stress. FEBS Lett 414:289–292
Kuthanova A, Opatrny Z, Fischer L (2008) Is internucleosomal DNA fragmentation an indicator of programmed death in plant cells? J Exp Bot 59(8):2233–2240
Le TT, Vijver MG, Kinraide TB, Peijnenburg WJ, Hendriks AJ (2013) Modelling metal-metal interactions and metal toxicity to lettuce Lactuca sativa following mixture exposure (Cu(2+)-Zn(2+) and Cu(2+)-Ag(+)). Environ Pollut 176:185–192
Legislation Decree 152/06, Part V, Annex 5: Italian legislation on contaminated sites. ISPRA, Rome
Liu W, Li P, Qi X, Zhou Q, Sun T, Yang Y (2005) DNA changes in barley (Hordeum vulgare) seedlings induced by cadmium pollution using RAPD analysis. Chemosphere 61:158–167
Monteiro C, Santos C, Pinho S, Oliveira H, Pedrosa T, Dias MC (2012) Cadmium-induced cyto- and genotoxicity are organ-dependent in lettuce. Chem Res Toxicol 25(7):1423–1434
Mousavi SR, Galavi M, Eskandari H (2013) Effects of treated municipal wastewater on fluctuation trend of leaf area index and quality of maize (Zea mays). Water Sci Technol 67(4):797–802
Oliveira I, Sousa A, Ferreira IC, Bento A, Estevinho L, Pereira JA (2008) Total phenols, antioxidant potential and antimicrobial activity of walnut (Juglans regia L.) green husks. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2326–2331
Ouzounidou G, Ntougias S, Asfi M, Gaitis F, Zervakis GI (2012) Raw and fungal-treated olive-mill wastewater effects on selected parameters of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth—the role of proline. J Environ Sci Health B 47(7):728–735
Papa S, Bartoli G, Nacca F, D'Abrosca B, Cembrola E, Pellegrino A, Fiorentino A, Fuggi A, Fioretto A (2012) Trace metals, peroxidase activity, PAHs contents and ecophysiological changes in Quercus ilex leaves in the urban area of Caserta (Italy). J Environ Manage 113:501–509
Petriccione M, Ciniglia C (2012) Comet assay to assess the genotoxicity of Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.) husks with statistical evaluation. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:166–171
Petriccione M, Forte V, Valente D, Ciniglia C (2013) DNA integrity of onion root cells under catechol influence. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1422-y
Shakir L, Ejaz S, Ashraf M, Qureshi NA, Anjum AA, Iltaf I, Javeed A (2012) Ecotoxicological risks associated with tannery effluent wastewater. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2:180–191
Stampar F, Solar A, Hudina M, Veberic R, Colaric M (2006) Traditional walnut liqueur–cocktail of phenolics. Food Chem 95(4):627–631
Talapatra SK, Karmacharya B, De SC, Talapatra B (1988) (−)-Regiolone, an α-tetralone from Juglans regia: structure, stereochemistry and conformation. Phytochemistry 27:3929–3932
Tanyolaç D, Ekmekçi Y, Ünalan S (2007) Changes in photochemical and antioxidant enzyme activities in maize (Zea mays L.) leaves exposed to excess copper. Chemosphere 67:89–98
Van Doorn WG (2011) Classes of programmed cell death in plants, compared to those in animals. J Exp Bot 62:4749–4761
Van Doorn WG, Woltering EJ (2005) Many ways to exit? Cell death categories in plants. Trends Plant Sci 10:117–122
Van Doorn WG, Beers EP, Dangl JL, Franklin-Tong WE, Gallois P, Hara-Nishimura I, Jones AM, Kawai-Yamada M, Lam E, Mundy J, Mur LAJ, Petersen M, Smertenko A, Taliansky M, Van Breusegem F, Wolpert T, Woltering E, Zhivotowsky B, Bozhkov PV (2011) Morphological classification of plant cell deaths. Cell Death Differ 18:1241–1246
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophyll a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313
Williams J, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Xie Z, Wu L, Chen N, Liu C, Zheng Y, Xu S, Li F, Xu Y (2012) Phytoextraction of Pb and Cu contaminated soil with maize and microencapsulated EDTA. Int J Phytoremediation 14(8):727–740
Xing J, Saeys W, De Baerdemaeker J (2007) Combination of chemometric tools and image processing for bruise detection on apples. Comput Electron Agric 56:1–13
Yang CM, Lee CN, Chou CH (2012) Effects of three allelopathic phenolics on chlorophyll accumulation of rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings: I. Inhibition of supply-orientation. Bot Bull Acad Sin 43:299–304
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Markus Hecker
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petriccione, M., Papa, S. & Ciniglia, C. Cell-programmed death induced by walnut husk washing waters in three horticultural crops. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 3491–3502 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2205-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2205-9