Abstract
Background
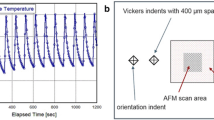
Measurement of local stress amplitude at the stress concentration point is a key component of mechanical design from the viewpoint of preventing metal fatigue. Copper electroplating method, which is a stress measurement method utilizing grains grown in a copper foil by cyclic loading, is suitable for such microscopic stress measurement. Reports have shown that the maximum shear stress and principal stress, which are important components in the evaluation of fatigue strength, can be measured by examining the density and crystallographic features of grown grains.
Objective
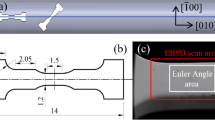
Electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) analysis of grown grains can be utilized to understand the crystallographic features of the grains, but EBSD equipment requires technical skill to operate, which makes it inconvenient. In this paper, we explore the feasibility of stress measurement by analyzing the crystallographic features of grown grains using the X-ray diffraction (XRD) method, which is more versatile than the EBSD method.
Methods
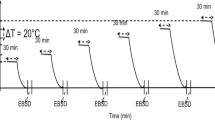
Cyclic loading tests were conducted using smooth specimens with copper foil adhered under various biaxial stress conditions of bending and torsion. The surfaces of the grains-grown copper foil were then analyzed by the XRD method.
Results
The peak of diffraction intensity tended to shift from the (220) plane to the (111) plane as the biaxial stress ratio increased. We quantified this tendency using the Lotgering factor and developed an empirical formula for determining the relationship between the Lotgering factor and the biaxial stress ratio.
Conclusions
Our proposed empirical formula enables principal stress measurement within a biaxial stress ratio C ranging from –0.45 to 0, and the measurement accuracy is comparable to that of the conventional EBSD method.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohkubo H (1968) Copper electroplating method of stress analysis. Memoirs Fac Eng Nagoya Univ 29–1:1
Kato A, Mizuno T (1985) Stress concentration factors of grooved shafts in torsion. J Strain Analysis 20–3:173–177
Kato A (1987) Stress measurement by copper electroplating aided by a personal computer. Exp Mech 27–2:132–137
Nagase Y, Yoshizaki T (1993) Fatigue gauge utilizing slip-initiation phenomenon in electroplated copper foil. Exp Mech 33–1:49–54
Kato A (1995) Stress measurement by copper electroplating based on grain growth. Exp Mech 35–1:24–30
Kitaoka S, Chen J, Egami N, Hasegawa J (1996) Measurement of biaxial stress using electrodeposited copper foil with a microcircular hole (Method using the probability of the occurrence of slip). JSME Int J 39–4(A):533–539
Kitaoka S, Ono Y (2006) Biaxial stress measurement by electrodeposited copper foil with circular holes. Strain 42–1:49–56
Ono Y, Kitaoka S (2008) Cyclic stress measurement method using grain size and occurrence rate of grown grains in electrodeposited copper foil. Strain 47–2:154–161
Ono Y, Li C, Hino D (2010) Cyclic biaxial stress measurement method using the grain growth direction in electrodeposited copper foil. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2010:928216
Ono Y, Morito S, Li C (2012) Stress measurement using EBSD analysis of grains in copper foil. Exp Mech 52–5:493–502
Ono Y, Morito S (2014) Effect of ambient temperature on stress measurement using copper foil. Strain 50–4:292–300
Ono Y (2019) Effect of load frequency on cyclic stress measurement method using electrodeposited copper foil. Adv Exp Mech 4:90–95
Stephens RI, Fatemi A, Stephens RR, Fuchs HO (2001) Metal Fatigue in Engineering, 2nd edn. Wiley & Sons, New York, NY
Ono Y, Morito S (2013) Investigation into early fatigue damage in electrodeposited copper. Int J Fatigue 54:7–16
David B (1974) Elementary Engineering Fracture Mechanics Noordhoff, Netherlands, NL
Lotgering FK (1959) Topotactical reactions with ferrimagnetic oxides having hexagonal crystal structures-I. J Inorg Nucl Chem 9–2:113–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, K., Ono, Y., Izumi, C. et al. Cyclic Stress Measurement Using XRD Analysis of Grains Grown in Electrodeposited Copper Foil. Exp Mech 63, 1309–1320 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-023-00991-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-023-00991-6