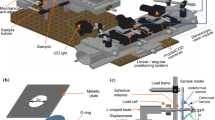
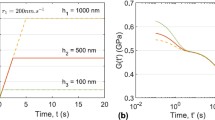
Abstract
We developed a dynamic inflation experiment to measure the elastodynamic behavior of soft materials. In the experiments, a shock tube was used to apply dynamic pressurization to thin polydimethylsiloxane specimens. Two high-speed cameras were used to image the deforming specimen and three-dimensional digital image correlation was used to determine the three-dimensional displacement field of the specimen surface. We applied dynamic Kirchhoff plate bending theory and concepts from structural dynamics to derive a mathematical expression for the dynamic Young’s modulus. The phase velocity of the initial transverse wave propagation response and the vibration frequency of the long-time response were captured during our experiments and were applied in the calculation of the dynamic Young’s modulus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleby-Thomas GJ, Hazell PJ, Wilgeroth JM, Shepherd CJ, Wood DC, Roberts A (2011) On the dynamic behavior of three readily available soft tissue simulants. J Appl Phys 109. doi:10.1063/1.3573632
Ari AB (2006) Eye injuries on the battlefields of Iraq and Afghanistan: public health implications. Optometry 77(7):329–39. doi:10.1016/j.optm.2006.03.015. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16814236
Bailoor S, Bhardwaj R, Nguyen TD (2015) Effectiveness of eye armor during blast loading. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. doi:10.1007/s10237-015-0667-z. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25828209
Bisplinghoff JA, McNally C, Manoogian SJ, Duma SM (2009) Dynamic material properties of the human sclera. J Biomech 42(10):1493–7. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.03.043. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19428016
Boyce BL, Grazier JM, Jones RE, Nguyen TD, Nguyen JMG (2008) Full-field deformation of bovine cornea under constrained inflation conditions. Biomaterials 29(28):3896–3904. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.06.011. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18603294
Cernak I, Noble-Haeusslein L (2010) Traumatic brain injury: an overview of pathobiology with emphasis on military populations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(2):255. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=47846416&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Champion HR, Holcomb JB, Young LA (2009) Injuries from explosions: physics, biophysics, pathology, and required research focus. J Trauma 66(5):1468–77. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a27e7f. discussion 1477. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19430256
Coudrillier B, Tian J, Alexander S, Myers KM, Quigley Ha, Nguyen TD (2012) Biomechanics of the human posterior sclera: age- and glaucoma-related changes measured using inflation testing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53(4):1714–28. doi:10.1167/iovs.11-8009
DePalma RG, Burris DG, Champion HR, Hodgson MJ (2005) Blast injuries. N Engl J Med 352 (13):1335–42. doi:10.1056/NEJMra042083. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15800229
Doyle BJ, Corbett TJ, Cloonan AJ, O’Donnell MR, Walsh MT, Vorp DA, McGloughlin TM (2009) Experimental modelling of aortic aneurysms: novel applications of silicone rubbers. Med Eng Phys 31(8):1002
Ellis B, Smith R (2008) Polymers: A Property Database, 2nd Edn. CRC Press. https://books.google.com/books?id=S-TKBQAAQBAJ
Elsheikh A, Anderson K (2005) Comparative study of corneal strip extensometry and inflation tests. J R Soc Interface 2(3):177–85. doi:10.1098/rsif.2005.0034
Fan JT, Weerheijm J, Sluys LJ (2015) High-strain-rate tensile mechanical response of a polyurethane elastomeric material. Polymer 65:72
Ferreira P, Carvalho Á, Correia TR, Antunes BP, Correia IJ, Alves P (2013) Functionalization of polydimethylsiloxane membranes to be used in the production of voice prostheses. Sci Technol Adv Mater 14 (5):055,006. http://stacks.iop.org/1468-6996/14/i=5/a=055006
Flavell W (1972) Fibres, films, plastics and rubbers. w. j. roff and j. r. scott. butterworths, london. 1971. pp. 688. price 15.00. British Polymer Journal 4(3):267–268. doi:10.1002/pi.4980040314
Friberg TR, Lace JW (1988) A comparison of the elastic properties of human choroid and sclera. Exp Eye Res 47(3):429. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cmedm%25&AN=3181326&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Hamilton KE, Pye DC (2008) Young’s modulus in normal corneas and the effect on applanation tonometry. Optometry And Vision Science: Official Publication Of The American Academy Of Optometry 85(6):445. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cmedm%25&AN=18521022&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Hines-Beard J, Marchetta J, Gordon S, Chaum E, Geisert EE, Rex TS (2012) A mouse model of ocular blast injury that induces closed globe anterior and posterior pole damage. Exp Eye Res 99:63. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cmedm%25&AN=22504073&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Johnston ID, McCluskey DK, Tan CKL, Tracey MC (2014) Mechanical characterization of bulk sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J Micromech Microeng 24 (3):035,017. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=94771920&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Katz E, Ofek B, Adler J, Abramowitz HB, Krausz MM (1989) Primary blast injury after a bomb explosion in a civilian bus. Ann Surg 209(4):484. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cmedm%25&AN=2930293&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Khanafer K, Duprey A, Schlicht M, Berguer R (2009) Effects of strain rate, mixing ratio, and stress-strain definition on the mechanical behavior of the polydimethylsiloxane (pdms) material as related to its biological applications. Biomed Microdevices 11(2):503
Lim J, Hong J, Chen WW, Weerasooriya T (2011) Mechanical response of pig skin under dynamic tensile loading. International Journal of Impact Engineering 38(2):130. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=55499924&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Mata A, Fleischman AJ, Roy S (2005) Characterization of polydimethylsiloxane (pdms) properties for biomedical micro/nanosystems. Biomed. Microdevices 7(4):281
Mates SP, Rhorer R, Forster A, Everett RK, Simmonds KE, Bagchi A (2011) Modeling and DIC Measurements of Dynamic Compression Tests of a Soft Tissue Simulant. In: Dyn. Behav. Mater. Vol 1. Springer, New York, pp 307–316. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-0216-9_43.
Moss WC, King MJ, Blackman EG (2009) Skull flexure from blast waves: A mechanism for brain injury with implications for helmet design. Phys Rev Lett:103. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.108702. 0809.3468
Mrozek RA, Leighliter B, Gold CS, Beringer IR, Yu JH, VanLandingham MR, Moy P, Foster MH, Lenhart JL (2015) The relationship between mechanical properties and ballistic penetration depth in a viscoelastic gel. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 44:109
Myers KM, Coudrillier B, Boyce BL, Nguyen TD (2010) The inflation response of the posterior bovine sclera. Acta Biomater 6(11):4327–35. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2010.06.007. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20558331
Nie X, Song B, Ge Y, Chen WW, Weerasooriya T (2008) Dynamic Tensile Testing of Soft Materials. Exp Mech 49(4):451–458. doi:10.1007/s11340-008-9133-5
Nie X, Cheng JI, Chen WW (2011a) Dynamic tensile response of porcine muscle. J Appl Mech 78 (2):021,009–021,001
Nie X, Prabhu R, Chen W, Caruthers J, Weerasooriya T (2011b) A kolsky torsion bar technique for characterization of dynamic shear response of soft materials. Exp Mech 51(9): 1527
Palchesko RN, Zhang L, Sun Y, Feinberg AW (2012) Development of polydimethylsiloxane substrates with tunable elastic modulus to study cell mechanobiology in muscle and nerve. PLoS ONE 7(12):1
Petras JM, Bauman RA, Elsayed NM (1997) Visual system degeneration induced by blast overpressure. Toxicology 121(1):41. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cmedm%25&AN=9217314&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Placet V, Delobelle P (2015) Mechanical properties of bulk polydimethylsiloxane for microfluidics over a large range of frequencies and aging times. J Micromech Microeng 25(3):035,009. http://stacks.iop.org/0960-1317/25/i=3/a=035009
Polyzois GL, Eleni PN, Krokida MK (2011) Optical properties of pigmented polydimethylsiloxane prosthetic elastomers: effect of ”outdoor” and ”indoor” accelerating aging. Journal of craniofacial surgery 22(5):1574
Ramesh KT (2008) High Rates and Impact Experiments. In: Sharpe WN (ed) Springer Handb. Exp. Solid Mech. Springer, US, pp 929–960, doi:10.1007/978-0-387-30877-7_33.
Rao JS (1999) Dynamics of Plates. Marcel Dekker
Rashid B, Destrade M, Gilchrist MD (2014) Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in tension at dynamic strain rates. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 33:43
Richler D, Rittel D (2014) On the testing of the dynamic mechanical properties of soft gelatins. Exp Mech 54(5):805. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=asf&AN=95905672&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Ritenour AE, Blackbourne LH, Kelly JF, McLaughlin DF, Pearse La, Holcomb JB, Wade CE (2010) Incidence of primary blast injury in US military overseas contingency operations: a retrospective study. Ann Surg 251(6):1140–4. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181e01270. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20485126
Salisbury CP, Cronin DS (2009) Mechanical Properties of Ballistic Gelatin at High Deformation Rates. Exp Mech 49(6):829–840. doi:10.1007/s11340-008-9207-4
Saraf H, Ramesh KT, Lennon AM (2007a) Measurement of the dynamic bulk and shear response of soft human tissues. Exp Mech 47(3):439
Saraf H, Ramesh K T, Lennon A M, Merkle A C, Roberts J C (2007b) Mechanical properties of soft human tissues under dynamic loading. J Biomech 40(9):1960
Sarntinoranont M, Lee SJ, Hong Y, King MA, Subhash G, Kwon J, Moore DF (2012) High-strain-rate brain injury model using submerged acute rat brain tissue slices. J Neurotrauma 29(2):418. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=psyh&AN=2012-02952-021&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Schultz DS, Lotz JC, Lee SM, Trinidad ML, Stewart JM (2008) Structural factors that mediate scleral stiffness. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49(10):4232. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cmedm%25&AN=18539943&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Song B, Chen W, Ge Y, Weerasooriya T (2007) Dynamic and quasi-static compressive response of porcine muscle. J Biomech 40(13):2999–3005. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2007.02.001. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17448479
Stapczynski JS (1982) Blast injuries. Ann Emerg Med 11(12):687–694
Subhash G, Kwon J, Mei R, Moore D (2012) Non-newtonian behavior of ballistic gelatin at high shear rates. Exp Mech 52(6):551
Thevamaran R, Daraio C (2014) An Experimental Technique for the Dynamic Characterization of Soft Complex Materials. Exp Mech 54(8):1319–1328. doi:10.1007/s11340-014-9896-9
Timoshenko SP, Woinowsky-Krieger S (1959) Theory of plates and shells. McGraw-Hill International Ed., Singapore. iD: 860490846
Tonge TK, Atlan LS, Voo LM, Nguyen TD (2013a) Full-field bulge test for planar anisotropic tissues: part I–experimental methods applied to human skin tissue. Acta Biomater 9(4):5913–25. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2012.11.035. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23261928
Tonge TK, Voo LM, Nguyen TD (2013b) Full-field bulge test for planar anisotropic tissues: part II–a thin shell method for determining material parameters and comparison of two distributed fiber modeling approaches. Acta Biomater 9(4):5926–42. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2012.11.034. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23220451
VIC3D (2010) Vic-3D 2010 Reference Manual. Correlated Solution, www.correlatedsolutions.com
Wang Z, Volinsky AA, Gallant ND (2014) Crosslinking effect on polydimethylsiloxane elastic modulus measured by custom-built compression instrument. J Appl Polym Sci 131(22):n/a–n/a
Warren T, Forrestal M (2010) Comments on the effect of radial inertia in the kolsky bar test for an incompressible material. Exp Mech 50(8):1253. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=asf&AN=54325857&site=ehost-live&scope=site
White CS (1968) The scope of blast and shock biology and problem areas in relating physical and biological parameters. Ann N Y Acad Sci 152(1):89–102
Woo SLY, Kobayashi AS, Schlegel WA, Lawrence C (1972) Kobayashi_Woo_1972.pdf. Exp Eye Res 14(1):29–39. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/5039845
Wu CL, Lin HC, Hsu JS, Yip MC, Fang W (2009) Static and dynamic mechanical properties of polydimethylsiloxane/carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Thin Solid Films 517(17):4895. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=40308020&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ravi Yatnalkar and Matt Shaeffer for the design, building, and technical support of the shock tube inflation experimental setup. This research is financially supported with contract W91CRB-13-P-0090 from the US Army Aberdeen Test Center and US Army Natick Soldier Research, Development & Engineering Center, and the US Army Medical Research, Vision Research Program under grant number W81XWH- 10-1-0766.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bentil, S.A., Ramesh, K.T. & Nguyen, T.D. A Dynamic Inflation Test for Soft Materials. Exp Mech 56, 759–769 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-015-0122-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-015-0122-1