Abstract
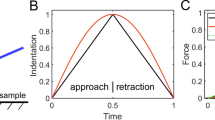
Indentation relaxation test is investigated from theoretical and experimental points of view. Analytical expressions are derived based on the conical indentation of a homogeneous linear viscoelastic half space. Two loading kinetics prior to the hold displacement segment are studied—i.e., constant displacement rate and constant strain rate. Effects of loading procedure on measured relaxation behavior are considered. It is pointed out that a constant strain rate loading is required to perform depth-independent relaxation measurements and the strain rate affects the relaxation spectrum up to a critical time constant. Few experiments on poly(methyl methacrylate) are then performed to check the consistency of the analytical results. Some experimental limitations are also discussed. Good agreement is found between analytical calculations and experimental measurement trends, especially for the constant strain rate loading effect on the measured relaxation behavior.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M. Wheeler, D.E.J. Armstrong, W. Heinz, and R. Schwaiger: High temperature nanoindentation: The state of the art and future challenges. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 19, 354 (2015).
P.S. Phani and W.C. Oliver: A direct comparison of high temperature nanoindentation creep and uniaxial creep measurements for commercial purity aluminum. Acta Mater. 111, 31 (2016).
Y. Li, X. Fang, S. Lu, Q. Yu, G. Hou, and X. Feng: Effects of creep and oxidation on reduced modulus in high-temperature nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 678, 65 (2016).
N.M. Everitt, M.I. Davies, and J.F. Smith: High temperature nanoindentation—The importance of isothermal contact. Philos. Mag. 91, 1221 (2011).
M. Sakai and S. Shimizu: Indentation rheometry for glass-forming materials. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 282, 236 (2001).
S. Yang, Y.W. Zhang, and K. Zeng: Analysis of nanoindentation creep for polymeric materials. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 3655 (2004).
M.L. Oyen: Spherical indentation creep following ramp loading. J. Mater. Res. 20, 2094 (2005).
M.L. Oyen: Analytical techniques for indentation of viscoelastic materials. Philos. Mag. 86, 5625 (2006).
C.A. Tweedie and K.J. Van Vliet: Contact creep compliance of viscoelastic materials via nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 21, 1576 (2006).
E.G. Herbert, W.C. Oliver, A. Lumsdaine, and G.M. Pharr: Measuring the constitutive behavior of viscoelastic solids in the time and frequency domain using flat punch nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 24, 626 (2009).
P.E. Mazeran, M. Beyaoui, M. Bigerelle, and M. Guigon: Determination of mechanical properties by nanoindentation in the case of viscous materials. Int. J. Mater. Res. 103, 715 (2012).
V. Maier, B. Merle, M. Göken, and K. Durst: An improved long-term nanoindentation creep testing approach for studying the local deformation processes in nanocrystalline metals at room and elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Res. 28, 1177 (2013).
J. Dean, J. Campbell, G. Aldrich-Smith, and T.W. Clyne: A critical assessment of the “stable indenter velocity” method for obtaining the creep stress exponent from indentation data. Acta Mater. 80, 56 (2014).
M. Sakai, M. Sasaki, and A. Matsuda: Indentation stress relaxation of sol–gel-derived organic/inorganic hybrid coating. Acta Mater. 53, 4455 (2005).
J. Mattice, A. Lau, M. Oyen, and R. Went: Spherical indentation load-relaxation of soft biological tissues. J. Mater. Res. 21, 2003 (2006).
C.Y. Zhang, Y.W. Zhang, K.Y. Zeng, L. Shen, and Y.Y. Wang: Extracting the elastic and viscoelastic properties of a polymeric film using a sharp indentation relaxation test. J. Mater. Res. 21, 2991 (2006).
J.W. Andrews, J. Bowen, and D. Cheneler: Optimised determination of viscoelastic properties using compliant measurement systems. Soft Matter 9, 5581 (2013).
G. Peng, Y. Ma, Y. Feng, Y. Huan, C. Qin, and T. Zhang: Nanoindentation creep of nonlinear viscoelastic polypropylene. Polym. Test. 43, 38 (2015).
N.G. Patel, A. Sreeram, R.I. Venkatanarayanan, S. Krishnan, and P.A. Yuya: Elevated temperature nanoindentation characterization of poly(para-phenylene vinylene) conjugated polymer films. Polym. Test. 41, 17 (2015).
R. Goodall and T.W. Clyne: A critical appraisal of the extraction of creep parameters from nanoindentation data obtained at room temperature. Acta Mater. 54, 5489 (2006).
M.R. Vanlandingham, N.K. Chang, P.L. Drzal, C.C. White, and S.H. Chang: Viscoelastic characterization of polymers using instrumented indentation. I. Quasi-static testing. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 43, 1794 (2005).
K.I. Schiffmann: Nanoindentation creep and stress relaxation tests of polycarbonate: Analysis of viscoelastic properties by different rheological models. Int. J. Mater. Res. 97, 1199 (2006).
J.L. Bucaille, E. Felder, and G. Hochstetter: Identification of the viscoplastic behavior of a polycarbonate based on experiments and numerical modeling of the nano-indentation test. J. Mater. Sci. 37, 3999 (2002).
G. Kermouche, J.L. Loubet, and J.M. Bergheau: Extraction of stress–strain curves of elastic-viscoplastic solids using conical/pyramidal indentation testing with application to polymers. Mech. Mater. 40, 271 (2008).
W. Findley: Creep and Relaxation of Nonlinear Viscoelastic Materials (Dover Publication, Inc., New York 1978).
N.W. Tschoegl, W.G. Knauss, and I. Emri: Poisson’s ratio in linear viscoelasticity—A critical review. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 6, 3 (2002).
T.C.T. Ting: The contact stresses between a rigid indenter and a viscoelastic half-space. J. Appl. Mech. 33, 845 (1966).
G.A.C. Graham: The contact problem in the linear theory of viscoelasticity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 27 (1965).
A.E.H. Love: Boussinesq’s problem for a rigid cone. Q. J. Math. os-10, 161 (1939).
I.N. Sneddon: Boussinesq’s problem for a rigid cone. Math. Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 44, 492 (1948).
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng: Scaling, dimensional analysis, and indentation measurements. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44, 91 (2004).
M. Vandamme and F.J. Ulm: Viscoelastic solutions for conical indentation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 3142 (2006).
G. Kermouche, J.L. Loubet, and J.M. Bergheau: Cone indentation of time-dependent materials: The effects of the indentation strain rate. Mech. Mater. 39, 24 (2007).
N.W. Tschoegl: The Phenomenological Theory of Linear Viscoelastic Behavior 3rd ed. (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1989). p. 1–34.
J.D. Ferry: Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1980).
F. Schwarzl and A.J. Staverman: Higher approximations of relaxation spectra. Physica 18, 791 (1952).
J.D. Ferry and M.L. Williams: Second approximation methods for determining the relaxation time spectrum of a viscoelastic material. J. Colloid Sci. 7, 347 (1952).
B.N. Lucas, W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr, and J-L. Loubet: Time dependent deformation during indentation testing. MRS Proc. 436, 233 (1997).
G. Guillonneau, G. Kermouche, S. Bec, and J.L. Loubet: Extraction of mechanical properties with second harmonic detection for dynamic nanoindentation testing. Exp. Mech. 52, 933 (2012).
J.L. Loubet, M. Bauer, A. Tonck, S. Bec, and B. Gauthier-Manuel: Nanoindentation with a surface force apparatus. In Mechanical Properties and Deformation Behavior of Materials Having Ultra-Fine Microstructures, Vol. 233 (1993); p. 429.
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004).
G. Guillonneau, G. Kermouche, J-M. Bergheau, and J-L. Loubet: A new method to determine the true projected contact area using nanoindentation testing. C. R. Mec. 343, 410 (2015).
E.G. Herbert, P. Sudharshan Phani, and K.E. Johanns: Nanoindentation of viscoelastic solids: A critical assessment of experimental methods. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 19, 334 (2015).
A.F. Yee and M.T. Takemori: Dynamic bulk and shear relaxation in glassy polymers. I. Experimental techniques and results on PMMA. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 20, 205 (1982).
D. Tabor: The hardness of solids. Rev. Phys. Technol. 1, 145 (1970).
P. Fernández, D. Rodríguez, M.J. Lamela, and A. Fernández-Canteli: Study of the interconversion between viscoelastic behaviour functions of PMMA. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 15, 169 (2011).
H. Lu, X. Zhang, and W.G. Knauss: Uniaxial, shear, and poisson relaxation and their conversion to bulk relaxation: Studies on poly(methyl methacrylate). Polym. Eng. Sci. 37, 1053 (1997).
J.J.C. Cruz Pinto and J.R.S. André: Toward the accurate modeling of amorphous nonlinear materials—Polymer stress relaxation (I). Polym. Eng. Sci. 56, 348 (2016).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the LABEX MANUTECH-SISE (ANR-10-LABX-0075) of Université de Lyon, within the program “Investissements d’Avenir” (ANR-11-IDEX-0007) operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR). The authors would also like to acknowledge financial support from Institut Carnot Ingénierie@Lyon. The authors finally acknowledge Dr. M. Laurent-Brocq and G. Bracq from ICMPE for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baral, P., Guillonneau, G., Kermouche, G. et al. Theoretical and experimental analysis of indentation relaxation test. Journal of Materials Research 32, 2286–2296 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.203
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.203