Abstract
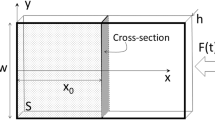
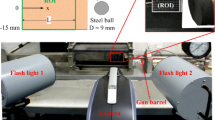
This paper deals with the analysis of an aluminium beam impacted in a three point bending configuration using a Hopkinson bar device. Full-field deformation measurements were performed using Digital Image Correlation on images captured with an ultra high speed camera (16 frames at a time resolution of 10 μs). The performance of the deformation and strain measurements were evaluated and the data were then used quantitatively to analyse the very complex dynamic behaviour of the beam. It was shown that the deformation of the beam was controlled by the interaction between the striker and the flexural bending wave triggered by the initial impact. The principle of virtual work was used to reconstruct the impact force from the shear strains and to analyze how this impact force relates to the acceleration of the specimen (inertia forces) and the development of the bending stresses. The results are in good agreement with expectations. This opens up new perspectives in the quantitative use of full-field measurements to extract elasto-plastic constitutive parameters from such impact tests.



























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grédiac M (2004) The use of full-field measurement methods in composite material characterization: interest and limitations. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 35(7–8):751–761
Avril S, Bonnet M, Bretelle A-S, Grédiac M, Hild F, Ienny P, Latourte F, Lemosse D, Pagano S, Pagnacco E, Pierron F (2008) Overview of identification methods of mechanical parameters based on full-field measurements. Exp Mech 48(4):381–402
Meuwissen MHH, Oomens CWJ, Baaijens FPT, Petterson R, Janssen JD (1998) Determination of the elasto-plastic properties of aluminium using a mixed numerical-experimental method. J Mater Process Technol 75:204–211
Meuwissen MHH (1998) An inverse method for the echanical characterisation of metals. PhD thesis, Eindhoven Technical University
Kajberg J, Lindkvist G (2004) Characterization of materials subjected to large strains by inverse modelling based on in-plane displacement fields. Int J Solids Struct 41:3439–3459
Cooreman S, Lecompte D, Sol H, Vantomme J, Debruyne D (2008) Identification of mechanical material behaviour through inverse modeling and DIC. Exp Mech 48(4):421–433
Latourte F, Chrysochoos A, Pagano S, Wattrisse B (2008) Elastoplastic behavior identification for heterogeneous loadings and materials. Exp Mech 48(4):435–449
Grédiac M, Pierron F (2006) Applying the virtual fields method to the identification of elasto-plastic constitutive parameters. Int J Plast 22:602–627
Pannier Y, Avril S, Rotinat R, Pierron F (2006) Identification of elasto-plastic constitutive parameters from statically undetermined tests using the virtual fields method. Exp Mech 46(6):735–755
Avril S, Pierron F, Pannier Y, Rotinat R (2008) Stress reconstruction and constitutive parameter identification in elastoplasticity using measurements of deformation fields. Exp Mech 48(4):403–419
Fuller PWW (2009) An introduction to high speed photography and photonics. J Imag Sci 57(6):293–302
Honour J (2009) A brief history of principles used in high speed cameras. J Imag Sci 57(6):303–316
Field JE, Proud WG, Walley SM (2009) Review of optical and X-ray techniques used at the Cavendish laboratory. J Imag Sci 57(6):317–325
Grantham SG, Siviour CR, Proud WG, Field JE (2004) High-strain rate brazilian testing of an explosive simulant using speckle metrology. Meas Sci Technol 15:1867–1870
Kajberg J, Sundin KG, Melin LG, Ståhle P (2004) High strain rate tensile and viscoplastic parameter identification using micoscopic high-speed photography. Int J Plast 20:561–575
Kajberg J, Wikman B Viscoplastic parameter estimation by high strain-rate experiments and inverse modelling—speckle measurements and high-speed photography. Int J Solids Struct 44:145–164 (2007)
Siviour CR (2009) A measurement of wave propagation in the split hopkinson pressure bar. Meas Sci Technol 20:065702
Tiwari V, Sutton MA, McNeill SR (2007) Assessment of high speed imaging systems for 2D and 3D deformation measurements: methodology development and validation. Exp Mech 47(4):561–579
Kirugulige MS, Tippur HV (2009) Measurement of fracture parameters for a mixed-mode crack driven by stress waves using image correlation technique and high speed digital photography. Strain 45:108–122
Luo H, Lu H, Leventis N (2006) The compressive behavior of isocyanate-crosslinked silica aerogel at high strain rates. Mech Time-Depend Mater 10:83–111
Tiwari V, Sutton MA, McNeill SR, Xu S, Deng X, Fourney WL, Bretall D (2009) Application of 3D image correlation for full-field transient plate deformation measurements during blast loading. Int J Impact Eng 36:862–874
Field JE, Walley SM, Proud WG, Goldrein HT, Siviour CR (2004) Review of experimental techniques for high rate deformation and shock studies. Int J Impact Eng 30:725–755
Mohr D, Gary G, Lundberg B (2010) Evaluation of stress-strain curve estimates in dynamic experiments. Int J Impact Eng 37(2):161–169
Avril S, Pierron F, Yan J, Sutton MA (2008) Identification of viscoplastic parameters and characterization of Lüders behavior using digital image correlation and the virtual fields method. Mech Mater 40(9):729–742
Moulart R, Pierron F, Hallett S, Wisnom M (2009) Full-field strain measurements at high rate on notched composites tested with a tensile hopkinson bar. In: SEM annual congress on experimental mechanics. Society for Experimental Mechanics, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA, 1–4 June 2009
Hallett SR (2000) Three-point beam impact tests on T300/914 carbon-fibre composites. Compos Sci Technol 60:115–124
Correlated solutions Inc. Vic 2D image correlation package. http://www.correlatedsolutions.com
Avril S, Feissel P, Pierron F, Villon P (2008) Estimation of the strain field from full-field displacement noisy data: comparing finite element global least squares and polynomial diffuse approximation. Eur J Comput Mech 17(5–7):857–868
Avril S, Feissel P, Pierron F, Villon P (2010) Comparison of two approaches for controlling the uncertainty in data differentiation: application to full-field measurements in solid mechanics. Meas Sci Technol 21:015703 (11 pp)
Lee W-S, Shyu J-C, Chiou S-T (1999) Effect of strain rate on impact response and dislocation substructure of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Scr Mater 42(1):51–56
Grédiac M, Pierron F, Avril S, Toussaint E (2006) The virtual fields method for extracting constitutive parameters from full-field measurements: a review. Strain 42:233–253
Avril S, Pierron F (2007) General framework for the identification of elastic constitutive parameters from full-field measurements. Int J Solids Struct 44:4978–5002
Giraudeau A, Pierron F (2005) Identification of stiffness and damping properties of thin isotropic plates using the virtual fields method: theory and simulations. J Sound Vib 284(3–5):757–781
Giraudeau A, Guo B, Pierron F (2006) Stiffness and damping identification from full-field measurements on vibrating plates. Exp Mech 46(6):777–787
Giraudeau A, Pierron F, Guo B (2010) An alternative to modal analysis for material stiffness and damping identification from vibrating plates. J Sound Vib 329(10):1653–1672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierron, F., Sutton, M.A. & Tiwari, V. Ultra High Speed DIC and Virtual Fields Method Analysis of a Three Point Bending Impact Test on an Aluminium Bar. Exp Mech 51, 537–563 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-010-9402-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-010-9402-y