Abstract
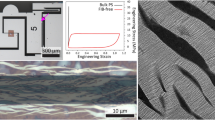
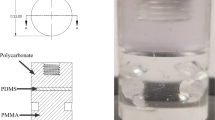
In this paper a micro tensile test which allows the determination and observation of the crack growth behaviour in thin polymer layers is presented. The setup consists of micromanipulators and piezo actuators for straining the sample while an atomic force microscope (AFM) is used for scanning the crack tip area with high lateral resolution. The stress in the specimen is determined by an optical microscope for observation of the deflection of a force sensing beam. The material under investigation is an amorphous and strongly entangled thermoplastic polyimide which can be patterned photolithographically and is spin cast to form layers of 3 μm thickness. The results show the potential of the setup to measure crack length, crack tip opening and nominal stress. The stress-crack length-diagram then allows to determine different stages during crack growth.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chasiotis I, Knauss WG (2002) A new microtensile tester for the study of MEMS materials with the aid of atomic force microscopy. Exp Mech 42(1):51–57
Cho SW, Cardenas-Garcia JF, Chasiotis I (2005) Measurement of nanodisplacements and elastic properties of MEMS via the microscopic hole method. Sens Actuators A Phys 120(1):163–171
Cho SW, Chasiotis I (2007) Elastic properties and representative volume element of polycrystalline silicon for MEMS. Exp Mech 47(1):37–49
Chasiotis I, Cho SW, Jonnalagadda K (2006) Fracture toughness and subcritical crack growth in polycrystalline silicon. J Appl Mech 73(5):714–722
Cho SW, Jonnalagadda K, Chasiotis I (2007) Mode I and mixed mode fracture of polysilicon for MEMS. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 30(1):21–31
Lee Y, Tada J, Isono Y (2005) Mechanical characterization of single crystal silicon and UV-LIGA nickel thin films using tensile tester operated in AFM. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 28(8):675–686
Isono Y, Namazu T, Terayama N (2006) Development of AFM tensile test technique for evaluating mechanical properties of sub-micron thick DLC films. J Microelectromech Syst 15(1):169–180
Bobji MS, Bhushan B (2001) In situ microscopic surface characterization studies of polymeric thin films during tensile deformation using atomic force microscopy. J Mater Res 16(3):844–855
Tambe NS, Bhushan B (2004) In situ study of nano-cracking in multilayered magnetic tapes under monotonic and fatigue loading using an AFM. Ultramicroscopy 100(3-4):359–373
Li XD, Xu WJ, Sutton MA, Mello M (2006) Nanoscale deformation and cracking studies of advanced metal evaporated magnetic tapes using atomic force microscopy and digital image correlation techniques. Mater Sci Technol 22(7):835–844
Nishino T, Nozawa A, Kotera M, Nakamae K (2000) In situ observation of surface deformation of polymer films by atomic force microscopy. Rev Sci Instrum 71(5):2094–2096
Opdahl A, Somorjai GA (2001) Stretched polymer surfaces: atomic force microscopy measurement of the surface deformation and surface elastic properties of stretched polyethylene. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 39(19):2263–2274
Roggemann MC, Williams JG (2002) Use of an atomic force microscope to measure surface deformations in polymeric systems. J Adhes Sci Technol 16(7):905–920
Bhushan B, Mokashi PS, Ma T (2003) A technique to measure poisson’s ratio of ultrathin polymeric films using atomic force microscopy. Rev Sci Instrum 74(2):1043–1047
Bamberg E, Grippo CP, Wanakamol P, Slocum AH, Boyce MC, Thomas EL (2006) A tensile test device for in situ atomic force microscope mechanical testing. Precis Eng J Int Soc Precis Eng Nanotechnol 30(1):71–84
Li XD, Xu WJ, Sutton MA, Mello M (2007) In situ nanoscale in-plane deformation studies of ultrathin polymeric films during tensile deformation using atomic force microscopy and digital image correlation techniques. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 6(1):4–12
Michler GH, Godehardt R (2000) Deformation mechanisms of semi-crystalline polymers on the submicron scale. Cryst Res Technol 35(6-7):863–875
Thomas C, Ferreiro V, Coulon G, Seguela R (2007) In situ AFM investigation of crazing in polybutene spherulites under tensile drawing. Polymer 48(20):6041–6048
Haque MA, Saif MTA (2002) In-situ tensile testing of nano-scale specimens in SEM and TEM. Exp Mech 42(1):123–128
LLC HD MicroSystems (1998) Pyralin PI2720 Processing Guidelines
Kajii H, Taneda T, Ohmori Y (2003) Organic light-emitting diode fabricated on a polymer substrate for optical links. Thin Solid Films 438:334–338
Lee JG, Seol YG, Lee NE (2006) Polymer thin film transistor with electroplated source and drain electrodes on a flexible substrate. Thin Solid Films 515(2):805–809
Tung S, Witherspoon SR, Roe LA, Silano A, Maynard DP, Ferraro N (2001) A MEMS-based flexible sensor and actuator system for space inflatable structures. Smart Mater Struct 10(6):1230–1239
Aslam M, Gregory C, Hatfield JV (2004) Polyimide membrane for micro-heated gas sensor array. Sens Actuators B Chem 103(1–2):153–157
Kuoni A, Holzherr R, Boillat M, de Rooij NF (2003) Polyimide membrane with ZnO piezoelectric thin film pressure transducers as a differential pressure liquid flow sensor. J Micromechanics Microengineering 13(4):S103–S107
ISO527-3 (1995) Plastics-determination of tensile properties-part 3. Technical report
Lang U, Reichen M, Dual J (2006) Fabrication of a tensile test for polymer micromechanics. Microelectron Eng 83(4–9):1182–1184
Grellmann W (2005) Kunststoffprüfung, p 104. Carl Hanser Verlag, München
Ward IM (1983) Mechanical properties of solid polymers, 2nd edn, pp 83–84. Wiley, Chichester
Jones DRH, Ashby M (1998) Engineering materials, volume 2: an introduction to microstructure, processing and design, 2nd edn, p 238. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Popelar SF, Popelar CH, Kenner VH (1993) Time-dependent fracture of polyimide films. J Electron Packag 115:264–269
Frisch-Fay R (1962) Flexible bars, pp 83–91. Butterworths, London
Gerlach G (1997) Grundlagen der Mikrosystemtechnik, p 29. Carl Hanser Verlag, München
Anderson TL (1995) Fracture mechanics: fundamentals and applications, p 630. CRC, Boca Raton
Neuber H (1985) Kerbspannungslehre, pp 125–127. Springer, Berlin
Pilkey WD (1997) Peterson’s stress concentration factors, p 65. Wiley, New York
Sommer E (1984) Bruchmechanische Bewertung von Oberflächenrissen, pp 28–35. Springer, Berlin
Sähn S, Göldner H (1989) Bruch- und Beurteilungskriterien in der Festigkeitslehre, p 32. VEB Fachbuchverlag Leipzig, Leipzig
Plummer CJG, Hedrick JL, Kausch HH, Hilborn JG (1995) Microdeformation in thin-films of 3fda/pmda polyimide and polyimide nanofoams. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 33(12):1813–1820
Jang BZ, Pater RH, Soucek MD, Hinkley JA (1992) Plastic-deformation mechanisms in polyimide resins and their semiinterpenetrating networks. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 30(7):643–654
Donald AM, Kramer EJ (1982) The competition between shear deformation and crazing in glassy-polymers. J Mater Sci 17(7):1871–1879
Lang U (2008) Experimental methods for evaluating the mechanical properties of thin layers of intrinsically conductive polymers (Diss. ETH No. 17754). PhD thesis, ETH Zurich
Keller J, Vogel D, Schubert A, Michel B (2004) Displacement and strain field measurements from SPM images. In: Bhushan B, Fuchs H, Hosaka S (eds) Applied scanning probe methods, volume I of nanoScience and technology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 253–276
Vendroux G, Schmidt N, Knauss WG (1998) Submicron deformation field measurements: part 3. Demonstration of deformation determinations. Exp Mech 38(3):154–160
Feddersen CE (1971) Evaluation and prediction of residual strength of center cracked tension panels. In: Rosenfield MS (ed) Damage tolerance in aircraft structures, volume ASTM STP 486. ASTM, Philadelphia, pp 50–86
Rösler J, Harders H, Bäker M (2003) Mechanisches Verhalten der Werkstoffe, p 141. BG Teubner, Stuttgart
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Prof. Bharat Bhushan from the Ohio State University, Prof. Taher Saif from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Dr. Hans-Jakob Schindler from Mat-Tec AG (Winterthur, Switzerland), Dr. Pieter van Schendel from Nanosurf AG (Liestal, Switzerland), Dipl.-Ing. Bettina Seiler and Dr. Michael Dost from CWM GmbH (Chemnitz, Germany) and finally Dr. Nicola Naujoks from the Nanotechnology Group of ETH Zurich for very helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lang, U., Süss, T., Wojtas, N. et al. Novel Method for Analyzing Crack Growth in Polymeric Microtensile Specimens by In Situ Atomic Force Microscopy. Exp Mech 50, 463–472 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-009-9240-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-009-9240-y