Abstract
Purpose
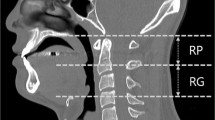
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common clinical condition in which the upper airway partially or completely narrows or collapses during sleep. The objective of our research was to examine the relation between the abnormal internal carotid artery (ICA) and the pharyngeal wall among individuals suffering from OSA, and to compare it to a group of control subjects.
Methods
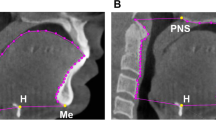
In this retrospective study, the closest distances of the ICA to the pharyngeal walls and midlines were measured on CT images and compared between groups.
Results
The closest distance of the ICA to the right pharyngeal wall was 3.8 ± 2.4 mm and the closest distance to the left pharyngeal wall was 4.1 ± 2.3 mm in patients with OSA, which was significantly less than the controls (respectively, 4.4 ± 1.6 mm and 14.4 ± 1.7 mm) (p < 0.001). The closest distances of the ICA to the right and left pharyngeal walls (p = 0.001) and to the right and left midline (p = 0.00002) were significantly lower in patients with moderate to severe OSA compared to mild patients according to apnea / hypopnea index (AHI). In the retroglossal bifurcation of the common carotid artery (CCA), the closest distances of the ICA to the right (p = 0.027) and left pharyngeal walls (p = 0.018) and to the right (p = 0.01) and left midline (p = 0.012) were significantly lower than the retroepiglottic bifurcation of the CCA.
Conclusion
We observed that the distance of the aberrant ICA to the pharyngeal wall is less in individuals with OSA than in individuals without OSA, the distance of the aberrant ICA to the pharyngeal wall decreased as the severity of AHI increased.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2005) The International classification of sleep disorders: diagnostic and coding manual, 2nd edn. Westchester, II: American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J et al (1993) The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199304293281704
White DP (2005) Pathogenesis of obstructive and central sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:1363–1370. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200412-1631SO
Ayoub N, Eble P, Kniha K et al (2019) Three-dimensional evaluation of the posterior airway space: differences in computed tomography and cone beam computed tomography. Clin Oral Investig 23:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2478-y
Schwab RJ, Gefter WB, Hoffman EA et al (1993) Dynamic upper airway imaging during awake respiration in normal subjects and patients with sleep disordered breathing. Am Rev Respir Dis 148:1385–1400. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/148.5.1385
Kersin B, Karaman M, Aynaci E et al (2020) Investigation of the effectiveness of surgical treatment on respiratory functions in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Ear Nose Throat J 99:537–542. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561319840818
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M et al (2000) Longitudinal study of moderate weight change and sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA 284:3015–3021. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.284.23.3015
Young T, Finn L, Austin D et al (2003) Menopausal status and sleep-disordered breathing in the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:1181–1185. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200209-1055OC
Altin R, Ozdemir H, Mahmutyazicioglu K et al (2005) Evaluation of carotid artery wall thickness with high-resolution sonography in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Ultrasound 33:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcu.20093
Dempsey JA, Skatrud JB, Jacques AJ et al (2002) Anatomic determinants of sleep-disordered breathing across the spectrum of clinical and nonclinical male subjects. Chest 122:840–851. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.122.3.840
Weibel J, Fields WS (1965) Tortuosity, coiling, and kinking of the internal carotid artery. I. Etiology and radiographic anatomy. Neurology 15:7–18. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.15.1.7
Desai B, Toole JF (1975) Kinks, coils, and carotids: a review. Stroke 6:649–653. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.6.6.649
Beigelman R, Izaguirre AM, Robles M et al (2010) Are kinking and coiling of carotid artery congenital or acquired? Angiology 61:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003319709336417
Togay-Isikay C, Kim J, Betterman K et al (2005) Carotid artery tortuosity, kinking, coiling: stroke risk factor, marker, or curiosity? Acta Neurol Belg 105:68–72
Lubarsky M, Helmer R, Knight C et al (2008) Internal carotid artery dissection following wooden arrow injury to the posterior pharynx. Case report J Neurosurg Pediatr 1:334–336. https://doi.org/10.3171/PED/2008/1/4/334
Picel AC, Davidson TM (2011) An aberrant internal carotid artery discovered during evaluation of obstructive sleep apnea: a report of 2 cases with consideration of a possible association. Ear Nose Throat J 90:29–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/014556131109000109
Wasserman JM, Sclafani SJ, Goldstein NA (2006) Intraoperative evaluation of a pulsatile oropharyngeal mass during adenotonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70:371–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2005.07.002
La Barbera G, La Marca G, Martino A et al (2006) Kinking, coiling, and tortuosity of extracranial internal carotid artery: is it the effect of a metaplasia? Surg Radiol Anat 28:573–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-006-0149-1
Pfeiffer J, Ridder GJ (2008) A clinical classification system for aberrant internal carotid arteries. Laryngoscope 118:1931–1936. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLG.0b013e318180213b
Ekici F, Tekbas G, Onder H et al (2012) Course anomalies of extracranial internal carotid artery and their relationship with pharyngeal wall: an evaluation with multislice CT. Surg Radiol Anat 34:625–631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-0958-3
Lee YH, Kweon SS, Choi BY et al (2014) Self-reported snoring and carotid atherosclerosis in middle-aged and older adults: the Korean Multi-Rural Communities Cohort Study. J Epidemiol 24:281–286. https://doi.org/10.2188/jea.je20130114
Li Y, Liu J, Wang W et al (2012) Association of self-reported snoring with carotid artery intima-media thickness and plaque. J Sleep Res 21:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2869.2011.00936.x
Apaydin M, Ayik SO, Akhan G et al (2013) Carotid intima-media thickness increase in patients with habitual simple snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is associated with metabolic syndrome. J Clin Ultrasound 41:290–296. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcu.22040
Bozkus F, Dikmen N, Gungor G et al (2017) The effect of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and hypothyroidism to intima-media thickness of carotid artery. Sleep Breath 21:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1384-2
Fox N, Ayas N, Park JE et al (2014) Carotid intima media thickness in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: comparison with a community-based cohort. Lung 192:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-014-9556-y
Gomes Ade M, Santos OM, Marambaia PP et al (2013) Anatomic variant of the internal carotid artery in the pharynx. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 79:791. https://doi.org/10.5935/1808-8694.20130142
Gluncic V, Petanjek Z, Marusic A et al (2001) High bifurcation of common carotid artery, anomalous origin of ascending pharyngeal artery and anomalous branching pattern of external carotid artery. Surg Radiol Anat 23:123–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-001-0123-x
Zajac HJ, Lachowski K, Lis A et al (2019) The anatomical relation of the extracranial internal carotid artery in the parapharyngeal space. Adv Clin Exp Med 28:601–607. https://doi.org/10.17219/acem/78350
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Associate Professor Zahide Yılmaz from the Neurology Clinic of Derince Training and Research Hospital for her contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [Gokhan Duygulu]; Methodology: [Gokhan Duygulu]; Formal analysis and investigation: [Gokhan Duygulu]; Writing—original draft preparation: [Gokhan Duygulu]; Writing—review and editing: [Gokhan Duygulu]; Funding acquisition: [None]; Resources: [Gokhan Duygulu]; Supervision: [Gokhan Duygulu].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This retrospective chart review study involving human participants was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Human Investigation Committee (IRB) of Kocaeli University approved this study.
Competing interests
The author (s) reports there are no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duygulu, G. Relationship of aberrant internal carotid artery with pharyngeal wall in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 27, 2415–2422 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-023-02871-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-023-02871-8