Abstract
Introduction
Several studies suggest in middle-aged subjects a relationship between arterial stiffness, a cardiovascular risk marker, and moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). No extensive data are present in older subjects. This study explores this association in a sample of healthy older subjects suffering OSA.
Methods
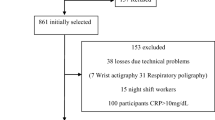
A total of 101 volunteers aged 75.3 ± 0.7 years were examined at the hospital sleep center. Each subject was assessed for medical history, body mass index and 24-h blood pressure measures, biological blood samples, and home polygraphy in 2002–2003 (P2) as well as in 2009–2010 (P4). Arterial stiffness was also assessed using carotid-femoral and carotid-radial pulse wave velocity (cfPWV and crPWV) during P4 examination.
Results
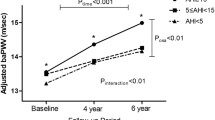
The total group consisted of 59 women and 42 men with a mean apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of 17.8 ± 12.1 and a mean oxygen desaturation index (ODI) of 9.8 ± 8.9. No-OSA (AHI < 15) represented 50% of the sample, and severe cases (AHI > 30) 17%. No significant differences had been founded between men and women for blood pressure, cfPWV, and crPWV. Considering the severity of the AHI, no significant differences between groups were present for PWV and blood pressure values. No difference for PWV was present for subjects with and without hypertension. No correlation was found between PWV value and AHI and ODI values at P2 or between P2 and P4 visits. cfPWV was higher in patients demonstrating incident hypertension during the follow-up.
Conclusions
In this sample of older subjects, PWV is not affected by AHI and ODI but was associated with incident hypertension. These results may suggest potential protective and adaptive mechanisms in older sleep apnea patients.
Clinical trial registrations
NCT 00759304 and NCT 00766584.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHI:
-
apnea-hypopnea index
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- CPAP:
-
continuous positive airway pressure
- HT:
-
hypertension
- HDL:
-
high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LDL:
-
low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- ODI:
-
oxygen desaturation index
- OSA:
-
obstructive sleep apnea
- P2:
-
clinical visits of the cohort between 2002 and 2003
- P4:
-
clinical visits of the cohort between 2009 and 2010
- PWV:
-
pulse wave velocity
- cfPWV:
-
carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity
- crPWV:
-
carotid-radial pulse wave velocity
- SaO2 :
-
oxygen saturation
- TRG:
-
plasma triglycerides
References
Young T, Palta M, DempseyJ SJ, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235
Peppard PE, Young T, Barnet JH, Palta M, Hagen EW, Hla KM (2013) Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathings in adults. Am J Epidemiol 177:1006–1014
Senaratna CV, Perret JL, Lodge CJ, Lowe JA, Campbell BE, Matheson MC, Hamilton GS, Dharmage SC (2017) Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in the general population: a systematic review. Sleep Med Rev 34:70–81
Hongyo K, Ito N, Yamamoto K, Yamamoto K, Takeda M, Oguro R, Takami Y, Takeya Y, Sugimoto K, Rakugi H (2017) Factors associated with the severity of obstructive sleep apnea in older adults. Geriatr Gerontol Int 17:614–621
Tkacova R, McNicholas WT, Javorsky M, Fietze I, Sliwinski P, Parati G, Grote L, Hedner J. European Sleep Apnoea Database study collaborators (2014) Nocturnal intermittent hypoxia predicts prevalent hypertension in the European sleep Apnoea database cohort study. Eur Respir J 44:931–941
Greco C, Spallone V (2015) Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and diabetes. Fortuitous association or interaction? Curr Diabetes Rev 12:129–155
Destors M, Tamisier R, Baguet JP, Ley P, Pepin JL (2014) Cardiovascular morbidity associated with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Rev Mal Resp 31:375–385
Mc Nicholas WT, Bonsignore M et al (2007) Management committee of EU COST ACTION B26. Sleep apnea as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: current evidence, basic mechanisms and research priorities. Eur Respir J 29:156–178
Chung S, Yoon IY, Lee CH, Kim JW (2010) The association of nocturnal hypoxemia with arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction in male patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Respiration 79:363–369
Kraiczi H, Caidahl K, Samuelsson A, Peker J, Hedner J (2001) Impairment of vascular endothelial function and left ventricular filling: association with the severity of apnea-induced hypoxemia during sleep. Chest 119:1085–1091
Levy P, Pepin JL, Arnaud C, Buguet JP, Dematteis M, Mach F (2009) Obstructive sleep apnea and atherosclerosis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 51:400–410
Butt M, Khair OA, Dwivedi G, Shantsila A, Shantsila E, Lip GY (2011) Myocardial perfusion by myocardial contrast echocardiography and endothelial dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea. Hypertension 58:417–424
Wada T, Kodaira K, Fuijshiro K, Maie K, Tsukiyama E, Fukumoto T, Uchida T, Yamasaki S (1994) Correlation of ultrasound-measured common carotid artery stiffness with pathological findings. Arterioscler Thromb 14:479–482
Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Giannattasio C, Hayoz D, Pannier B, Vlachopoulos C, Wilkinson I, Struijker Bourdier H (2006) European network for non-invasive investigation of large arteries. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J 21:2588–2605
Vachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stephanadis C (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 121:505–511
Doonan RJ, Scheffer P, Lalli M, Kimoff RJ, Petridou ET, Daskalopoulos ME, Daskalopoulou SS, Daskalopoulos ME, Daskapoulou SS (2011) Increased arterial stiffness in obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review. Hypertension Res 34:23–32
Jelic S, Bartels MN, Mateika JH, Ngai P, DrMeersman RE, Basner RC (2002) Arterial stiffness increases during obstructive sleep apneas. Sleep 25:850–855
Sarinc Ulasli S, Sariaydin M, Ozkececi G, Gunay E, Halici B, Unlu M (2016) Arterial stiffness in obstructive sleep apnoea: is there difference between daytime and nighttime? Respirology 21:1480–1485
Chung S, Yoon I, Lee CH, Kim JW (2010) The association of nocturnal hypoxemia with arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction in male patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Respiration 79:363–369
Phillips CL, Butlin M, Wong KK, Avolio AP (2013) Is obstructive sleep apnoea causally related to arterial stiffness? A critical review of the experimental evidence. Sleep Med Rev 17:7–18
Charalambos V, Konstatinos A, Christodoulos S (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular event and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:1318–1327
Laurent S, Boutourie P, Asmar R (2002) Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hpertensive patients. Hypertension 39:10–15
Vlachopoulos C, Xaplanteris P, Aboyans V, Brodman M, Cifkova R, Cosentino F, De Carlo M, Gallino A, Landmesser U, Laurent S, Lekakis J, Mikhailidis DP, Naka KK, Protogerou AD, Rizzoni D, Schmidt-Trucksass A, Van Bortel L, Weber T, Yamashina A, Zimlichmann R, Boutourie P, Cockcroft J, O’Rourke M, Park JB, Schillacci G, Sillesen H, Townsend RR (2015) The role of vascular biomarkers for primary and secondary prevention. A position paper from the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on peripheral circulation : Endorsed by the Association for Research into Arterial Structure and Physiology (ARTERY) Society. Atherosclerosis 241:507–532
Cruickshank K, Riste L, Anderson SG, Wright JS, Dunn G, Gosling RH (2002) Aortic pulse wave velocity and its relationship to mortality in diabetes and glucose intolerance: an integrated index of vascular function? Circulation 106:2085–2090
Meaume S, Benetos A, Henri OF, Rudnichi A, Safar ME (2001) Aortic pulse wave velocity predicts cardiovascular mortality in subjets >70 years of age. Artherioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:2046–2050
Barthélémy JC, Pichot V, Dauphinot V, Celle S, Laurent B, Garcin A, Maudoux D, Kerleroux J, Lacour JR, Kossovsky M, Gasoz JM, Roche F (2007) Autonomic nervous system activity and decline as prognostic indicators of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. The PROOF study. Neuroepidemiology 29:18–28
Sforza E, Sabri M, DaCosta A, Isaaz K, Barthélémy JC, Roche F (2015) Echocardiographic findings in healthy elderly people with sleep-disordered breathing. J Clin Sleep Med 11:975–980
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A et al (2007) 2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 25:1105–1187
O’Rourke MF, Staessen JA, Vlachopoulos C, Duprez D, Plant GE (2002) Clinical applications of arterial stiffness; definitions and reference values. Am J Hypertension 15:426–444
(1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The report of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 22:667–89
Pavlova MK, Duffy JF, Shea SA (2008) Polysomnographic respiratory abnormalities in asymptomatic individuals. Sleep 31:241–248
Pepin JL, Tamisier R, Baguet JP, Lévy P (2013) Arterial health is related to obstructive sleep apnea severity and improves with CPAP treatment. Sleep Med Rev 17:3–5
Seetho JW, Asher R, Parke RJ, Craig S, Duffy N, Hardy KJ, Wilding JP (2015) Effect of CPAP on arterial stiffness in severely obese patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 19:1155–1165
Toprak A, Reddy J, Chen W, Srinivasan S, Berenson G (2009) Relation of pulse pressure and arterial stiffness to concentric left ventricular hypertrophy in young me (from the Bogalusa heart study). Am J Cardiol 103:978–984
Watanabe H, Ohtsuka S, Kakihana M, Sugishita Y (1993) Coronary circulation in dogs with an experimental decrease in aortic compliance. J Am Coll Cardiol 21:1497–1506
Litvin AY, Sukmarova ZN, Elfimova EM, Aksenova AV, Galitsin PV, Rogoza AN, Chazova IE (2013) Effect of CPAP on vascular risk factors in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and arterial hypertension. Vasc Health Risk Manag 9:229–235
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouidid K, Stefanadis C (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness. J of Am Coll Cardiology 55:1318–1327
Wang J, Yu W, Gao M, Zhang F, Gu C, Yu Y, Wei Y (2015) Impact of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome on endothelial function, arterial stiffening and serum inflammatory markers: an updated meta-analysis and metaregression of 18 studies. J Am Heart Assoc 4(11). https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.115.002454
Tamisier R, Borel J, Millasseau S (2016) Arterial stiffness in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: an individual meta-analysis of contributing factors. J Hypertens Suppl 2:e100. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.hip.000001593.31023.87
Bruno RM, Rossi L, Fabrini M, Durani E, Di Coscio E, Maestri M, Guidi P, Frenzilli G, Salvetti A, Taddei S, Bonanni E, Ghiadoni L (2013) Renal vasodilating capacity and endothelial function are impaired in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and no traditional cardiovascular risk factors. J Hypertens 31:1456–1464
Sforza E, Roche F (2016) Chronic intermittent hypoxia and obstructive sleep apnea: an experimental and clinical approach. Hypoxia 4:99–108
Lavie P, Lavie L (2009) Unexpected survival advantages in elderly people with moderate sleep apnoea. J Sleep Res 18:397–403
Acknowledgments
The authors of this study would like to thank all the study participants and Delphine Maudoux for her help in data acquisition as well as Arnauld Garcin.
Funding
French Minister of Health provided financial support in the form of PHRC 1998 and 2001 funding (funding of salaries and clinical research devices). The sponsor had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The University Hospital and the local Ethics Committee (CCPRB Rhone-Alpes Loire) approved the PROOF as well as the SYNAPSE Study. The National Committee for Information and Liberty (CNIL) gave also at this time consent for data collection. All subjects gave their written consent prior to participation in the study.
Conflicts of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge, or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sforza, E., Millasseau, S., Hupin, D. et al. Arterial stiffness alteration and obstructive sleep apnea in an elderly cohort free of cardiovascular event history: the PROOF cohort study. Sleep Breath 23, 201–208 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-018-1683-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-018-1683-x