Abstract
Purpose
The dopamine transporter (DAT) is a marker of the occurrence and development of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and other diseases with nigrostriatal degeneration. 2β-Carbomethoxy-3β-(4-chlorophenyl)-8-(2-[18F]-fluoroethyl)nortropane ([18F]FECNT), an 18F-labelled tropane derivative, was reported to be a useful positron-emitting probe for DAT. However, the rapid formation of brain-penetrating radioactive metabolites is an impediment to the proper quantitation of DAT in PET studies with [18F]FECNT. Deuterium-substituted analogues have presented better in vivo stability to reduce metabolites. This study aimed to synthesize a deuterium-substituted DAT radiotracer, [18F]FECNT-d4, and to make a preliminary investigation of its properties as a DAT tracer in vivo.
Procedures
The ligand [18F]FECNT-d4 was obtained by one-step radiolabelling reaction. The lipophilicity was measured by the shake-flask method. Binding properties of [18F]FECNT-d4 were estimated by in vitro binding assay, biodistribution, and microPET imaging in rats. In vivo stability of [18F]FECNT-d4 was estimated by radio-HPLC.
Results
[18F]FECNT-d4 was synthesized at an average activity yield of 46 ± 17 % (n = 15) and the molar activity was 67 ± 12 GBq/μmol. The deuterated tracer showed suitable lipophilicity and the ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier (brain uptake of 1.72 % ID at 5 min). [18F]FECNT-d4 displayed a high binding affinity for DAT comparable to that of [18F]FECNT in rat striatum homogenates. Biodistribution results in normal rats showed that [18F]FECNT-d4 exhibited a higher ratio of the target to non-target (striatum/cerebellum) at 15 min post administration (5.00 ± 0.44 vs 3.84 ± 0.24 for [18F]FECNT-d4 vs [18F]FECNT). MicroPET imaging studies of [18F]FECNT-d4 in normal rats showed that the ligand selectively localized to DAT-rich striatal regions and the accumulation could be blocked with DAT inhibitor. Furthermore, in the unilateral PD model rat, a significant reduction of the signal was found in the lesioned side relative to the unlesioned side. Striatal standardized uptake value of [18F]FECNT-d4 remained ~4.02 in the striatum between 5 and 20 min, whereas that of [18F]FECNT fell rapidly from 4.11 to 2.95. Radio-HPLC analysis of the plasma demonstrated better in vivo stability of [18F]FECNT-d4 than [18F]FECNT.
Conclusion
The deuterated compound [18F]FECNT-d4 may serve as a promising PET imaging agent to assess DAT-related disorders.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marshall V, Grosset D (2003) Role of dopamine transporter imaging in routine clinical practice. Mov Disord 18:1415–1423
McHugh PC, Buckley DA (2015) The structure and function of the dopamine transporter and its role in CNS diseases. Vitam Horm 98:339–369
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
Poewe W, Seppi K, Tanner CM, Halliday GM, Brundin P, Volkmann J, Schrag AE, Lang AE (2017) Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17013
Halldin C, Erixon-Lindroth N, Pauli S, Chou YH, Okubo Y, Karlsson P, Lundkvist C, Olsson H, Guilloteau D, Emond P, Farde L (2003) [11C]PE2I: a highly selective radioligand for PET examination of the dopamine transporter in monkey and human brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30:1220–1230
Hantraye P, Brownell A, Elmaleh D, Spealman RD, Wullner U, Brownell GL, Madras BK, Isacson O (1992) Dopamine fiber detection by [11C]-CFT and PET in a primate model of parkinsonism. Neuroreport 3:265–268
Cumming P, Maschauer S, Riss PJ, Tschammer N, Fehler SK, Heinrich MR, Kuwert T, Prante O (2014) Radiosynthesis and validation of [18F]FP-CMT, a phenyltropane with superior properties for imaging the dopamine transporter in living brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:1148–1156
Suzuki M, Ito H, Kodaka F, Takano H, Kimura Y, Fujiwara H, Sasaki T, Takahata K, Nogami T, Nagashima T, Nengaki N, Kawamura K, Zhang MR, Varrone A, Halldin C, Okubo Y, Suhara T (2014) Reproducibility of PET measurement for presynaptic dopaminergic functions using L-[beta-[11]C]DOPA and [18F]FE-PE2I in humans. Nucl Med Commun 35:231–237
Chalon S, Hall H, Saba W, Garreau L, Dollé F, Halldin C, Emond P, Bottlaender M, Deloye JB, Helfenbein J, Madelmont JC, Bodard S, Mincheva Z, Besnard JC, Guilloteau D (2006) Pharmacological characterization of (E)-N-(4-fluorobut-2-enyl)-2beta-carbomethoxy-3beta-(4'-tolyl)nortropane (LBT-999) as a highly promising fluorinated ligand for the dopamine transporter. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:147–152
Goodman MM, Kilts CD, Keil R, Shi B, Martarello L, Xing D, Votaw J, Ely TD, Lambert P, Owens MJ, Camp VM, Malveaux E, Hoffman JM (2000) 18F-Labeled FECNT: a selective radioligand for PET imaging of brain dopamine transporters. Nucl Med Biol 27:1–12
Davis MR, Votaw JR, Bremner JD, Byas-Smith MG, Faber TL, Voll RJ, Hoffman JM, Grafton ST, Kilts CD, Goodman MM (2003) Initial human PET imaging studies with the dopamine transporter ligand 18F-FECNT. J Nucl Med 44:855–861
Zoghbi SS, Shetty HU, Ichise M, Fujita M, Imaizumi M, Liow JS, Shah J, Musachio JL, Pike VW, Innis RB (2006) PET imaging of the dopamine transporter with 18F-FECNT: a polar radiometabolite confounds brain radioligand measurements. J Nucl Med 47:520–527
Nye JA, Votaw JR, Bremner JD, Davis MR, Voll RJ, Camp VM, Goodman MM (2014) Quantification of dopamine transporter density with [18F]FECNT PET in healthy humans. Nucl Med Biol 41:217–222
Varrone A, Steiger C, Schou M, Takano A, Finnema SJ, Guilloteau D, Gulyás B, Halldin C (2009) In vitro autoradiography and in vivo evaluation in cynomolgus monkey of [18F]FE-PE2I, a new dopamine transporter PET radioligand. Synapse 63:871–880
Peyronneau MA, Saba W, Dolle F, Goutal S, Coulon C, Bottlaender M, Valette H (2012) Difficulties in dopamine transporter radioligand PET analysis: the example of LBT-999 using [18F] and [11C] labelling: part II: Metabolism studies. Nucl Med Biol 39:347–359
Parcella K, Eastman K, Yeung KS, Grant-Young KA, Zhu J, Wang T, Zhang Z, Yin Z, Parker D, Mosure K, Fang H, Wang YK, Lemm J, Zhuo X, Hanumegowda U, Liu M, Rigat K, Donoso M, Tuttle M, Zvyaga T, Haarhoff Z, Meanwell NA, Soars MG, Roberts SB, Kadow JF (2017) Improving metabolic stability with deuterium: the discovery of BMT-052, a pan-genotypic HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 8:771–774
Roston D, Islam Z, Kohen A (2013) Isotope effects as probes for enzyme catalyzed hydrogen-transfer reactions. Molecules 18:5543–5567
Kuchar M, Mamat C (2015) Methods to increase the metabolic stability of 18F-radiotracers. Molecules 20:16186–16220
Pirali T, Serafini M, Cargnin S, Genazzani AA (2019) Applications of deuterium in medicinal chemistry. J Med Chem 62:5276–5297
Schmidt C (2017) First deuterated drug approved. Nat Biotechnol 35:493−494
Harbeson SL, Morgan AJ, Liu JF, Aslanian AM, Nguyen S, Bridson GW, Brummel CL, Wu L, Tung RD, Pilja L, Braman V, Uttamsingh V (2017) Altering metabolic profiles of drugs by precision deuteration 2: discovery of a deuterated analog of ivacaftor with differentiated pharmacokinetics for clinical development. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 362:359–367
Jahan M, Eriksson O, Johnström P, Korsgren O, Sundin A, Johansson L, Halldin C (2011) Decreased defluorination using the novel betacell imaging agent [18F]FE-DTBZ-d4 in pigs examined by PET. EJNMMI Res 1:1–13
Mori W, Yamasaki T, Fujinaga M, Ogawa M, Zhang Y, Hatori A, Xie L, Kumata K, Wakizaka H, Kurihara Y, Ohkubo T, Nengaki N, Zhang MR (2019) Development of 2-(2-(3-(4-([18F]Fluoromethoxy- d2)phenyl)-7-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-2-yl)ethyl)-4-isopropoxyisoindoline-1,3-dione for positron-emission-tomography imaging of phosphodiesterase 10A in the brain. J Med Chem 62:688–698
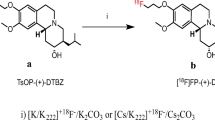
Chen ZP, Wang SP, Li XM, Liu CY, Tang J, Cao GX, Luo SN, Zhang LF, Jin J (2008) A one-step automated high-radiochemical-yield synthesis of [18F]FECNT from mesylate precursor. Appl Radiat Isot 66:1881–1885
Xu L, Trudell ML (1996) Stereoselective synthesis of 2beta-carbomethoxy-3beta-phenyltropane derivatives. J Heterocyclic Chem 33:2037–2039
Tang J, Xu Y, Liu C, Fang Y, Cao S, Zhao C, Huang H, Zou M, Chen Z (2020) PET imaging with [18F]FP-(+)-DTBZ in 6-OHDA-induced partial and full unilaterally-lesioned model rats of Parkinson’s disease and the correlations to the biological data. Nucl Med Biol 90-91:1–9
Raaphorst RM, Luurtsema G, Schokker CJ, Attia KA, Schuit RC, Elsinga PH, Lammertsma AA, Windhorst AD (2018) Improving metabolic stability of fluorine-18 labeled verapamil analogs. Nucl Med Biol 64-65:47–56
Sun Y, Liu C, Chen Z, Li B, Lv Z, Wang J, Lou J, Tang J, Wang Y, Zhang G, Liu X (2020) A phase 2, open-label, multi-center study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of 99mTc-TRODAT-1 SPECT to detect Parkinson’s disease. Ann Nucl Med 34:31–37
Lammertsma AA, Hume SP (1996) Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. Neuroimage 4:153–158
Waterhouse RN (2003) Determination of lipophilicity and its use as a predictor of blood–brain barrier penetration of molecular imaging agents. Mol Imaging Biol 5:376–389
Pan J, Pourghiasian M, Hundal N, Lau J, Bénard F, Dedhar S, Lin KS (2013) 2-[18F]fluoroethanol and 3-[18F]fluoropropanol: facile preparation, biodistribution in mice, and their application as nucleophiles in the synthesis of [18F]fluoroalkyl aryl ester and ether PET tracers. Nucl Med Biol 40:850–857
Cumming P, Maschauer S, Riss PJ, Grill E, Pischetsrieder M, Kuwert T, Prante O (2015) Perturbed development of striatal dopamine transporters in fatty versus lean Zucker rats: a follow-up small animal PET study. Mol Imaging Biol 17:521–528
Serriere S, Tauber C, Vercouillie J, Guilloteau D, Deloye J, Garreau L, Galineau L, Chalon S (2014) In vivo PET quantification of the dopamine transporter in rat brain with [18F]LBT-999. Nucl Med Biol 41:106–113
Ribeiro MJ, Vercouillie J, Arlicot N, Tauber C, Gissot V, Mondon K, Barantin L, Cottier JP, Maia S, Deloye JB, Emond P, Guilloteau D (2020) Usefulness of PET With [18F]LBT-999 for the evaluation of presynaptic dopaminergic neuronal loss in a clinical environment. Front Neurol 11:754
Arlicot N, Vercouillie J, Malherbe C, Bidault R, Gissot V, Maia S, Barantin L, Cottier J, Deloye J, Guilloteau D, Ribeiro M (2019) PET imaging of dopamine transporter with [18F]LBT-999: initial evaluation in healthy volunteers. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.23736/S1824-4785.19.03175-3
Varrone A, Stepanov V, Nakao R, Toth M, Gulyas B, Emond P, Deloye JB, Vercouillie J, Stabin MG, Jonsson C, Guilloteau D, Halldin C (2011) Imaging of the striatal and extrastriatal dopamine transporter with [18F]LBT-999: quantification, biodistribution, and radiation dosimetry in nonhuman primates. J Nucl Med 52:1313–1321
Kloss MW, Rosen GM, Rauckman EJ (1983) N-demethylation of cocaine to norcocaine: evidence for participation by cytochrome P-450 and FAD-containing monooxygenase. Mol Pharmacol 23:482–485
Couth RT, Su P, Baker GB (1994) Involvement of CYP2D6, CYP3A4, and other cytochrome P-450 isozymes in N-dealkylation reactions. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 4:177–186
Gu X-H, Zong R, Kula NS, Baldessarinib RJ, Neumeyer JL (2001) Synthesis and biological evaluation of a series of novel N- or O-fluoroalkyl derivatives of tropane: potential positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agents for the dopamine transporter. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1123:3049–3053
Amini N, Nakao R, Schou M, Halldin C (2013) Identification of PET radiometabolites by cytochrome P450, UHPLC/Q-ToF-MS and fast radio-LC: applied to the PET radioligands [11C]flumazenil, [18F]FE-PE2I, and [11C]PBR28. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:1303–1310
Sasaki T, Ito H, Kimura Y, Arakawa R, Takano H, Seki C, Kodaka F, Fujie S, Takahata K, Nogami T, Suzuki M, Fujiwara H, Takahashi H, Nakao R, Fukumura T, Varrone A, Halldin C, Nishikawa T, Suhara T (2012) Quantification of dopamine transporter in human brain using PET with [18F]FE-PE2I. J Nucl Med 53:1065–1073
Malherbe C, Bidault R, Netter C, Guilloteau D, Vercouillie J, Arlicot N (2019) Development of a fast and facile analytical approach to quantify radiometabolites in human plasma samples using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography. Am J Anal Chem 10:185–201
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671723, 81801742), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20201133), Wuxi Municipal Science and Technology Development Fund (WX18IIAN048, N20192015), Program from Jiangsu Commission of Health (H2018086), and Wuxi Municipal Health Commission (Q201946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1479 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, S., Tang, J., Liu, C. et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of [18F]FECNT-d4 as a Novel PET Agent for Dopamine Transporter Imaging. Mol Imaging Biol 23, 733–744 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-021-01603-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-021-01603-2