Abstract
Purpose
The endeavor of deciphering intricate phenomena within the field of molecular medicine dictates the necessity to investigate tumor/disease microenvironment real-time on cellular level. We, hereby, design simple and robust intravital microscopy strategies, which can be used to elucidate cellular or molecular interactions in a fluorescent mouse model.
Procedures
We crossbred transgenic TIE2GFP mice with nude BALB/c mice, allowing the breeding of immunocompetent and immunodeficient mouse models expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) in vascular endothelium. Then, we surgically exposed various tissues of interest to perform intravital microscopy.
Results
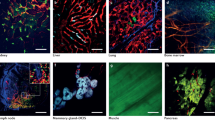
By utilizing simple tissue preparation procedures and confocal or two-photon microscopy, we produced high-resolution static snapshots, dynamic sequences, and 3D reconstructions of orthotopically grown mammary tumor, skin inflammation, brain, and muscle. The homogenous detection of GFP expressed by endothelial cells and a combination of fluorescence agents enabled landmarking of tumor microenvironment and precise molecular tagging.
Conclusion
Simple intravital microscopy procedures on TIE2GFP mice allowed a real-time multi-color visualization of tissue microenvironment, underlining that robust microscopy strategies are relatively simple and can be readily available for many tissues of interest.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pittet MJ, Weissleder R (2011) Intravital imaging. Cell 147:983–991
Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2008) Imaging in the era of molecular oncology. Nature 452:580–589
Hak S, Reitan NK, Haraldseth O, de Lange DC (2010) Intravital microscopy in window chambers: a unique tool to study tumor angiogenesis and delivery of nanoparticles. Angiogenesis 13:113–130
Kedrin D, Gligorijevic B, Wyckoff J, Verkhusha VV, Condeelis J, Segall JE, van Rheenen J (2008) Intravital imaging of metastatic behavior through a mammary imaging window. Nat Methods 5:1019–1021
Entenberg D, Voiculescu S, Guo P, Borriello L, Wang Y, Karagiannis GS, Jones J, Baccay F, Oktay M, Condeelis J (2018) A permanent window for the murine lung enables high-resolution imaging of cancer metastasis. Nat Methods 15:73–80
Laschke M, Vollmar MM (2011) The dorsal skinfold chamber: window into the dynamic interaction of biomaterials with their surrounding host tissue. Eur Cells Mater 22:147–167
Lehr HA, Leunig M, Menger MD, Nolte D, Messmer K (1993) Dorsal skinfold chamber technique for intravital microscopy in nude mice. Am J Pathol 143:1055–1062
Hak S, Helgesen E, Hektoen HH, Huuse EM, Jarzyna PA, Mulder WJ, Haraldseth O, Davies Cde L (2012) The effect of nanoparticle polyethylene glycol surface density on ligand-directed tumor targeting studied in vivo by dual modality imaging. ACS Nano 6:5648–5658
Hak S, Cebulla J, Huuse EM, Davies Cde L, Mulder WJ, Larsson HB, Haraldseth O (2014) Periodicity in tumor vasculature targeting kinetics of ligand-functionalized nanoparticles studied by dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and intravital microscopy. Angiogenesis 17:93–107
Murphy EA, Majeti BK, Barnes LA, Makale M, Weis SM, Lutu-Fuga K, Wrasidlo W, Cheresh DA (2008) Nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery to tumor vasculature suppresses metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9343–9348
Leimgruber A, Berger C, Cortez-Retamozo V, Etzrodt M, Newton AP, Waterman P, Figueiredo JL, Kohler RH, Elpek N, Mempel TR, Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2009) Behavior of endogenous tumor-associated macrophages assessed in vivo using a functionalized nanoparticle. Neoplasia 11:459–468
Miller MA, Chandra R, Cuccarese MF et al (2017) Radiation therapy primes tumors for nanotherapeutic delivery via macrophage-mediated vascular bursts. Sci Transl Med 9:eaal0225
Entenberg D, Pastoriza JM, Oktay MH, Voiculescu S, Wang Y, Sosa MS, Aguirre-Ghiso J, Condeelis J (2017) Time-lapsed, large-volume, high-resolution intravital imaging for tissue-wide analysis of single cell dynamics. Methods 128:65–77
Mulder WJM, Castermans K, van Beijnum JR, Oude Egbrink MG, Chin PT, Fayad ZA, Löwik CW, Kaijzel EL, Que I, Storm G, Strijkers GJ, Griffioen AW, Nicolay K (2009) Molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis using αvβ3-integrin targeted multimodal quantum dots. Angiogenesis 12:17–24
Wagner M, Baer C, Zuschratter W, et al. (2017) Intravital microscopy of monocyte homing and tumor-related angiogenesis in a murine model of peripheral arterial disease. J Vis Exp 126:e56290
Pai S, Danne KJ, Qin J et al (2013) Visualizing leukocyte trafficking in the living brain with 2-photon intravital microscopy. Front Cell Neurosci 6:67
Wang Z (2016) Imaging nanotherapeutics in inflamed vasculature by intravital microscopy. Theranostics 6:2431–2438
Seynhaeve ALB, ten Hagen TLM (2018) Intravital microscopy of tumor-associated vasculature using advanced dorsal skinfold window chambers on transgenic fluorescent mice. J Vis Exp 131:e55115
Sofias AM, Andreassen T, Hak S (2018) Nanoparticle ligand-decoration procedures affect in vivo interactions with immune cells. Mol Pharm 15:5754–5761
Weissleder R, Nahrendorf M, Pittet MJ (2014) Imaging macrophages with nanoparticles. Nat Mater 13:125–138
Funding
This work was supported by the Central Norway Regional Health Authority “Helse Midt-Norge” [AMS: PhD stipend (90062100), travel grant (90284100); SH: researcher grant (90262100)], and the Norwegian Research Council (SH: 230788/F20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All procedures were approved by the Norwegian Animal Research Authorities.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary Video 1
(MP4 41361 kb)
Supplementary Video 2
(MP4 711 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sofias, A.M., Åslund, A.K.O., Hagen, N. et al. Simple and Robust Intravital Microscopy Procedures in Hybrid TIE2GFP-BALB/c Transgenic Mice. Mol Imaging Biol 22, 486–493 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-019-01442-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-019-01442-2