Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to introduce synchrotron radiation X-ray phase computed tomography (SR-PCT) as a new method of visualizing ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide (USPIO) distribution into the brains of mice with neuroinflammation.
Procedures
The sensitivity of the technique was assessed by performing back-to-back SR-PCT and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in mice stereotaxically injected with a range of USPIO concentrations. Eight mice with cerebral ischemia were then intravenously injected with USPIOs and imaged back-to-back with MRI and SR-PCT.
Results
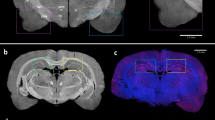
SR-PCT proved sensitive enough to detect iron in nanomolar quantities. In stroke-induced animals, SR-PCT showed hyperintense areas in the regions of MR signal loss and immunostaining for macrophages. SR-PCT, moreover, identified brain anatomy as clearly as histology, without the need for sectioning or staining, with an examination time of 44 min per brain at an isotropic spatial resolution of 8 μm.
Conclusion
SR-PCT has potential for cellular imaging in intact brain, with unequaled neuroanatomy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM (2009) Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 8(11):1006–1018
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K et al (2009) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 119(3):e21–e181
Iadecola C, Anrather J (2011) The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med 17(7):796–808
Stoll G, Bendszus M (2009) Imaging of inflammation in the peripheral and central nervous system by magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroscience 158(3):1151–1160
Chauveau F, Marinescu M, Cho TH, Wiart M, Berthezene Y, Nighoghossian N (2012) MRI assessment of post-ischemic neuroinflammation in stroke: Experimental and clinical studies. Neuroimaging—methods, Bright P (ed) InTech, doi:10.5772/25150, http://www.intechopen.com/books/neuroimaging-methods/mri-assessment-of-post-ischemic-neuroinflammation-in-stroke-experimental-and-clinical-studies
Cloetens P, Pateyron-Salomé M, Buffière J, Peix G, Baruchel J, Peyrin F et al (1997) Observation of microstructure and damage in materials by phase sensitive radiography and tomography. J Appl Phys 81:5878–5886
Giuliani A, Frati C, Rossini A, Komlev VS, Lagrasta C, Savi M et al (2011) High-resolution X-ray microtomography for three-dimensional imaging of cardiac progenitor cell homing in infarcted rat hearts. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 5(8):e168–e178
Torrente Y, Gavina M, Belicchi M, Fiori F, Komlev V, Bresolin N et al (2006) High-resolution X-ray microtomography for three-dimensional visualization of human stem cell muscle homing. FEBS Lett 580(24):5759–5764
Sigovan M, Bessaad A, Alsaid H, Lancelot E, Corot C, Neyran B et al (2010) Assessment of age modulated vascular inflammation in ApoE−/− mice by USPIO-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Investig Radiol 45(11):702–707
Marinescu M, Chauveau F, Durand A, Riou A, Cho TH, Dencausse A et al (2012) Monitoring therapeutic effects in experimental stroke by serial USPIO-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol 23(1):37–47
Sigovan M, Boussel L, Sulaiman A, Sappey-Marinier D, Alsaid H, Desbleds-Mansard C et al (2009) Rapid-clearance iron nanoparticles for inflammation imaging of atherosclerotic plaque: initial experience in animal model. Radiology 252(2):401–409
Desestret V, Brisset JC, Moucharrafie S, Devillard E, Nataf S, Honnorat J et al (2009) Early-stage investigations of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide-induced signal change after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Stroke 40(5):1834–1841
Chauveau F, Moucharrafie S, Wiart M, Brisset JC, Berthezene Y, Nighoghossian N et al (2010) In vivo MRI assessment of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion by electrocoagulation: pitfalls of procedure. Exp Transl Stroke Med 2(1):4–8
Wiart M, Davoust N, Pialat JB, Desestret V, Moucharaffie S, Cho TH et al (2007) MRI monitoring of neuroinflammation in mouse focal ischemia. Stroke 38(1):131–137
Denes A, Vidyasagar R, Feng J, Narvainen J, McColl BW, Kauppinen RA et al (2007) Proliferating resident microglia after focal cerebral ischaemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(12):1941–1953
Paganin D, Mayo SC, Gureyev TE, Miller PR, Wilkins SW (2002) Simultaneous phase and amplitude extraction from a single defocused image of a homogeneous object. J Microsc 206(Pt 1):33–40
Dejus RJ, Sanchez del Rio M (1996) Xop: a graphical user interface for spectral calculations and X-ray optics utilities. Rev Sci Instrum 67:3356
Salome M, Peyrin F, Cloetens P, Odet C, Laval-Jeantet AM, Baruchel J et al (1999) A synchrotron radiation microtomography system for the analysis of trabecular bone samples. Med Phys 26(10):2194–2204
Franklin K, Paxinos G (1997) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Henning EC, Ruetzler CA, Gaudinski MR, Hu TC, Latour LL, Hallenbeck JM et al (2009) Feridex preloading permits tracking of CNS-resident macrophages after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29(7):1229–1239
Kleinschnitz C, Schutz A, Nolte I, Horn T, Frank M, Solymosi L et al (2005) In vivo detection of developing vessel occlusion in photothrombotic ischemic brain lesions in the rat by iron particle enhanced MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(11):1548–1555
Saleh A, Wiedermann D, Schroeter M, Jonkmanns C, Jander S, Hoehn M (2004) Central nervous system inflammatory response after cerebral infarction as detected by magnetic resonance imaging. NMR Biomed 17(4):163–169
Byun J, Verardo MR, Sumengen B, Lewis GP, Manjunath BS, Fisher SK (2006) Automated tool for the detection of cell nuclei in digital microscopic images: application to retinal images. Mol Vis 12:949–960
Rausch M, Baumann D, Neubacher U, Rudin M (2002) In vivo visualization of phagocytotic cells in rat brains after transient ischemia by USPIO. NMR Biomed 15(4):278–283
Stroh A, Zimmer C, Werner N, Gertz K, Weir K, Kronenberg G et al (2006) Tracking of systemically administered mononuclear cells in the ischemic brain by high-field magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 33(3):886–897
Jensen TH, Bech M, Bunk O, Menzel A, Bouchet A, Le Duc G et al (2011) Molecular X-ray computed tomography of myelin in a rat brain. NeuroImage 57(1):124–129
Schulz G, Weitkamp T, Zanette I, Pfeiffer F, Beckmann F, David C et al (2010) High-resolution tomographic imaging of a human cerebellum: comparison of absorption and grating-based phase contrast. J R Soc Interface 7(53):1665–1676
Stampanoni M, Reichold J, Weber B, Habertür D, Schittny J, Eller J et al (2010) Deciphering complex, functional structures with synchrotron-based absorption and phase contrast tomographic microscopy. Proc SPIE 7804:L1–L13
Zhu P, Zhang K, Wang Z, Liu Y, Liu X, Wu Z et al (2010) Low-dose, simple, and fast grating-based X-ray phase-contrast imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(31):13576–13581
Connor DM, Benveniste H, Dilmanian FA, Kritzer MF, Miller LM, Zhong Z (2009) Computed tomography of amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease using diffraction enhanced imaging. NeuroImage 46(4):908–914
Noda-Saita K, Yoneyama A, Shitaka Y, Hirai Y, Terai K, Wu J et al (2006) Quantitative analysis of amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease by phase-contrast X-ray computed tomography. Neuroscience 138(4):1205–1213
Pinzer BR, Cacquevel M, Modregger P, McDonald SA, Bensadoun JC, Thuering T et al (2012) Imaging brain amyloid deposition using grating-based differential phase contrast tomography. NeuroImage 61(4):1336–1346
Acknowledgments
This work was performed within the framework of the LABEX PRIMES (ANR-11-LABX-0063) of Université de Lyon, within the program “Investissements d'Avenir” (ANR-11-IDEX-0007) operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR). This work was supported by the ESRF (project MD-499) by allocation of beam time. The authors would like to thank Sébastien Ballet and Anne Dencausse of Guerbet for providing the USPIOs and performing relaxometry measurements for iron dosage. Part of the experiments was performed on the “Animage” platform of CERMEP-Imagerie du Vivant, Lyon, France. We would like to thank Géraldine LeDuc and Elodie Boller from ESRF for assistance in preparing the experiments and Carole Frindel from Creatis (UMR CNRS 5220 U1044 INSERM) for helping with the movie and 3D images.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Movie S1
Slice-by-slice overview of a whole SR-PCT exam. (AVI 29820 kb)
Figure S1
Comparison of three typical images obtained with SR-PCT at different slice positions (a1–c1) with corresponding Cresyl violet-stained slices from Franklin Paxinos Atlas (reproduced with permission) [19] (a2–c2). This atlas was also used to label the data. Arrowhead shows the ischemic lesion. (DOC 2328 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marinescu, M., Langer, M., Durand, A. et al. Synchrotron Radiation X-Ray Phase Micro-computed Tomography as a New Method to Detect Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in the Brain. Mol Imaging Biol 15, 552–559 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-013-0639-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-013-0639-6