Abstract
Purpose
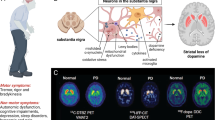
We used a novel apoptosis-targeting peptide called ApoPep-1 in order to evaluate whether ApoPep-1 can be used as a diagnostic indicator in a model of Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Procedures
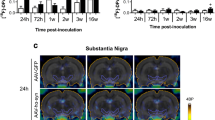
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) was given to mice to produce the PD model. Cy7.5-labeled ApoPep-1 was given intravenously and optical imaging was taken at 1, 2, and 3 weeks after MPTP treatment. Immunohistochemical study was performed with brain sections.
Results
Increased ApoPep-1 signal was observed in the brain of MPTP-treated mice by in vivo and ex vivo imaging study. With histological evaluation, ApoPep-1 signal demonstrated a strong correlation with loss of dopaminergic neurons or increase of apoptotic cells. Moreover, the neuroprotective effect of amantadine in the MPTP model was effectively evaluated using optical imaging of ApoPep-1.
Conclusions
We conclude that ApoPep-1 is the effective probe for imaging of apoptosis in the MPTP model and can be applied in brain diseases with apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- SNpc:
-
Substantia nigra parts compacta
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling assay
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- TH:
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase
References
von Bohlen Und Halbach O (2005) Modeling neurodegenerative diseases in vivo review. Neurodegener Dis 2(6):313–320
George JL, Mok S, Moses D et al (2009) Targeting the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 7(1):9–36
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Yi H et al (2009) Mitochondria in neurodegenerative disorders: regulation of the redox state and death signaling leading to neuronal death and survival. J Neural Transm 116(11):1371–1381
Winklhofer KF, Haass C (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(1):29–44
Levy OA, Malagelada C, Greene LA (2009) Cell death pathways in Parkinson’s disease: proximal triggers, distal effectors, and final steps. Apoptosis 14(4):478–500
Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman R, Brown D, Tatton N (2003) Apoptosis in Parkinson’s disease: signals for neuronal degradation. Ann Neurol 53(Suppl 3):S61–S70, discussion S70–72
Tait JF (2008) Imaging of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 49(10):1573–1576
Smith G, Nguyen QD, Aboagye EO (2009) Translational imaging of apoptosis. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 9(9):958–967
Blankenberg FG (2008) In vivo detection of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 49(Suppl 2):81S–95S
De Saint-Hubert M, Prinsen K, Mortelmans L, Verbruggen A, Mottaghy FM (2009) Molecular imaging of cell death. Methods 48(2):178–187
Fischer K, Voelkl S, Berger J et al (2006) Antigen recognition induces phosphatidylserine exposure on the cell surface of human CD8+ T cells. Blood 108(13):4094–4101
Smrz D, Draberova L, Draber P (2007) Non-apoptotic phosphatidylserine externalization induced by engagement of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. J Biol Chem 282(14):10487–10497
Wang K, Purushotham S, Lee JY et al (2010) In vivo imaging of tumor apoptosis using histone H1-targeting peptide. J Control Release 148(3):283–291
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39(6):889–909
Schapira AH (2010) Complex I: inhibitors, inhibition and neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol 224(2):331–335
Bredesen DE, Rao RV, Mehlen P (2006) Cell death in the nervous system. Nature 443(7113):796–802
Jenner P, Olanow CW (2006) The pathogenesis of cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 66(10 Suppl 4):S24–S36
Liang CL, Wang TT, Luby-Phelps K, German DC (2007) Mitochondria mass is low in mouse substantia nigra dopamine neurons: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 203(2):370–380
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8(4):382–397
Novikova L, Garris BL, Garris DR, Lau YS (2006) Early signs of neuronal apoptosis in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the progressive neurodegenerative mouse 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine/probenecid model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 140(1):67–76
Ruiz-Vela A, Korsmeyer SJ (2007) Proapoptotic histone H1.2 induces CASP-3 and -7 activation by forming a protein complex with CYT c, APAF-1 and CASP-9. FEBS Lett 581(18):3422–3428
Ohsawa S, Hamada S, Yoshida H, Miura M (2008) Caspase-mediated changes in histone H1 in early apoptosis: prolonged caspase activation in developing olfactory sensory neurons. Cell Death Differ 15(9):1429–1439
Reis J, John D, Heimeroth A et al (2006) Modulation of human motor cortex excitability by single doses of amantadine. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(12):2758–2766
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grant no. RTI04-01-01 from the Regional Technology Innovation Program of the Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MKE) & Converging Research Center Program through the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010K001054).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1203 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, MJ., Wang, K., Kim, IS. et al. Molecular Imaging of Cell Death in an Experimental Model of Parkinson’s Disease with a Novel Apoptosis-Targeting Peptide. Mol Imaging Biol 14, 147–155 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-011-0497-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-011-0497-z