Abstract
Purpose
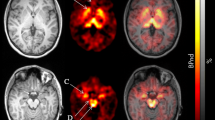
The appetite suppressants fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine were widely prescribed before being withdrawn from the market in 1997. Both drugs are known to have the potential to damage brain serotonin (5-HT) axons and axon terminals in animals, including nonhuman primates. This study used quantitative positron emission tomography (PET) with [11C] McN5652, a serotonin transporter (SERT) ligand to determine whether humans previously exposed to fenfluramines showed reductions in SERT binding parameters.
Procedures
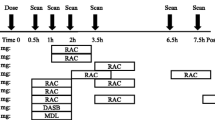
Subjects previously treated with fenfluramines for weight loss (N = 15) and age-matched controls (N = 17) underwent PET studies with [11C] McN5652. Global and regional distribution volumes (DVs) of [11C] McN5652 were compared in the two subject groups using parametric statistical analyses.
Results
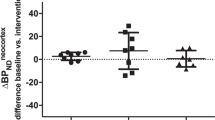
Compared to controls, subjects previously exposed to fenfluramines had significant reductions in [11C]McN5652 binding in 14 of 15 regions of interest, more than four years after drug discontinuation.
Conclusions
These results are the first to provide direct evidence for fenfluramine-induced 5-HT neurotoxicity in humans.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colman E (2005) Anorectics on trial: a half-century of federal regulation of prescription appetite suppressants. Ann Intern Med 143:380–385
Connolly HM, Crary JL, McGoon MD, Hensrud DD, Edwards BS, Edwards WD, Schaff HV (1997) Valvular heart disease associated with fenfluramine-phentermine. N Engl J Med 337:581–588. Erratum in: N Engl J Med 337:1783 (1997 Aug 28)
Harvey J, McMaster S (1975) Fenfluramine: evidence for a neurotoxic action on midbrain and a long-term depletion of serotonin. Psychopharmacol Commun 1:217–228
Sanders-Bush E, Bushing JA, Sulser F (1975) Long-term effects of p-chloroamphetamine and related drugs on central serotonergic mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 192:33–41
Harvey J, McMaster S, Fuller R (1977) Comparison between the neurotoxic and serotonin depleting effects of various halogenated derivatives of amphetamine in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 202:581–589
Clineschmidt B, Zachel A, Totaro J, Pflueger A, McGuffin J (1978) Fenfluramine and brain serotonin. Ann NY Acad Sci 305:222–241
Schuster CR, Lewis M, Seiden L (1986) Fenfluramine: neurotoxicity. Psychopharmacol Bull 22:148–151
Kleven MS, Schuster CR, Seiden LS (1988) Effects of depletion of brain serotonin by repeated fenfluramine on neurochemical and anorectic effects of acute fenfluramine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:822–828
Kleven MS, Seiden LS (1989) D-,L-, DL-fenfluramine cause long lasting depletions of serotonin in rat brain. Brain Res 505:351–353
Appel NM, Contrera JF, De Souza EB (1990) Fenfluramine selectively and differentially decreases the density of serotonergic nerve terminals in rat brain: evidence from immunocytochemical studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 249:928–943
Johnson MP, Nichols DE (1990) Comparative serotonin neurotoxicity of the stereoisomers of fenfluramine and norfenfluramine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 36:105–109
Molliver DC, Molliver ME (1990) Anatomic evidence of a neurotoxic effect of (-) fenfluramine upon serotonergic projections in the rat. Brain Res 511:165–168
Zaczek R, Battaglia G, Culp S, Appel NM, Contrera JF, De Souza EB (1990) Effects of repeated fenfluramine administration on indexes of monoamine function in rat brain: pharmacokinetic, dose response, regional specificity and time-course data. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:104–112
Caccia S, Aneli M, Ferrrese A, Fracaso C, Garattini S (1993) The role of d-norfenfluramine in the indole-depleting effect of fenfluramine. Eur J Pharmacol 233:71–77
Westphalen R, Dodd P (1995) The nature of D-L-induced 5-HT re-uptake transporter loss in rats. Mol Neurobiol 11:165–175
McCann U, Hatzidimitriou G, Ridenour A, Fischer C, Yuan J, Katz J, Ricaurte G (1994) Dexfenfluramine and serotonin neurotoxicity: further preclinical evidence that clinical caution is indicated. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 269:792–798
McCann UD, Szabo Z, Scheffel U, Dannals RF, Ricaurte GA (1998) Positron emission tomographic evidence of toxic effect of MDMA (“Ecstasy”) on brain serotonin neurons in human beings. Lancet 352:1433–1437
McCann UD, Szabo Z, Seckin E, Rosenblatt P, Mathews WB, Ravert HT, Dannals RF, Ricaurte GA (2005) Quantitative PET studies of the serotonin transporter in MDMA users and controls using [11C]McN5652 and [11C]DASB. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1741–1750
Buchert R, Thomasius R, Nebeling B, Petersen K, Obrocki J, Jenicke L, Wilke F, Wartberg L, Zapletalova P, Clausen M (2003) Long-term effects of “ecstasy” use on serotonin transporters of the brain investigated by PET. J Nucl Med 44:375–384
Buchert R, Thomasius R, Wilke F, Petersen K, Nebeling B, Obrocki J, Schulze O, Schmidt U, Clausen M (2004) A voxel-based PET investigation of the long-term effects of “Ecstasy” consumption on brain serotonin transporters. Am J Psychiatry 161:1181–1189
Scheffel U, Szabo Z, Mathews WB, Finley PA, Dannals RF, Ravert HT, Szabo K, Yuan J, Ricaurte GA (1998) In vivo detection of short-and long-term MDMA neurotoxicity-a positron emission tomography study in the living baboon brain. Synapse 29(2):183–192
Szabo Z, McCann UD, Wilson AA, Scheffel U, Owonikoko T, Mathews WB, Ravert HT, Hilton J, Dannals RF, Ricaurte GA (2002) Comparison of (+)-(11)C-McN5652 and (11)C-DASB as serotonin transporter radioligands under various experimental conditions. J Nucl Med 43:678–692
Scheffel U, Szabo Z, Mathews WB, Finley PA, Yuan J, Callahan B, Hatzidimitriou G, Dannals RF, Ravert HT, Ricaurte GA (1996) Fenfluramine-induced loss of serotonin transporters in baboon brain visualized with PET. Synapse 24(4):395–398
Szabo Z, Scheffel U, Mathews WB, Ravert HT, Szabo K, Kraut M, Palmon S, Ricaurte GA, Dannals RF (1999) Kinetic analysis of [11C]McN5652: a serotonin transporter radioligand. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:967–981
Wilson AA, Ginovart N, Schmidt M, Meyer JH, Threlkeld PG, Houle S (2000) Novel radiotracers for imaging the serotonin transporter by positron emission tomography: synthesis, radiosynthesis, and in vitro and ex vivo evaluation of (11)C-labeled 2(phenylthio)araalkylamines. J Med Chem 43:310–311
Hilton J, Yokoi F, Dannals RF, Ravert HT, Szabo Z, Wong DF (2000) Column-switching HPLC for the analysis of plasma in PET imaging studies. Nucl Med Biol 27:627–630
Szabo Z, Owonikoko T, Peyrot M, Varga J, Mathews WB, Ravert HT, Dannals RF, Wand G (2004) Positron emission tomography imaging of the serotonin transporter in subjects with a history of alcoholism. Biol Psychiatry 55:766–771
Varga J, Szabo Z (2002) A modified regression model for the Logan plot. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:240–244
Frankle WG, Huang Y, Hwang DR, Talbot PS, Slifstein M, Van Heertum R, Abi-Dargham A, Laruelle M (2004) Comparative evaluation of serotonin transporter radioligands 11C-DASB and 11C-McN 5652 in healthy humans. J Nucl Med 45:682–694
Murphy DL, Andrews AM, Wichems CH, Li O, Tohda M, Greenberg B (1998) Brain serotonin neurotransmission: an overview and update with an emphasis on serotonin subsystem heterogeneity, multiple receptors, interactions with other neurotransmitter systems, and consequent implications for understanding the actions of serotonergic drugs. J Clin Psychiatry 59:4–12, Review
Arango V, Underwood MD, Mann JJ (2002) Serotonin brain circuits involved in major depression and suicide. Prog Brain Res 136:443–453, Review
Hornung JP (2003) The human raphe nuclei and the serotonergic system. J Chem Neuroanat 26:331–343, Review
Golding D (1970) Unusual effect of fenfluramine. Br Med J 1:238
Oswald I, Lewis SA, Dunleavy DLF, Brezinova V, Briggs M (1970) Drugs of dependence though not of abuse. Br Med J 3:70–73
Harding T (1971) Fenfluramine dependence. Br Med J 2:305
Harding T (1972) Depression following fenfluramine withdrawal. Br J Psychiatry 121:338–339
Toornvliet AC, Pijl H, Meinders AE (1994) Major depression during dexfenfluramine treatment. Int J Obesity 18:650
Raison CL, Klein HM (1997) Psychotic mania associated with fenfluramine and phentermine use. Am J Psychiatry 154:711
Preval H, Palyurek AM (1997) Psychotic episode associated with dexfentluramine. Am J Psychiatry 154:1624–1625
Verbaten MN (2003) Specific memory deficits in ecstasy users. The results of a meta-analysis. Hum Psychopharmacol 18:281–290
Staley JK, Krishnan-Sarin S, Zoghbi S, Tamagnan G, Fujita M, Seibyl JP, Maciejewski PK, O’Malley S, Innis RB (2001) Sex differences in [123I]beta-CIT SPECT measures of dopamine and serotonin transporter availability in healthy smokers and nonsmokers. Synapse 41:275–284
Staley JK, Sanacora G, Tamagnan G, Maciejewski PK, Malison RT, Berman RM, Vythilingam M, Kugaya A, Baldwin RM, Seibyl JP, Charney D, Innis RB (2006) Sex differences in diencephalon serotonin transporter availability in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 59:40–47
Acknowledgments
This manuscript was supported by PHS Grants DA00206 (Ricaurte); AA11653 (Szabo), NSF Grant No. 843 (Szabo), and NCRR grant M01RR002719 (Klag). We thank Paul Nuzzo for his assistance with statistical analyses, and Audra de Ridder for her assistance with recruiting subjects. We appreciate the important contributions of Jozsef Varga, Ph.D. whose work was pivotal for the development of the image analysis package PMT that was used in this project.
We appreciate the following contributions to PET imaging and image analysis: David Clough, CNMT and Karen Edmonds, CNMT for performance of PET studies; John Hilton for HPLC analysis of tracer metabolites. None of the authors has a financial or other conflict of interest that might potentially bias this work.
Role of Authors. Drs. McCann and Ricaurte designed the study and supervised all aspects of the research related to fenfluramine subjects, except for PET scanning procedures. Dr. Szabo supervised all of the PET studies described. Drs. Vranesic and Seckin assisted in PET data analysis. Dr. Wand was responsible for the recruitment and assessment of control subjects. Ms. Duval assisted with the data analysis and figure preparation for the manuscript. Dr. Dannals supervised synthesis of the radiotracer utilized. Drs. McCann, Ricaurte, and Szabo took the lead in writing the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript and suggested changes when deemed appropriate.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCann, U.D., Szabo, Z., Vranesic, M. et al. Quantitative Positron Emission Tomography Studies of the Serotonin Transporter in Humans Previously Treated with the Appetite Suppressants Fenfluramine or Dexfenfluramine. Mol Imaging Biol 9, 151–157 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-007-0082-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-007-0082-7