Abstract
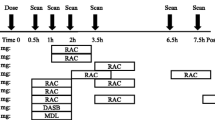
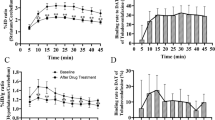
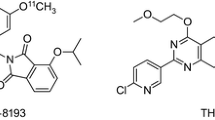
Desipramine (DMI), talopram and talsupram, three of the most potent norepinephrine transporter (NET) inhibitors reported to date, were radiolabeled in high yields and at high specific radioactivity (58–75 GBq/μmol) by the methylation of nor-precursors with [C-11]methyl triflate. The regional brain distribution of each radioligand following intravenous injection into cynomolgus monkey was examined in vivo with positron emission tomography (PET). For all three radioligands, the regional brain distribution of radioactivity was slightly heterogeneous, with higher uptake of radioactivity in the mesencephalon, thalamus and lower brainstem than in striatum. The rank order of maximal brain radioactivity (as percentage of injected dose) was [11C]DMI (2.7%) > [11C]talsupram (1.3%) > [11C]talopram (0.7%). The appearance of radioactive metabolites in plasma was similar for each radioligand (75–85% of radioactivity in plasma at 45 min). These metabolites were all more polar than their parent radioligand. The data show that these radioligands are inferior to existing radioligands for the study of brain NET with PET in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halldin C, Gulyás B, Langer O, Farde L (2001) Brain radioligands– state of the art and new trends. Q J Nucl Med 45:139–152
Haka MS, Kilbourn MR (1989). Synthesis and regional mouse brain distribution of [11C]nisoxetine, a norepinephrine transporter inhibitor. Nucl Med Biol 16:771–774
Schou M, Halldin C, Sóvágó J, Pike VW, Gulyás B, Mozley PD, Johnson DP, Hall H, Innis RB, Farde L (2003) Specific in vivo binding to the norepinephrine transporter demonstrated with the PET radioligand, (S,S)-[11C]MeNER. Nucl Med Biol 30:707–714
Wilson AA, Johnson DP, Mozley PD, Hussey D, Ginovart N, Nobrega J, Garcia A, Meyer J, Houle S (2003) Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of novel radiotracers for the in vivo imaging of the norepinephrine transporter. Nucl Med Biol 30:85–92
Ding Y-S, Lin K-S, Garza V, Carter P, Alexoff D, Logan J, Shea C, Xu Y, King P (2003). Evaluation of a new norepinephrine transporter PET ligand in baboons, both in brain and peripheral organs. Synapse 50: 345–352
Schou M, Halldin C, Sovago J, Pike VW, Hall H, Gulyás B, Mozley PD, Dobson D, Shchukin E, Innis RB, Farde L (2004) PET evaluation of novel radiofluorinated reboxetine analogs as norepinephrine transporter probes in the monkey brain. Synapse 53:57–67
Bowden CL, Schatzberg AF, Rosenbaum A, Contreras SA, Samson JA, Dessain E, Sayler M (1993) Fluoxetine and desipramine in major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol 13:305–311
Bøgesø KP, Christiansen AV, Hyttel J, Liljefors T (1985) 3-Phenyl-1-indanamines. Potential antidepressant activity and potent inhibitors of dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin uptake. J Med Chem 28:1817–1828
Hyttel J (1982) Citalopram—pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6:277–295
Cusack B, Nelson A, Richelson E (1994) Binding of antidepressants to human brain receptors: Focus on newer generation compounds. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 114:559–565
Owens MJ, Morgan WN, Plott SJ, Nemeroff CB (1997) Neurotransmitter receptor and transporter binding profile of antidepressants and their metabolites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:1305–1322
Bäckström I, Marcusson J (1990) High- and low-affinity [3H]desipramine-binding sites in human postmortem brain tissue. Neuropsychobiology 23:68–73
Gross-Isseroff R, Israeli M, Biegon A (1988) Autoradiographic analysis of [3H]desmethylimipramine binding in the human brain postmortem. Brain Res 456:120–126
Van Dort ME, Kim J-H, Tluczek L, Wieland DM (1997) Synthesis of 11C-labeled desipramine and its metabolite 2-hydroxydesipramine: Potential radiotracers for PET studies of the norepinephrine transporter. Nucl Med Biol 24:707–711
McConathy J, Owens MJ, Kilts CD, Malveaux EJ, Camp VM, Votaw JR, Nemeroff CB, Goodman MM (2004) Synthesis and biological evaluation of [11C]talopram and [11C]talsupram: Candidate PET ligands for the norepinephrine transporter. Nucl Med Biol 31:705–718
Sandell J, Langer O, Larsen P, Dolle F, Vaufrey F, Demphel S, Crouzel C, Halldin C (2000) Improved specific radioactivity of the PET radioligand [11C]FLB 457 by use of the GE medical systems PETtrace MeI MicroLab. J Labelled Compd Radiopharm 43:331–338
Wienhard K, Dahlbom M, Eriksson L, Michel C, Bruckbauer T, Pietrzyk U, Heiss W (1994) The ECAT Exact HR: Performance of a new high resolution positron scanner. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18:110–118
Karlsson P, Farde L, Halldin C, Swahn C-G, Sedvall G, Foged C, Hansen K, Skrumsager B (1993) PET examination of [11C]NNC 687 and [11C]NNC 756 as new radioligands for the D1-dopamine receptor. Psychopharmacology 113:149–156
Charnay Y, Leger L, Vallet P, Hof P, Juovet M, Bouras C (1995) [3H]Nisoxetine binding sites in the cat brain: An autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 69:259–270
Donnan G, Kaczmarczyk S, Paxinos G, Chilco P, Kalnins R, Woodhouse D, Mendelsohn F (1991) Distribution of catecholaminergic uptake sites in human brain as determined by quantitative [3H]mazindol autoradiography. J Comp Neurol 304:419–434
Tejani-Butt S (1992) [3H]Nisoxetine: A radioligand for quantitation of norepinephrine uptake sites by autoradiography or by homogenate binding. J Pharm Exp Ther 260:427–436
Halldin C, Swahn C-G, Farde L, Sedvall G (1995) Radioligand disposition and metabolism. In: Comar D, (ed) PET for Drug Development and Evaluation. Academic Publishers: Kluwer, pp. 55–65
Waterhouse RN (2003) Determination of lipophilicity and its use as a predictor of blood brain barrier penetration of molecular imaging agents. Mol Imaging Biol 5:376–389
pKa, LogD and Log P values were predicted with the Pallas 3.0 for Windows software
Doze P, Van Waarde A, Elsinga PH, Hendrikse NH, Vaalburg W (2000) Enhanced cerebral uptake of receptor ligands by modulation of P-glycoprotein function in the blood–brain barrier. Synapse 36:66–74
Balle T, Halldin C, Andersen L, Alfrangis LH, Badolo L, Jensen K.G., Chou YW, Andersen K, Perregaard J, Farde L (2004) New α1-adrenoceptor antagonists derived from the antipsychotic sertindole—carbon-11 labelling and PET examination of brain uptake in the cynomolgus monkey. Nucl Med Biol 31:327–336
Hara K, Yanagihara N, Minami K, Ueno S, Toyohira Y, Sata T, Kawamura M, Bruss M, Bonisch H, Shigematsu A, Izumi F (1998) Ketamine interacts with the noradrenaline transporter at a site partly overlapping the desipramine binding site. N-S Arch Pharmacol 358:328–333
Uryu K, Minami K, Yanagihara N, Hara K, Toyohira Y, Izumi F, Shigematsu A (2000) Inhibition by neuromuscular blocking drugs of norepinephrine transporter in cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells. Anesth Analg 91:546–551
The authors would like to thank H. Lundbeck A/S for supplying the precursors and standards of talopram and talsupram. We are also grateful for the technical assistance of Mr. A Amir and Mr. P. Truong and the other members of the PET group at Karolinska Institutet. Mr. M Schou was supported by the Karolinska Institutet-National Institutes of Health graduate training partnership program. This work was also supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the Natinal Institute of Health (National Institute of Mental Health).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schou, M., Sóvágó, J., Pike, V.W. et al. Synthesis and Positron Emission Tomography Evaluation of Three Norepinephrine Transporter Radioligands: [C-11]Desipramine, [C-11]Talopram and [C-11]Talsupram. Mol Imaging Biol 8, 1–8 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-005-0027-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-005-0027-y