Abstract
Introduction
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease with different prognoses and responses to systemic treatment depending on its molecular characteristics, which makes it imperative to develop new biomarkers for an individualized diagnosis and personalized oncological treatment. Ex vivo high-resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (HRMAS 1H MRS) is the most common technique for metabolic quantification in human surgical and biopsy tissue specimens.
Objective
To perform a review of the current available literature on the clinical applications of HRMAS 1H MRS metabolic analysis in tissue samples of breast cancer patients.
Methods
This systematic scoping review included original research papers published in the English language in peer-reviewed journals. Study selection was performed independently by two reviewers and preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed.
Results
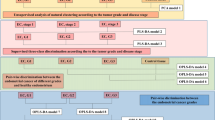
The literature search returned 159 studies and 26 papers were included as part of this systematic review. There was considerable variation regarding tissue type, aims, and statistical analysis methods across the different studies. To facilitate the interpretation of the results, the included studies were grouped according to their aims or main outcomes into: feasibility and tumor diagnosis (n = 6); tumor heterogeneity (n = 2); correlation with proteomics/transcriptomics (n = 3); correlation with prognostic factors (n = 11); and response evaluation to NAC (n = 4).
Conclusion
There is a lot of potential in including metabolic information of breast cancer tissue obtained with HRMAS 1H MRS. To date, studies show that metabolic concentrations quantified by this technique can be related to the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response in breast cancer patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathen, T. F., Geurts, B., Sitter, B., Fjøsne, H. E., Lundgren, S., Buydens, L. M., et al. (2013). Feasibility of MR metabolomics for immediate analysis of resection margins during breast cancer surgery. PLoS ONE, 8(4), e61578.
Bathen, T. F., Jensen, L. R., Sitter, B., Fjösne, H. E., Halgunset, J., Axelson, D. E., et al. (2007). MR-determined metabolic phenotype of breast cancer in prediction of lymphatic spread, grade, and hormone status. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 104(2), 181–189.
Bathen, T. F., Sitter, B., Sjobakk, T. E., Tessem, M.-B., & Gribbestad, I. S. (2010). Magnetic resonance metabolomics of intact tissue: A biotechnological tool in cancer diagnostics and treatment evaluation. Cancer Research, 70(17), 6692–6696.
Bitencourt, A. G. V., Pinker, K., & Thakur, S. (2019). Elevated glycine detected on in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a breast cancer patient: Case report and literature review. BJR Case Reports, 5, 20190090.
Borgan, E., Sitter, B., Lingjærde, O. C., Johnsen, H., Lundgren, S., Bathen, T. F., et al. (2010). Merging transcriptomics and metabolomics: Advances in breast cancer profiling. BMC Cancer, 10(1), 628.
Bramer, W. M., Giustini, D., de Jonge, G. B., Holland, L., & Bekhuis, T. (2016). De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. Journal of the Medical Library Association, 104(3), 240–243.
Cao, M. D., Döpkens, M., Krishnamachary, B., Vesuna, F., Gadiya, M. M., Lønning, P. E., et al. (2012a). Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 5 (GDPD5) expression correlates with malignant choline phospholipid metabolite profiles in human breast cancer. NMR in Biomedicine, 25(9), 1033–1042.
Cao, M. D., Giskeødegård, G. F., Bathen, T. F., Sitter, B., Bofin, A., Lønning, P. E., et al. (2012b). Prognostic value of metabolic response in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. BMC Cancer, 12(1), 39.
Cao, M. D., Lamichhane, S., Lundgren, S., Bofin, A., Fjøsne, H., Giskeødegård, G. F., et al. (2014). Metabolic characterization of triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer, 14, 941.
Cao, M. D., Sitter, B., Bathen, T. F., Bofin, A., Lønning, P. E., Lundgren, S., et al. (2012c). Predicting long-term survival and treatment response in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy by MR metabolic profiling. NMR in Biomedicine, 25(2), 369–378.
Chae, E. Y., Shin, H. J., Kim, S., Baek, H.-M., Yoon, D., Kim, S., et al. (2016). The role of high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for predicting the invasive component in patients with ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed on preoperative biopsy. PLoS ONE, 11(8), e0161038.
Cheng, L. L., Chang, I.-W., Smith, B. L., & Gonzalez, R. G. (1998). Evaluating human breast ductal carcinomas with high-resolution magic-angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 135(1), 194–202.
Choi, J. S., Baek, H. M., Kim, S., Kim, M. J., Youk, J. H., Moon, H. J., et al. (2012). HR-MAS MR spectroscopy of breast cancer tissue obtained with core needle biopsy: Correlation with prognostic factors. PLoS ONE, 7(12), e51712.
Choi, J. S., Baek, H.-M., Kim, S., Kim, M. J., Youk, J. H., Moon, H. J., et al. (2013). Magnetic resonance metabolic profiling of breast cancer tissue obtained with core needle biopsy for predicting pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. PLoS ONE, 8(12), e83866.
Choi, J. S., Yoon, D., Koo, J. S., Kim, S., Park, V. Y., Kim, E.-K., et al. (2017). Magnetic resonance metabolic profiling of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: Correlation with currently used molecular markers. Oncotarget, 8(38), 63405–63416.
Emwas, A. H. M., Salek, R. M., Griffin, J. L., & Merzaban, J. (2013). NMR-based metabolomics in human disease diagnosis: Applications, limitations, and recommendations. Metabolomics, 9(5), 1048–1072.
Euceda, L. R., Haukaas, T. H., Giskeødegård, G. F., Vettukattil, R., Engel, J., Silwal-Pandit, L., et al. (2017). Evaluation of metabolomic changes during neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with bevacizumab in breast cancer using MR spectroscopy. Metabolomics, 13(4), 37.
Fardanesh, R., Marino, M. A., Avendano, D., Leithner, D., Pinker, K., & Thakur, S. B. (2019). Proton MR spectroscopy in the breast: Technical innovations and clinical applications. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26700.
Ferlay, J., Colombet, M., Soerjomataram, I., Mathers, C., Parkin, D. M., Piñeros, M., et al. (2019). Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. International Journal of Cancer, 144(8), 1941–1953.
Fuss, T. L., & Cheng, L. L. (2016). Evaluation of cancer metabolomics using ex vivo high resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Metabolites, 6(1), E11.
Ganji, S. K., Maher, E. A., & Choi, C. (2016). In vivo 1 HMRSI of glycine in brain tumors at 3T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 75(1), 52–62.
Giskeødegård, G. F., Grinde, M. T., Sitter, B., Axelson, D. E., Lundgren, S., Fjøsne, H. E., et al. (2010). Multivariate modeling and prediction of breast cancer prognostic factors using MR metabolomics. Journal of Proteome Research, 9(2), 972–979.
Giskeødegård, G. F., Lundgren, S., Sitter, B., Fjøsne, H. E., Postma, G., Buydens, L. M. C., et al. (2012). Lactate and glycine-potential MR biomarkers of prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. NMR in Biomedicine, 25(11), 1271–1279.
Glunde, K., & Bhujwalla, Z. M. (2011). Metabolic tumor imaging using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Seminars in Oncology, 38(1), 26–41.
Gogiashvili, M., Horsch, S., Marchan, R., Gianmoena, K., Cadenas, C., Tanner, B., et al. (2018). Impact of intratumoral heterogeneity of breast cancer tissue on quantitative metabolomics using high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy. NMR in Biomedicine, 31(2), e3862.
Gogiashvili, M., Nowacki, J., Hergenröder, R., Hengstler, J. G., Lambert, J., & Edlund, K. (2019). HR-MAS NMR based quantitative metabolomics in breast cancer. Metabolites, 9(2), 19.
Günther, U. L. (2015). Metabolomics biomarkers for breast cancer. Pathobiology, 82(3–4), 153–165.
Haukaas, T., Euceda, L., Giskeødegård, G., & Bathen, T. (2017). Metabolic portraits of breast cancer by HR MAS MR spectroscopy of intact tissue samples. Metabolites, 7(2), 18.
Haukaas, T. H., Euceda, L. R., Giskeødegård, G. F., Lamichhane, S., Krohn, M., Jernström, S., et al. (2016). Metabolic clusters of breast cancer in relation to gene- and protein expression subtypes. Cancer & Metabolism, 4(1), 12.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Green, S. (2011). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. London: The Cochrane Collaboration.
Jagannathan, N. R., & Sharma, U. (2017). Breast tissue metabolism by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Metabolites, 7(2), E25.
Kaushik, A. K., & DeBerardinis, R. J. (2018). Applications of metabolomics to study cancer metabolism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta: Reviews on Cancer, 1870(1), 2–14.
Li, T., & Deng, P. (2017). Nuclear Magnetic Resonance technique in tumor metabolism. Genes and Diseases, 4(1), 28–36.
McCartney, A., Vignoli, A., Biganzoli, L., Love, R., Tenori, L., Luchinat, C., et al. (2018). Metabolomics in breast cancer: A decade in review. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 67(April), 88–96.
McGowan, J., Sampson, M., Salzwedel, D. M., Cogo, E., Foerster, V., & Lefebvre, C. (2016). PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 75, 40–46.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7), e1000097.
Park, V. Y., Yoon, D., Koo, J. S., Kim, E.-K., Kim, S. Il, Choi, J. S., et al. (2016). Intratumoral agreement of high-resolution magic angle spinning magnetic resonance spectroscopic profiles in the metabolic characterization of breast cancer. Medicine, 95(15), e3398.
Paul, A., Kumar, S., Raj, A., Sonkar, A. A., Jain, S., Singhai, A., et al. (2018). Alteration in lipid composition differentiates breast cancer tissues: A 1H HRMAS NMR metabolomic study. Metabolomics, 14(9), 119.
Selli, C., & Sims, A. H. (2019). Neoadjuvant therapy for breast cancer as a model for translational research. Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Research, 13, 117822341982907.
Shin, H. J., Kim, S., Baek, H. M., Yoon, D., Kim, S., Cha, J. H., et al. (2016). Prediction of indolent breast cancer with favorable prognostic factors by metabolic profiling using in vivo and ex vivo MR metabolomics. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 47(2), 159–174.
Sitter, B., Bathen, T. F., Singstad, T. E., Fjøsne, H. E., Lundgren, S., Halgunset, J., et al. (2010). Quantification of metabolites in breast cancer patients with different clinical prognosis using HR MAS MR spectroscopy. NMR in Biomedicine, 23(4), 424–431.
Sitter, B., Lundgren, S., Bathen, T. F., Halgunset, J., Fjosne, H. E., & Gribbestad, I. S. (2006). Comparison of HR MAS MR spectroscopic profiles of breast cancer tissue with clinical parameters. NMR in Biomedicine, 19(1), 30–40.
Sitter, B., Sonnewald, U., Spraul, M., Fjösne, H. E., & Gribbestad, I. S. (2002). High-resolution magic angle spinning MRS of breast cancer tissue. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(5), 327–337.
Tayyari, F., Gowda, G. A. N., Olopade, O. F., Berg, R., Yang, H. H., Lee, M. P., et al. (2018). Metabolic profiles of triple-negative and luminal A breast cancer subtypes in African-American identify key metabolic differences. Oncotarget, 9(14), 11677–11690.
Thakur, S. B., Horvat, J. V., Hancu, I., Sutton, O. M., Bernard-Davila, B., Weber, M., et al. (2019). Quantitative in vivo proton MR spectroscopic assessment of lipid metabolism: Value for breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26622.
Thomas, M. A., Lipnick, S., Velan, S. S., Liu, X., Banakar, S., Binesh, N., et al. (2009). Investigation of breast cancer using two-dimensional MRS. NMR in Biomedicine, 22(1), 77–91.
Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O’Brien, K. K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., et al. (2018). PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Annals of Internal Medicine, 169(7), 467.
Waks, A. G., & Winer, E. P. (2019). Breast cancer treatment. JAMA, 321(3), 288.
Yoon, H., Yoon, D., Yun, M., Choi, J. S., Park, V. Y., Kim, E. K., et al. (2016). Metabolomics of breast cancer using high-resolution magic angle spinning magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Correlations with 18F-FDG positron emission tomography-computed tomography, dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted imaging MRI. PLoS ONE, 11(7), e0159949.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant (P30 CA008748) and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JG conducted the literature review and constructed the article database. AGVB and SBT performed the study selection and reviewed the selected studies. All authors were involved in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Katja Pinker received payment for activities not related to the present article including lectures including service on speakers bureaus and for travel/accommodations/meeting expenses unrelated to activities listed from the European Society of Breast Imaging (MRI educational course, annual scientific meeting) and the IDKD 2019 (educational course).
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bitencourt, A.G.V., Goldberg, J., Pinker, K. et al. Clinical applications of breast cancer metabolomics using high-resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (HRMAS 1H MRS): systematic scoping review. Metabolomics 15, 148 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1611-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1611-5