Abstract
Introduction
The interactions between plants and insect herbivores are complex and multifaceted. Rice and its specialist insect pest the brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) constitute an ideal system for studying plant–insect interactions.
Objectives
Combined metabolomics analyses of rice plant and BPH were conducted to understand the mechanism of host rice plant defense and BPH insect response.
Methods
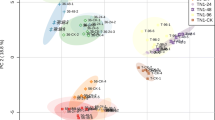
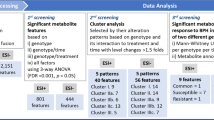
Metabolite dynamics in rice leaf sheath and BPH honeydew was investigated using the gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) method. The GC–MS data were analyzed by principal component analysis and partial least squares-discriminant analysis.
Results
Twenty-six metabolites were detected in the leaf sheath extracts. Rice leaf sheath metabolomics analysis results show that BPH feeding induces distinct changes in the metabolite profiles of YHY15 and TN1 plants. These results suggest that BPH infestation enhance fatty acid oxidation, the glyoxylate cycle, gluconeogenesis and the GABA shunt in TN1 plants, and glycolysis and the shikimate pathway in YHY15. We propose that the BPH15 gene mediates a resistance reaction that increases the synthesis of secondary metabolites through the shikimate pathway. Thirty-three metabolites were identified in BPH honeydew. Honeydew metabolomics analysis results show that when BPH insects were fed on resistant YHY15 plants, most of the amino acids in honeydew were significantly decreased compared to those of BPH fed on TN1 plants. Based on metabolomics results, we propose that BPH feeding on resistant YHY15 plants would enhance amino acid absorption. At the same time, urea was significantly increased in BPH fed on YHY15.
Conclusion
Metabolomics study is valuable in understanding the complex and multifaceted interaction between plants and insect herbivores and provide essential clue for development of novel control BPH strategies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allwood, J. W., Ellis, D. I., & Goodacre, R. (2008). Metabolomic technologies and their application to the study of plants and plant–host interactions. Physiologia Plantarum, 132(2), 117–135.
Arimura, G. I., Kost, C., & Boland, W. (2005). Herbivore-induced, indirect plant defences. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1734(2), 91–111.
Baldwin, I. T., & Callahan, P. (1993). Autotoxicity and chemical defense: Nicotine accumulation and carbon gain in solanaceous plants. Oecologia, 94(4), 534–541.
Bennett, R. N., & Wallsgrove, R. M. (1994). Tansley Review No. 72. Secondary metabolites in plant defence mechanisms. New Phytologist, 127(72), 617–633.
Bjerrum, J. T. (2015). Metabonomics. New York: Springer.
Bolton, M. D. (2009). Primary metabolism and plant defense—Fuel for the fire. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 22(5), 487–497.
Bolton, M. D., Kolmer, J. A., Xu, W. W., & Garvin, D. F. (2008). Lr34-mediated leaf rust resistance in wheat: Transcript profiling reveals a high energetic demand supported by transient recruitment of multiple metabolic pathways. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions, 21(12), 1515–1527.
Bouche, N., & Fromm, H. (2004). GABA in plants: Just a metabolite? Trends in Plant Science, 9(3), 110–115.
Bouché, N., Lacombe, B., & Fromm, H. (2003). GABA signaling: A conserved and ubiquitous mechanism. Trends in Cell Biology, 13(12), 607–610.
Bown, A. W., MacGregor, K. B., & Shelp, B. J. (2006). Gamma-aminobutyrate: Defense against invertebrate pests? Trends in Plant Science, 11(9), 424–427.
Brar, D. S., Virk, P. S., Jena, K. K., & Khush, G. S. (2009). Breeding for resistance to planthoppers in rice. In K. L. Heong & B. Hardy (Eds.), Planthoppers: New threats to the sustainability of intensive rice production systems in Asia (pp. 401–427). Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Chen, W., Gao, Y., Xie, W., Gong, L., Lu, K., Wang, W., et al. (2014). Genome-wide association analyses provide genetic and biochemical insights into natural variation in rice metabolism. Nature Genetics, 46(7), 714–721.
Cheng, X., Zhu, L., & He, G. (2013). Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper. Molecular Plant, 6(3), 621–634.
Claridge, M. F., & Hollander, J. D. (1980). The “biotypes” of the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Entomologia experimentalis et applicata, 27(1), 23–30.
Cochran, D. G. (1975). Excretion in insects. In D. J. Candy & B. A. Kilby (Eds.), Insect biochemistry and function (pp. 177–281). New York: Chapman Hall.
Cochran, D. G. (1985). Nitrogen excretion in cockroaches. Annual Review of Entomology, 30(1), 29–49.
Cots, J., Fargeix, C., Gindro, K., & Widmer, F. (2002). Pathogenic attack and carbon reallocation in soybean leaves (Glycine max L.): Reinitiation of the glyoxylate cycle as a defence reaction. Journal of Plant Physiology, 159(1), 91–96.
Du, B., Wei, Z., Wang, Z., Wang, X., Peng, X., Du, B., et al. (2015). Phloem-exudate proteome analysis of response to insect brown plant-hopper in rice. Journal of Plant Physiology, 183, 13–22.
Du, B., Zhang, W., Liu, B., Hu, J., Wei, Z., Shi, Z., et al. (2009). Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 106(52), 22163–22168.
Esquivel, C. J., Cassone, B. J., & Piermarini, P. M. (2014). Transcriptomic evidence for a dramatic functional transition of the malpighian tubules after a blood meal in the Asian tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 8(6), e2929.
Gut, H., Dominici, P., Pilati, S., Astegno, A., Petoukhov, M. V., Svergun, D. I., et al. (2009). A common structural basis for pH- and calmodulin-mediated regulation in plant glutamate decarboxylase. Journal of Molecular Biology, 392(2), 334–351.
Heil, M., Hilpert, A., Kaiser, W., & Linsenmair, K. E. (2000). Reduced growth and seed set following chemical induction of pathogen defence: Does systemic acquired resistance (SAR) incur allocation costs? Journal of Ecology, 88(4), 645–654.
Herrmann, K. M. (1995). The shikimate pathway as an entry to aromatic secondary metabolism. Plant Physiology, 107(1), 7.
Horgan, F. (2009). Mechanisms of resistance: A major gap in understanding planthopper–rice interactions. In K. L. Heong & B. Hardy (Eds.), Planthoppers: New threats to the sustainability of intensive rice production systems in Asia (pp. 281–302). Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Jansen, J. J., Allwood, J. W., Marsden-Edwards, E., van der Putten, W. H., Goodacre, R., & van Dam, N. M. (2009). Metabolomic analysis of the interaction between plants and herbivores. Metabolomics, 5(1), 150–161.
Jena, K. K., & Kim, S. M. (2010). Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice, 3(2–3), 161–171.
Jing, S., Liu, B., Peng, L., Peng, X., Zhu, L., Fu, Q., et al. (2012). Development and use of EST-SSR markers for assessing genetic diversity in the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål). Bulletin of Entomological Research, 102(01), 113–122.
Kaur, H., Heinzel, N., Schöttner, M., Baldwin, I. T., & Gális, I. (2010). R2R3-NaMYB8 regulates the accumulation of phenylpropanoid–polyamine conjugates, which are essential for local and systemic defense against insect herbivores in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant Physiology, 152(3), 1731–1747.
Kawano, T. (2003). Roles of the reactive oxygen species-generating peroxidase reactions in plant defense and growth induction. Plant Cell Reports, 21(9), 829–837.
Kinnersley, A. M., & Turano, F. J. (2000). Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and plant responses to stress. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 19(6), 479–509.
Leiss, K. A., Choi, Y. H., Abdel-Farid, I. B., Verpoorte, R., & Klinkhamer, P. G. (2009). NMR metabolomics of thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) resistance in Senecio hybrids. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 35(2), 219–229.
Lisec, J., Schauer, N., Kopka, J., Willmitzer, L., & Fernie, A. R. (2006). Gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling in plants. Nature Protocols, 1(1), 387–396.
Liu, C., Hao, F., Hu, J., Zhang, W., Wan, L., Zhu, L., et al. (2010). Revealing different systems responses to brown planthopper infestation for pest susceptible and resistant rice plants with the combined metabonomic and gene-expression analysis. Journal of Proteome Research, 9(12), 6774–6785.
Liu, Y., Wu, H., Chen, H., Liu, Y., He, J., Kang, H., et al. (2015). A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nature Biotechnology, 33(3), 301–305.
Luo, J., Fuell, C., Parr, A., Hill, L., Bailey, P., Elliott, K., et al. (2009). A novel polyamine acyltransferase responsible for the accumulation of spermidine conjugates in Arabidopsis seed. The Plant Cell, 21(1), 318–333.
Lv, W., Du, B., Shangguan, X., Zhao, Y., Pan, Y., Zhu, L., et al. (2014). BAC and RNA sequencing reveal the brown planthopper resistance gene BPH15 in a recombination cold spot that mediates a unique defense mechanism. BMC Genomics, 15(1), 674.
Maeda, H., & Dudareva, N. (2012). The shikimate pathway and aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 63, 73–105.
Narayan, V. S., & Nair, P. M. (1990). Metabolism, enzymology and possible roles of 4-aminobutyrate in higher plants. Phytochemistry, 29(2), 367–375.
Nicholson, J. K., & Lindon, J. C. (2008). Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature, 455(7216), 1054–1056.
Nicholson, J. K., Lindon, J. C., & Holmes, E. (1999). Metabonomics. Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica, 29(11), 1181–1189.
Paré, P. W., & Tumlinson, J. H. (1999). Plant volatiles as a defense against insect herbivores. Plant Physiology, 121(2), 325–332.
Park, S. W., Kaimoyo, E., Kumar, D., Mosher, S., & Klessig, D. F. (2007). Methyl salicylate is a critical mobile signal for plant systemic acquired resistance. Science, 318(5847), 113–116.
Qi, X., Chen, X., & Wang, Y. (2015). Plant metabolomics: Methods and applications (pp. 25–44). Netherlands: Springer.
Riach, A. C., Perera, M. V. L., Florance, H. V., Penfield, S. D., & Hill, J. K. (2015). Analysis of plant leaf metabolites reveals no common response to insect herbivory by Pieris rapae in three related host–plant species. Journal of Experimental Botany, 66(9), 2547–2556.
Scaraffia, P. Y., Isoe, J., Murillo, A., & Wells, M. A. (2005). Ammonia metabolism in Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 35(5), 491–503.
Scaraffia, P. Y., Tan, G., Isoe, J., Wysocki, V. H., Wells, M. A., & Miesfeld, R. L. (2008). Discovery of an alternate metabolic pathway for urea synthesis in adult Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 105(2), 518–523.
Schenk, P. M., Kazan, K., Manners, J. M., Anderson, J. P., Simpson, R. S., Wilson, I. W., et al. (2003). Systemic gene expression in Arabidopsis during an incompatible interaction with Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Physiology, 132(2), 999–1010.
Schwachtje, J., & Baldwin, I. T. (2008). Why does herbivore attack reconfigure primary metabolism? Plant Physiology, 146(3), 845–851.
Schwartzberg, E. G., & Tumlinson, J. H. (2014). Aphid honeydew alters plant defence responses. Functional Ecology, 28(2), 386–394.
Shah, J. (2003). The salicylic acid loop in plant defense. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 6(4), 365–371.
Shelp, B. J., Mullen, R. T., & Waller, J. C. (2012). Compartmentation of GABA metabolism raises intriguing questions. Trends in Plant Science, 17(2), 57–59.
Skopelitis, D. S., Paranychianakis, N. V., Paschalidis, K. A., Pliakonis, E. D., Delis, I. D., Yakoumakis, D. I., et al. (2006). Abiotic stress generates ROS that signal expression of anionic glutamate dehydrogenases to form glutamate for proline synthesis in tobacco and grapevine. The Plant Cell, 18(10), 2767–2781.
Smedegaard-Petersen, V., & Tolstrup, K. (1985). The limiting effect of disease resistance on yield. Annual review of Phytopathology, 23(1), 475–490.
Sōgawa, K. (1970). Studies on the feeding habits of the brown planthopper. II. Honeydew excretion. Japanese Journal of Applied Entomology and Zoology, 14(3), 134–139.
Sōgawa, K. (1982). The rice brown planthopper: Feeding physiology and host plant interactions. Annual Review of Entomology, 27(1), 49–73.
Sōgawa, K., & Pathak, M. D. (1970). Mechanisms of brown planthopper resistance in Mudgo variety of rice (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Applied Entomology and Zoology, 5(3), 145–158.
Tamura, Y., Hattori, M., Yoshioka, H., Yoshioka, M., Takahashi, A., Wu, J., et al. (2014). Map-based cloning and characterization of a brown planthopper resistance gene BPH26 from Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cultivar ADR52. Scientific Reports, 4, 5872–5879.
Tang, M., Lv, L., Jing, S., Zhu, L., & He, G. (2010). Bacterial symbionts of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(6), 1740–1745.
Uawisetwathana, U., Graham, S. F., Kamolsukyunyong, W., Sukhaket, W., Klanchui, A., Toojinda, T., et al. (2015). Quantitative 1H NMR metabolome profiling of Thai Jasmine rice (Oryza sativa) reveals primary metabolic response during brown planthopper infestation. Metabolomics, 11(6), 1640–1655.
Wang, Y., Cao, L., Zhang, Y., Cao, C., Liu, F., Huang, F., et al. (2015). Map-based cloning and characterization of BPH29, a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brown planthopper resistance in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 66(19), 6035–6045.
Weaver, L. M., & Herrmann, K. M. (1997). Dynamics of the shikimate pathway in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2(9), 346–351.
Wei, Z., Hu, W., Lin, Q., Cheng, X., Tong, M., Zhu, L., et al. (2009). Understanding rice plant resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens): A proteomic approach. Proteomics, 9(10), 2798–2808.
Wright, P. A. (1995). Nitrogen excretion: Three end products, many physiological roles. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 198(2), 273–281.
Xue, J., Zhou, X., Zhang, C. X., Yu, L. L., Fan, H. W., Wang, Z., et al. (2014). Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation. Genome Biology, 15(12), 521.
Yang, H., You, A., Yang, Z., Zhang, F., He, R., Zhu, L., et al. (2004). High-resolution genetic mapping at the Bph15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 110(1), 182–191.
Zangerl, A. R., Arntz, A. M., & Berenbaum, M. R. (1997). Physiological price of an induced chemical defense: Photosynthesis, respiration, biosynthesis, and growth. Oecologia, 109(3), 433–441.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grants from the State Key Development Program for Basic Research of China (Grant No. 2013CBA01400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31230060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights informed consent
This article does not contain any data related to human or animal studies.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, L., Zhao, Y., Wang, H. et al. Comparative metabolomics of the interaction between rice and the brown planthopper. Metabolomics 12, 132 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1077-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1077-7