Abstract
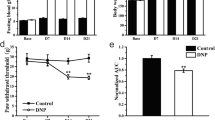
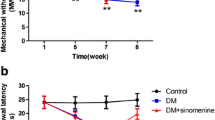
Diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP) is highly common in diabetes patients. P2X receptors play critical roles in pain sensitization. We previously showed that elevated P2X3 expression in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) contributes to DNP. However, the role of other P2X receptors in DNP is unclear. Here, we established the DNP model using a single high-dose streptozotocin (STZ) injection and investigated the expression of P2X genes in the DRG. Our data revealed elevated P2X2, P2X4, and P2X7 mRNA levels in DRG of DNP rats. The protein levels of P2X4 and P2X7 in DNP rats increased, but the P2X2 did not change significantly. To study the role of P2X4 and P2X7 in diabetes-induced hyperalgesia, we treated the DNP rats with TNP-ATP (2’,3’-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-adenosine 5’-triphosphate), a nonspecific P2X1–7 antagonist, and found that TNP-ATP alleviated thermal hyperalgesia in DNP rats. 2 Hz electroacupuncture is analgesic against DNP and could downregulate P2X4 and P2X7 expression in DRG. Our findings indicate that P2X4 and P2X7 in L4–L6 DRGs contribute to diabetes-induced hyperalgesia, and that EA reduces thermal hyperalgesia and the expression of P2X4 and P2X7.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BW:
-
Body weight
- DNP:
-
Diabetic neuropathic pain
- DRG:
-
Dorsal root ganglion
- EA:
-
Electroacupuncture
- FBG:
-
Fasting blood glucose
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IF:
-
Immunofluorescence
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- NS:
-
Normal saline
- P2X:
-
Purinergic ligand-gated cationic channel
- RT-qPCRs:
-
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reactions
- PWL:
-
Paw withdrawal latency
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- TNP-ATP:
-
2’,3’-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-adenosine 5’-triphosphate
- WB:
-
Western blotting
References
Tabish SA (2007) Is diabetes becoming the biggest epidemic of the twenty-first century? Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 1(2):V-viii.
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, Cavan D, Shaw JE, Makaroff LE (2017) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 128:40–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024
Rahimi-Madiseh M, Malekpour-Tehrani A, Bahmani M, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2016) The research and development on the antioxidants in prevention of diabetic complications. Asian Pac J Trop Med 9(9):825–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.07.001
Magadmi RM, Alsulaimani MA, Al-Rafiah AR, Ahmad MS, Esmat A (2021) Carvedilol exerts neuroprotective effect on rat model of diabetic neuropathy. Front Pharmacol 12:613634. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.613634
Smith HS, Argoff CE (2011) Pharmacological treatment of diabetic neuropathic pain. Drugs 71(5):557–589. https://doi.org/10.2165/11588940-000000000-00000
Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ (1998) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 15(7):539–553. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9136(199807)15:7<539::aid-dia668>3.0.co;2-s
Coppini DV (2016) Enigma of painful diabetic neuropathy: can we use the basic science, research outcomes and real-world data to help improve patient care and outcomes? Diabet Med 33(11):1477–1482. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.13089
Impellizzeri D, Peritore AF, Cordaro M, Gugliandolo E, Siracusa R, Crupi R, D’Amico R, Fusco R, Evangelista M, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R (2019) The neuroprotective effects of micronized PEA (PEA-m) formulation on diabetic peripheral neuropathy in mice. Faseb j 33(10):11364–11380. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201900538R
D’Amico R, Impellizzeri D, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R (2020) ALIAmides update: palmitoylethanolamide and its formulations on management of peripheral neuropathic pain. Int J Mol Sci 21(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155330
Kaczmarek-Hájek K, Lörinczi E, Hausmann R, Nicke A (2012) Molecular and functional properties of P2X receptors—recent progress and persisting challenges. Purinergic Signal 8(3):375–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-012-9314-7
Khakh BS, North RA (2006) P2X receptors as cell-surface ATP sensors in health and disease. Nature 442(7102):527–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04886
Bleehen T, Keele CA (1977) Observations on the algogenic actions of adenosine compounds on the human blister base preparation. Pain 3(4):367–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(77)90066-5
Huang Z, Xie N, Illes P, Di Virgilio F, Ulrich H, Semyanov A, Verkhratsky A, Sperlagh B, Yu SG, Huang C, Tang Y (2021) From purines to purinergic signalling: molecular functions and human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):162. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00553-z
He YQ, Lang XQ, Lin L, Ji L, Yuan XY, Chen Q, Ran YM, Chen HS, Li L, Wang JM, Wang ZG, Gregersen H, Zou DW, Liang HP, Yang M (2017) P2X3 receptor-mediated visceral hyperalgesia and neuronal sensitization following exposure to PTSD-like stress in the dorsal root ganglia of rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil 29(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12976
Cook SP, Vulchanova L, Hargreaves KM, Elde R, McCleskey EW (1997) Distinct ATP receptors on pain-sensing and stretch-sensing neurons. Nature 387(6632):505–508. https://doi.org/10.1038/387505a0
D’Amico R, Fusco R, Siracusa R, Impellizzeri D, Peritore AF, Gugliandolo E, Interdonato L, Sforza AM, Crupi R, Cuzzocrea S, Genovese T, Cordaro M, Di Paola R (2021) Inhibition of P2X7 purinergic receptor ameliorates fibromyalgia syndrome by suppressing NLRP3 pathway. Int J Mol Sci 22(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126471
Fei X, He X, Tai Z, Wang H, Qu S, Chen L, Hu Q, Fang J, Jiang Y (2020) Electroacupuncture alleviates diabetic neuropathic pain in rats by suppressing P2X3 receptor expression in dorsal root ganglia. Purinergic Signal 16(4):491–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-020-09728-9
Zhou YF, Ying XM, He XF, Shou SY, Wei JJ, Tai ZX, Shao XM, Liang Y, Fang F, Fang JQ, Jiang YL (2018) Suppressing PKC-dependent membrane P2X3 receptor upregulation in dorsal root ganglia mediated electroacupuncture analgesia in rat painful diabetic neuropathy. Purinergic Signal 14(4):359–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-018-9617-4
Snyder MJ, Gibbs LM, Lindsay TJ (2016) Treating painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: an update. Am Fam Physician 94(3):227–234
Peltier A, Goutman SA, Callaghan BC (2014) Painful diabetic neuropathy Bmj 348:g1799. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g1799
Heo I, Shin BC, Cho JH, Ha IH, Hwang EH, Lee JH, Kim KW, Kim MR, Jung SY, Kwon O, Kim NK, Son DW, Shin KM (2021) Multicentre randomised controlled clinical trial of electroacupuncture with usual care for patients with non-acute pain after back surgery. Br J Anaesth 126(3):692–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2020.10.038
Arriaga-Pizano L, Gómez-Jiménez DC, Flores-Mejía LA, Pérez-Cervera Y, Solórzano-Mata CJ, López-Macías C, Isibasi A, Torres-Rosas R (2020) Low back pain in athletes can be controlled with acupuncture by a catecholaminergic pathway: clinical trial. Acupunct Med 38(6):388–395. https://doi.org/10.1177/0964528420912251
Huang CZ, Li YL, Lan XL, He B, Yang J, Li J (2021) [Electroacupuncture combined with acupoint catgut embedding for postoperative pain after fistulotomy]. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 46(5):421–425. https://doi.org/10.13702/j.1000-0607.200603
Lv ZT, Shen LL, Zhu B, Zhang ZQ, Ma CY, Huang GF, Yin J, Yu LL, Yu SY, Ding MQ, Li J, Yuan XC, He W, Jing XH, Li M (2019) Effects of intensity of electroacupuncture on chronic pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Res Ther 21(1):120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1899-6
Manni L, Florenzano F, Aloe L (2011) Electroacupuncture counteracts the development of thermal hyperalgesia and the alteration of nerve growth factor and sensory neuromodulators induced by streptozotocin in adult rats. Diabetologia 54(7):1900–1908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2117-5
Zhou DM, Zhuang Y, Chen WJ, Li W, Miao B (2018) Effects of duloxetine on the toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in spinal dorsal horn in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Pain Med 19(3):580–588. https://doi.org/10.1093/pm/pnx125
Wang F, Ma J, Han F, Guo X, Meng L, Sun Y, Jin C, Duan H, Li H, Peng Y (2016) DL-3-n-butylphthalide delays the onset and progression of diabetic cataract by inhibiting oxidative stress in rat diabetic model. Sci Rep 6:19396. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19396
Erbaş O, Oltulu F, Yılmaz M, Yavaşoğlu A, Taşkıran D (2016) Neuroprotective effects of chronic administration of levetiracetam in a rat model of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 114:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2015.12.016
Kolb H (1987) Mouse models of insulin dependent diabetes: low-dose streptozocin-induced diabetes and nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Diabetes Metab Rev 3(3):751–778. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmr.5610030308
Wang-Fischer Y, Garyantes T (2018) Improving the reliability and utility of streptozotocin-induced rat diabetic model. J Diabetes Res 2018:8054073. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8054073
Berger AA, Liu Y, Possoit H, Rogers AC, Moore W, Gress K, Cornett EM, Kaye AD, Imani F, Sadegi K, Varrassi G, Viswanath O, Urits I (2021) Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and chronic pain. Anesth Pain Med 11(2):e113020. https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.113020
Esposito MF, Malayil R, Hanes M, Deer T (2019) Unique characteristics of the dorsal root ganglion as a target for neuromodulation. Pain Med 20(Suppl 1):S23-s30. https://doi.org/10.1093/pm/pnz012
Zou Y, Yang R, Li L, Xu X, Liang S (2021) Purinergic signaling: a potential therapeutic target for depression and chronic pain. Purinergic Signal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-021-09801-x
Burnstock G (2017) Purinergic signalling: therapeutic developments Front Pharmacol 8:661. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00661
Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther 110(3):433–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.08.013
Zhang WJ, Zhu ZM, Liu ZX (2020) The role and pharmacological properties of the P2X7 receptor in neuropathic pain. Brain Res Bull 155:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.11.006
Duveau A, Bertin E, Boué-Grabot E (2020) Implication of neuronal versus microglial P2X4 receptors in central nervous system disorders. Neurosci Bull 36(11):1327–1343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-020-00570-y
Krajewski JL (2020) P2X3-containing receptors as targets for the treatment of chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics 17(3):826–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-020-00934-2
Oury C, Lecut C, Hego A, Wéra O, Delierneux C (2015) Purinergic control of inflammation and thrombosis: role of P2X1 receptors. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 13:106–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2014.11.008
Bardoni R, Goldstein PA, Lee CJ, Gu JG, MacDermott AB (1997) ATP P2X receptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 17(14):5297–5304. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.17-14-05297.1997
Zheng XB, Zhang YL, Li Q, Liu YG, Wang XD, Yang BL, Zhu GC, Zhou CF, Gao Y, Liu ZX (2019) Effects of 1,8-cineole on neuropathic pain mediated by P2X2 receptor in the spinal cord dorsal horn. Sci Rep 9(1):7909. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44282-4
Kobayashi K, Yamanaka H, Noguchi K (2013) Expression of ATP receptors in the rat dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord. Anat Sci Int 88(1):10–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-012-0163-9
Yuan H, Ouyang S, Yang R, Li S, Gong Y, Zou L, Jia T, Zhao S, Wu B, Yi Z, Liu H, Shi L, Li L, Gao Y, Li G, Xu H, Liu S, Zhang C, Liang S (2018) Osthole alleviated diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X(4) receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res Bull 142:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.08.008
Wang A, Shi X, Yu R, Qiao B, Yang R, Xu C (2021) The P2X(7) Receptor is involved in diabetic neuropathic pain hypersensitivity mediated by TRPV1 in the rat dorsal root ganglion. Front Mol Neurosci 14:663649. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2021.663649
Horvath RJ, DeLeo JA (2009) Morphine enhances microglial migration through modulation of P2X4 receptor signaling. J Neurosci 29(4):998–1005. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4595-08.2009
Xiao J, Huang Y, Li X, Li L, Yang T, Huang L, Yang L, Jiang H, Li H, Li F (2016) TNP-ATP is beneficial for treatment of neonatal hypoxia-induced hypomyelination and cognitive decline. Neurosci Bull 32(1):99–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-015-0003-8
Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S, Mizokoshi A, Kohsaka S, Salter MW, Inoue K (2003) P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 424(6950):778–783. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01786
Kasuya G, Yamaura T, Ma XB, Nakamura R, Takemoto M, Nagumo H, Tanaka E, Dohmae N, Nakane T, Yu Y, Ishitani R, Matsuzaki O, Hattori M, Nureki O (2017) Structural insights into the competitive inhibition of the ATP-gated P2X receptor channel. Nat Commun 8(1):876. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00887-9
Gao F, Xiang HC, Li HP, Jia M, Pan XL, Pan HL, Li M (2018) Electroacupuncture inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through CB2 receptors in inflammatory pain. Brain Behav Immun 67:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.004
Chen H, Liu TY, Kuai L, Zhu J, Wu CJ, Liu LM (2013) Electroacupuncture treatment for pancreatic cancer pain: a randomized controlled trial. Pancreatology 13(6):594–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2013.10.007
He JR, Yu SG, Tang Y, Illes P (2020) Purinergic signaling as a basis of acupuncture-induced analgesia. Purinergic Signal 16(3):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-020-09708-z
Tang Y, Yin HY, Rubini P, Illes P (2016) Acupuncture-induced analgesia: a neurobiological basis in purinergic signaling. Neuroscientist 22(6):563–578. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858416654453
Wang S, Du J, Shao F, Wang W, Sun H, Shao X, Liang Y, Liu B, Fang J, Fang J (2020) Electroacupuncture regulates pain transition by inhibiting the mGluR5-PKCε signaling pathway in the dorsal root ganglia. J Pain Res 13:1471–1483. https://doi.org/10.2147/jpr.s251948
Ali U, Apryani E, Wu HY, Mao XF, Liu H, Wang YX (2020) Low frequency electroacupuncture alleviates neuropathic pain by activation of spinal microglial IL-10/β-endorphin pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 125:109898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109898
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81804181 to X.F.H. and 81774389 to Y.L.J.), the National Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (202110344013), and the Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Neurology of Zhejiang Province (2019E10011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiao Fen He, Yongliang Jiang, and Jianqiao Fang conceived of and designed the experiments. Yurong Kang, Hanzhi Wang, and Siying Qu performed the animal experiments. Xiao Fen He, Hanzhi Wang, Siying Qu, and Xiang Li performed immunofluorescence. Luhang Chen, Liqian Ma, and Qunqi Hu performed WB and PCR. Boyu Liu, Yi Liang, Junfan Fang, and Xiaomei Shao analyzed the data. Qunqi Hu, Xiaofen He, and Yiqi Ma wrote the manuscripts. Qunqi Hu and Yiqi Ma participated in figures preparations. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China (Approval No. IACUC-20190805–04).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Qq., He, Xf., Ma, Yq. et al. Dorsal root ganglia P2X4 and P2X7 receptors contribute to diabetes-induced hyperalgesia and the downregulation of electroacupuncture on P2X4 and P2X7. Purinergic Signalling 19, 29–41 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-022-09844-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-022-09844-8