Abstract
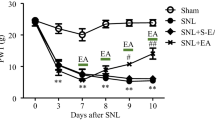
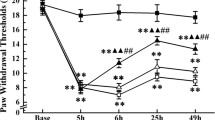
As an ancient analgesia therapy, acupuncture has been practiced worldwide nowadays. A good understanding of its mechanisms will offer a promise for its rational and wider application. As the first station of pain sensation, peripheral sensory ganglia express pain-related P2X receptors that are involved in the acupuncture analgesia mechanisms transduction pathway. While the role of their endogenous ligand, extracellular ATP (eATP), remains less studied. This work attempted to clarify whether acupuncture modulated eATP levels in the peripheral sensory nerve system during its analgesia process. Male Sprague–Dawley rats underwent acute inflammatory pain by injecting Complete Freund’s Adjuvant in the unilateral ankle joint for 2 days. A twenty-minute acupuncture was applied to ipsilateral Zusanli acupoint. Thermal hyperalgesia and tactile allodynia were assessed on bilateral hind paws to evaluate the analgesic effect. eATP of bilateral isolated lumbar 4-5 dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) and sciatic nerves were determined by luminescence assay. Nucleotidases NTPDase-2 and -3 in bilateral ganglia and sciatic nerves were measured by real-time PCR to explore eATP hydrolysis process. Our results revealed that acute inflammation induced bilateral thermal hyperalgesia and ipsilateral tactile allodynia, which were accompanied by increased eATP levels and higher mechano-sensitivity of bilateral DRGs and decreased eATP levels of bilateral sciatic nerves. Acupuncture exerted anti-nociception on bilateral hind paws, reversed the increased eATP and mechanosensitivity of bilateral DRGs, and restored the decreased eATP of bilateral sciatic nerves. NTPDase-2 and -3 in bilateral ganglia and sciatic nerves were inconsistently modulated during this period. These observations indicate that eATP metabolism of peripheral sensory nerve system was simultaneously regulated during acupuncture analgesia, which might open a new frontier for acupuncture research.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ADO:
-
Adenosine
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- AMP:
-
Adenosine monophosphate
- ARL67156:
-
6-N,N-Diethyl-β-γ-dibromomethylene-D-adenosine-5′-triphosphate
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CFA:
-
Complete Freund’s Adjuvant
- DRG:
-
Dorsal root ganglia
- EAP:
-
Electric acupuncture
- eATP:
-
Extracellular ATP
- exo-ATP:
-
Exogenous ATP
- L-L:
-
Luciferin-luciferase
- Nt5e:
-
Ecto-5′-nucleotidase
- NTPDases:
-
Nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolases
- P2 receptors:
-
Purinergic receptors
- PAP:
-
Prostatic acid phosphatase
- PS:
-
Physiological solution
- PWL:
-
Paw withdraw latency
- PWT:
-
Paw withdraw threshold
References
Gereau RW, Sluka KA, Maixner W, Savage SR, Price TJ, Murinson BB, Sullivan MD, Fillingim RB (2014) A pain research agenda for the 21st century. J Pain 15(12):1203–1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2014.09.004
Zhao ZQ (2008) Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 85(4):355–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.05.004
Tang Y, Yin HY, Liu J, Rubini P, Illes P (2019) P2x receptors and acupuncture analgesia. Brain Res Bull 151:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.10.015
Tang Y, Yin HY, Rubini P, Illes P (2016) Acupuncture-induced analgesia: a neurobiological basis in purinergic signaling. Neuroscientist 22(6):563–578. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858416654453
Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K (2010) Pain and purinergic signaling. Brain Res Rev 63(1-2):222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2009.11.003
Sawynok J (2016) Adenosine receptor targets for pain. Neuroscience 338:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.10.031
Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic p2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther 110(3):433–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.08.013
Barragán-Iglesias P, Mendoza-Garcés L, Pineda-Farias JB, Solano-Olivares V, Rodríguez-Silverio J, Flores-Murrieta FJ, Granados-Soto V, HIJPB R-G (2015) Participation of peripheral p2y1, p2y6 and p2y11 receptors in formalin-induced inflammatory pain in rats. Behavior 128:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2014.11.001
Burnstock G (2009) Acupuncture: a novel hypothesis for the involvement of purinergic signalling. Med Hypotheses 73(4):470–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2009.05.031 S0306-9877(09)00397-1 [pii]
Zheng YW, Wu MY, Shen XY, Wang LN (2020) Application of unrestrained conscious rats with acute inflammatory ankle pain to study of acupuncture analgesia. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 45(8):645–651. https://doi.org/10.13702/j.1000-0607.190703
Burkey TH, Hingtgen CM, Vasko MR (2004) Isolation and culture of sensory neurons from the dorsal-root ganglia of embryonic or adult rats. Methods Mol Med 99:189–202. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-770-X:189
Matsuka Y, Ono T, Iwase H, Mitrirattanakul S, Omoto KS, Cho T, Lam YY, Snyder B, Spigelman I (2008) Altered atp release and metabolism in dorsal root ganglia of neuropathic rats. Mol Pain 4:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-4-66
Shen D, Shen X, Schwarz W, Grygorczyk R, Wang L (2020) P2y13 and p2x7 receptors modulate mechanically induced adenosine triphosphate release from mast cells. Exp Dermatol 29(5):499–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.14093
Zhang X, Chen Y, Wang C, Huang LY (2007) Neuronal somatic atp release triggers neuron-satellite glial cell communication in dorsal root ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(23):9864–9869. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611048104
Fields RD (2011) Imaging single photons and intrinsic optical signals for studies of vesicular and non-vesicular atp release from axons. Front Neuroanat 5:11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2011.00032
Wang L, Hu L, Grygorczyk R, Shen X, Schwarz W (2015) Modulation of extracellular atp content of mast cells and drg neurons by irradiation: studies on underlying mechanism of low-level-laser therapy. Mediators Inflamm 2015:630361–630369. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/630361
Zimmermann H, Zebisch M, Strater N (2012) Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signalling 8(3):437–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-012-9309-4
Vongtau HO, Lavoie EG, Sévigny J, Molliver DC (2011) Distribution of ecto-nucleotidases in mouse sensory circuits suggests roles for nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-3 in nociception and mechanoreception. Neuroscience 193:387–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.044
Ma L, Thu T, Ren Y, Dirksen RT, Liu X (2016) Neuronal ntpdase3 mediates extracellular atp degradation in trigeminal nociceptive pathway. Plos One 11(10):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164028
Liu X, Yu L, Wang Q, Pelletier J, Fausther M, Sevigny J, Malmstrom HS, Dirksen RT, Ren Y-F (2012) Expression of ecto-atpase ntpdase2 in human dental pulp. J Dental Res 91(3):261–267. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034511431582
Niu X, Zhang M, Liu Z, Bai L, Sun C, Wang S, Wang X, Chen Z, Chen H, Tian J (2016) Interaction of acupuncture treatment and manipulation laterality modulated by the default mode network. Mol Pain 13:14. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806916683684
Lai H-C, Lin Y-W, Hsieh C-L (2019) Acupuncture-analgesia-mediated alleviation of central sensitization. Evid-Based Complement Alternat Med 2019:13–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6173412
Shenker N, Haigh R, Roberts E, Mapp P, Harris N, Blake D (2003) A review of contralateral responses to a unilateral inflammatory lesion. Rheumatology 42(11):1279–1286. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keg397
Shenker NG, Haigh RC, Mapp PI, Harris N, Blake DR (2008) Contralateral hyperalgesia and allodynia following intradermal capsaicin injection in man. Rheumatology 47(9):1417–1421. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ken251
Miura K, Ohara T, Zeredo JL, Okada Y, Toda K, Sumikawa K (2007) Effects of traditional "juci" (contralateral acupuncture) on orofacial nociceptive behavior in the rat. J Anesth 21(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-006-0443-4
Yan C-Q, Huo J-W, Wang X, Zhou P, Zhang Y-N, J-l L, Kim M, Shao J-K, Hu S-Q, Wang L-Q, Liu C-Z (2020) Different degree centrality changes in the brain after acupuncture on contralateral or ipsilateral acupoint in patients with chronic shoulder pain: a resting-state fmri study. Neural Plast 2020(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5701042
Todorov LD, Mihaylova-Todorova S, Westfall TD, Sneddon P, Kennedy C, Bjur RA, Westfall DP (1997) Neuronal release of soluble nucleotidases and their role in neurotransmitter inactivation. Nature 387(6628):76–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/387076a0
Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A, Zimmermann H (2009) Purinergic signalling in the nervous system: an overview. Trends Neurosci 32(1):19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2008.10.001
Tan H, Tumilty S, Chapple C, Liu L, McDonough S, Yin H, Yu S, Baxter GD (2019) Understanding acupoint sensitization: a narrative review on phenomena, potential mechanism, and clinical application. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019:6064358–6064359. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6064358
Bai F, Ma Y, Guo H, Li Y, Xu F, Zhang M, Dong H, Deng J, Xiong L (2019) Spinal cord glycine transporter 2 mediates bilateral st35 acupoints sensitization in rats with knee osteoarthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019:7493286–7493217. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7493286
Chen S, Miao Y, Nan Y, Wang Y, Zhao Q, He E, Sun Y, Zhao J (2015) The study of dynamic characteristic of acupoints based on the primary dysmenorrhea patients with the tenderness reflection on diji (sp 8). Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015:158012–158019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/158012
Gao YH, Li CW, Wang JY, Tan LH, Duanmu CL, Jing XH, Chang XR, Liu JL (2016) Effect of electroacupuncture on the cervicospinal p2x7 receptor/fractalkine/cx3cr1 signaling pathway in a rat neck-incision pain model. Purinergic Signalling 13(2):215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-016-9552-1
Braun N, Sevigny J, Robson SC, Hammer K, Hanani M, Zimmermann H (2004) Association of the ecto-atpase ntpdase2 with glial cells of the peripheral nervous system. Glia 45(2):124–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.10309
Hassan AHS, Ableitner A, Stein C, Herz A (1993) Inflammation of the rat paw enhances axonal-transport of opioid receptors in the sciatic-nerve and increases their density in the inflamed tissue. Neuroscience 55(1):185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(93)90465-r
Takano T, Chen X, Luo F, Fujita T, Ren Z, Goldman N, Zhao Y, Markman JD, Nedergaard M (2012) Traditional acupuncture triggers a local increase in adenosine in human subjects. J Pain 13(12):1215–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2012.09.012
Goldman N, Chen M, Fujita T, Xu Q, Peng W, Liu W, Jensen TK, Pei Y, Wang F, Han X, Chen JF, Schnermann J, Takano T, Bekar L, Tieu K, Nedergaard M (2010) Adenosine a1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat Neurosci 13(7):883–888. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2562
Huang M, Wang X, Xing B, Yang H, Sa Z, Zhang D, Yao W, Yin N, Xia Y, Ding G (2018) Critical roles of trpv2 channels, histamine h1 and adenosine a1 receptors in the initiation of acupoint signals for acupuncture analgesia. Sci Rep 8(1):6523–6533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24654-y
Sa Z-Y, Huang M, Zhang D, Ding G-H (2013) Relationship between regional mast cell activity and peripheral nerve discharges during manual acupuncture stimulation of “zusanli” (st 36). Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 38(2):118–122 CNKI:SUN:XCYJ.0.2013-02-010
Y-l Y, Tang J, Li L (2017) Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nerve growth factor, and growth-associated protein-43 in rats with sciatic nerve injury. J Anhui Tradit Chin Med College 4:51–55. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-7246.2017.04.016
Joseph SM, Buchakjian MR, Dubyak GR (2003) Colocalization of atp release sites and ecto-atpase activity at the extracellular surface of human astrocytes. J Biol Chem 278(26):23331–23342. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M302680200
Brisevac D, Adzic M, Laketa D, Parabucki A, Milosevic M, Lavrnja I, Bjelobaba I, Sevigny J, Kipp M, Nedeljkovic N (2015) Extracellular atp selectively upregulates ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 2 and ecto-5'-nucleotidase by rat cortical astrocytes in vitro. J Mol Neurosci 57(3):452–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0601-y
Zylka MJ, Sowa NA, Taylor-Blake B, Twomey MA, Herrala A, Voikar V, Vihko P (2008) Prostatic acid phosphatase is an ectonucleotidase and suppresses pain by generating adenosine. Neuron 60(1):111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.08.024
Sowa NA, Taylor-Blake B, Zylka MJ (2010) Ecto-5'-nucleotidase (cd73) inhibits nociception by hydrolyzing amp to adenosine in nociceptive circuits. J Neurosci 30(6):2235–2244. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5324-09.2010
Sowa NA, Voss MK, Zylka MJ (2010) Recombinant ecto-5′-nucleotidase (cd73) has long lasting antinociceptive effects that are dependent on adenosine a1 receptor activation. Mol Pain 6(20):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-6-20
Gerevich Z, Illes P (2004) P2y receptors and pain transmission. Purinergic Signalling 1(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-004-4740-9
Song XM, Xu XH, Zhu J, Guo Z, Li J, He C, Burnstock G, Yuan H, Xiang ZJPS (2015) Up-regulation of p2x7 receptors mediating proliferation of schwann cells after sciatic nerve injury. Purinergic Signalling 11(2):203–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9445-8
Zhang S, Wang X, Yan C-Q, Hu S-Q, Huo J-W, Wang Z-Y, Zhou P, Liu C-H, Liu C-Z (2018) Different mechanisms of contralateral- or ipsilateral-acupuncture to modulate the brain activity in patients with unilateral chronic shoulder pain: a pilot fmri study. J Pain Res 2018(11):505–514. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S152550
Hurt JK, Zylka MJ (2012) Papupuncture has localized and long-lasting antinociceptive effects in mouse models of acute and chronic pain. Mol Pain 8(28):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-8-28
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81574076, to L-N W, 8159950026 to D Z). We like to thank Prof. Ryszard Grygorczyk (Université de Montréal, Montreal, Canada) and Prof. Wolfgang Schwarz (Goethe-University, Frankfurt, Germany) for revising the paper.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81574076, to L-N W and 8159950026 to D Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization by Li-Na WANG and Xue-Yong SHEN; data collection by Dan SHEN and Ya-Wen ZHENG; data analysis by Dan SHEN; figure formation by Di ZHANG; data interpretation by Li-Na WANG; first manuscript writing by Dan SHEN; manuscript revision by Li-Na WANG and Xue-Yong SHEN. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Care Committee of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Shanghai, China) (No SZY201807008).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, D., Zheng, YW., Zhang, D. et al. Acupuncture modulates extracellular ATP levels in peripheral sensory nervous system during analgesia of ankle arthritis in rats. Purinergic Signalling 17, 411–424 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-021-09777-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-021-09777-8