Abstract
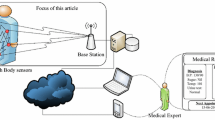
The emerging Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) has a great potential to strengthen health care sector, as it paves ways for the development of new services and applications. In making WBAN technically feasible, high Signal to Noise ratio (SNR) and low outage probability plays a vital role. In vivo communication is one where communication between living beings can be carried out wirelessly. It utilizes data gathered in real time for quick and accurate responses in emergency situations. To fully benefit from and further explore the potentiality of WBANs for realistic applications, it is critical to analyze the performance of in vivo WBAN communication over different frequency bands. Over the past many years, Medical Implant Communication System (MICS) band has extensively been used for implant medical applications and Terahertz (THz) band shows promising link capability to support increased data rates. In the proposed work, performance of an in vivo WBAN system, at MICS and Terahertz frequencies based upon IEEE 802.15.6 channel models (CM), CM1 and CM2 has been assessed. The effect of incorporating cooperative communication for in vivo WBAN is then presented to see how it enhances the network performance at both the bands. The impact on the system’s SNR and outage probability is investigated for number of relays. The outage behavior of amplify and forward cooperative communication with multiple relays is investigated over a Rayleigh fading channel. Results show considerable increase in the system SNR and decrease in outage probability with increase in number of relays, which strongly indicates the possibility of incorporating cooperative communication to elevate the performance of in vivo WBAN at both MICS and terahertz frequencies. Further, nature inspired optimization is done to reduce the outage probability. Results show that the projected technique surpasses the non-optimized technique and ensures favorable results. The results achieved at THz band have also been compared to that obtained at MICS band and it is demonstrated that better performance can be achieved at THz band by incorporating cooperative communication in the network.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demir, A. F., Ankarali, Z. E., Abbasi, Q. H., Liu, Y., Qaraqe, K., Serpedin, E., Arslan, H., & Gitlin, R. D. (2016). In vivo communications: Steps toward the next generation of implantable devices. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 11(2), 32–42. https://doi.org/10.1109/MVT.2016.2520492
Wang, J., Han, K., Chen, Z., Alexandridis, A., Zilic, Z., Pang, Y., & Lin, J. (2018). A software defined radio evaluation platform for WBAN systems. Sensors, 18(12), 4494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124494
Muzny, M., Henriksen, A., Giordanengo, A., Muzik, J., Grøttland, A., Blixgård, H., Gunnar, H., & Årsand, E. (2020). Wearable sensors with possibilities for data exchange: Analyzing status and needs of different actors in mobile health monitoring systems. International journal of medical informatics, 133, 104017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.104017
Elayan, H., Shubair, R. M., Almoosa, & N. (2018). In Vivo Communication in Wireless Body Area Networks. In Ismail L., Zhang L. (eds) Information innovation technology in smart cities. Springer, Singapore, pp. 273–287. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-1741-4_18.
Belaoura, W., Ghanem, K., Imran, M. A., Alomainy, A., & Abbasi, Q. H. (2020). A cooperative massive MIMO system for future in vivo nanonetworks. IEEE Systems Journal,, pp. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2020.2995671
Khan, J. Y., & Yuce, M. R. (2010). Wireless body area network (WBAN) for medical applications. InTechOpen.
Suriya, I., & Anbazhagan, R. (2019). Inverted-A based UWB MIMO antenna with triple-band notch and improved isolation for WBAN applications. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 99, 25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2018.11.030
Oh, J. Y., Kim, J. H., Lee, H. S., & Kim, J. Y. (2010). PSSK modulation scheme for high-data rate implantable medical devices. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 14(3), 634–640. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2009.2036255
Arif, A., Zubair, M., Ali, M., Khan, M. U., & Mehmood, M. Q. (2019). A compact, low-profile fractal antenna for wearable on-body WBAN applications. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 18(5), 981–985. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2019.2906829.
Pramanik, P. K. D., Nayyar, A., & Pareek, G. (2019). WBAN: Driving e-healthcare beyond telemedicine to remote health monitoring: architecture and protocols. In Telemedicine technologies, 89–119. Academic Press. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816948-3.00007-6.
Islam, M. N., & Yuce, M. R. (2016). Review of medical implant communication system (MICS) band and network. Ict Express, 2(4), 188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2016.08.010
Cho, N., Roh, T., Bae, J., & Yoo, H. J. (2009). A planar MICS band antenna combined with a body channel communication electrode for body sensor network. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 57(10), 2515–2522. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2009.2029952
Teshome, A. K., Kibret, B., & Lai, D. T. (2018). A review of implant communication technology in WBAN: Progress and challenges. IEEE reviews in biomedical engineering, 12, 88–99. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2018.2848228
Rubani, Q., Gupta, S. H., & Kumar, A. (2019). Design and analysis of circular patch antenna for WBAN at terahertz frequency. Optik, 185, 529–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.03.142
Zhao, L., Hao, Y. H., & Peng, R. Y. (2014). Advances in the biological effects of terahertz wave radiation. Military Medical Research, 1(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-014-0026-x
Abbasi, Q. H., Sallabi, H. E., Chopra, N., Yang, K., Qaraqe, K. A., & Alomainy, A. (2016). Terahertz channel characterization inside the human skin for nano-scale body-centric networks. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 6(3), 427–434. https://doi.org/10.1109/TTHZ.2016.2542213
Kaushik, M., Gupta, S. H., & Balyan, V. (2020). Power optimization of invivo sensor node operating at terahertz band using PSO. Optik, 202, 163530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163530
Jornet, J. M., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2011). Channel modeling and capacity analysis for electromagnetic wireless nanonetworks in the terahertz band. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communication, 10(10), 3211–3221. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2011.081011.100545
Elayan, H., Shubair, R. M., & Jornet, J. M. (2018). Characterizing THz propagation and intrabody thermal absorption in iWNSNs. IET Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation, 12(4), 525–532. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map.2017.0603
Torabi, M., Ajib, W., & Haccoun, D. (2009). Performance analysis of amplify-and-forward cooperative networks with relay selection over Rayleigh fading channels. In VTC Spring 2009-IEEE 69th Vehicular Technology Conference, pp. 1–5. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/VETECS.2009.507377
Akyildiz, I. F., Jornet, J. M., & Han, C. (2014). Terahertz band: Next frontier for wireless communications. Physical Communication, 12, 16–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2014.01.006
He, C., Liu, Y., Ketterl, T.P., Arrobo, G.E., & Gitlin, R.D. (2014). Performance evaluation for MIMO in vivo WBAN systems. In 2014 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on RF and Wireless Technologies for Biomedical and Healthcare Applications (IMWS-Bio2014),pp. 1–3. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IMWS-BIO.2014.7032380.
Monteiro, M.E., Rebelatto, J.L., & Brante, G. (2018). On the Energy Efficiency of Relay-Assisted In Vivo Nano-Networks Communications. In 2018 15th International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS),pp. 1–5. IEEE. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ISWCS.2018.8491066.
Zhou, Z., Zhou, S., Cui, S., & Cui, J. H. (2008). Energy-efficient cooperative communication in a clustered wireless sensor network. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(6), 3618–3628. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2008.918730
Sadek, A. K., Yu, W., & Liu, K. R. (2010). On the energy efficiency of cooperative communications in wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 6(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1145/1653760.1653765
Nosratinia, A., Hunter, T. E., & Hedayat, A. (2004). Cooperative communication in wireless networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 42(10), 74–80. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2004.1341264
Arora, N., Gupta, S. H., & Kumar, B. (2020). An approach to investigate the best location for the central node placement for energy efficient WBAN. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing,, pp. 1–12,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01847-w
Laneman, J. N., Tse, D. N., & Wornell, G. W. (2004). Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 50(12), 3062–3080. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.2004.838089
Yazdandoost, K., & Sayrafian, K. (2009). Channel model for body area network (BAN). IEEE p802. 15–08–0780–09–0006. IEEE 802.15 Working Group Document.
Dombrowski, C., & Gross, J. (2011). Reducing outage probability over wireless channels under hard real-time constraints. In proceedings of the 1st workshop on real-time wireless for industrial applications (Real Win).
Lüttge, U., & Souza, G. M. (2019). The Golden Section and beauty in nature: The perfection of symmetry and the charm of asymmetry. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 146, 98–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2018.12.008
Nematollahi, A. F., Rahiminejad, A., & Vahidi, B. (2020). A novel meta-heuristic optimization method based on golden ratio in nature. Soft Computing, 24(2), 1117–1151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03949-w
Rathee, D., Rangi, S., Chakarvarti, S. K., & Singh, V. R. (2014). Recent trends in wireless body area network (WBAN) research and cognition based adaptive WBAN architecture for healthcare. Health and Technology, 4(3), 239–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12553-014-0083-x
Hammood, D. A., Rahim, H. A., Ahmad, R. B., Alkhayyat, A., Salleh, M. E. M., Abdulmalek, M., Jusoh, M., & Abbasi, Q. H. (2018). Enhancement of the duty cycle cooperative medium access control for wireless body area networks. IEEE Access, 7, 3348–3359. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2886291
Zhou, X., Zhang, T., Song, L., & Zhang, Q. (2014). Energy efficiency optimization by resource allocation in wireless body area networks. In 2014 IEEE 79th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Seoul, PP. 1–6. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/VTCSpring.2014.7022907.
Huang, L., Yao, X., & Wang, W. (2017). Eoc: Energy optimization coding for wireless nanosensor networks in the terahertz band. IEEE Access, 5, 2583–2590. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2665487
Elayan, H., Shubair, R.M., Alomainy, A., Yang, K. (2016). In vivo terahertz EM channel characterization for nano-communications in WBANs. In 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), pp. 979–980. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/APS.2016.7696198
Nguyen, V., & Kim, B. K. (2016). Performance analysis of amplify-and-forward systems with single relay selection in correlated environments. Sensors, 16(9), 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091472
Nasaruddin, N., Yusnidar, Y. (2017). Performance Evaluation of Amplify-Quantize and Forward Protocol for Multi-relay Cooperative Networks. ECTI Transactions on Electrical Engineering, Electronics, and Communications, 15(1), 8–18. https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ECTI-EEC/article/view/171272
Gupta, S. H., Singh, R. K., & Sharan, S. N. (2016). An approach to implement PSO to optimize outage probability of coded cooperative communication with multiple relays. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 55(3), 2805–2810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2016.07.018
Waheed, M., Ahmad, R., Ahmed, W., Drieberg, M., & Alam, M. M. (2018). Towards efficient wireless body area network using two-way relay cooperation. Sensors, 18(2), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020565
Liao, Y., Leeson, M.S., & Higgins, M.D. (2015). An in-body communication link based on 400 MHz MICS band wireless body area networks. In 2015 IEEE 20th International Workshop on Computer Aided Modelling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), Guildford, pp. 152–155. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CAMAD.2015.7390499.
Katircioğlu, O., Isel, H., Ceylan, O., Taraktas, F., & Yagci, H.B., (2011). Comparing ray tracing, free space path loss and logarithmic distance path loss models in success of indoor localization with RSSI. In 2011 IEEE 19thTelecommunications Forum (TELFOR) Proceedings of Papers, Belgrade, pp. 313–316. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TELFOR.2011.6143552.
Elayan, H., Shubair, R.M., & Almoosa, N. (2018). In vivo communication in wireless body area networks. In Information Innovation Technology in Smart Cities, pp. 273–287. Singapore: Springer. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-1741-4_18.
Sebastian, M. T., Ubic, R., & Jantunen, H. (Eds.). (2017). Microwave materials and applications. John Wiley & Sons.
Abbasi, Q. H., Nasir, A. A., Yang, K., Qaraqe, K. A., & Alomainy, A. (2017). Cooperative in vivo nano-network communication at terahertz frequencies. IEEE Access, 5, 8642–8647. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2677498
Henein, M. Y., Zhao, Y., Nicoll, R., Sun, L., Khir, A. W., Franklin, K., Lindqvist, P., & Collaborators, G. R. (2011). The human heart: Application of the golden ratio and angle. International Journal of Cardiology, 150(3), 239–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.05.094
Delgado, J. A. V., & Mera, C. A. V. (2013). A bio-inspired patch antenna array using fibonacci sequences in trees [education column]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 55(5), 192–201. https://doi.org/10.1109/MAP.2013.6735514
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This manuscript does not contain any study performed with humans or animals by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, N., Gupta, S.H. & Kumar, B. Analyzing and Optimizing Cooperative Communication for in Vivo WBAN. Wireless Pers Commun 122, 429–450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08906-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08906-1