Abstract
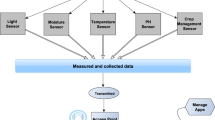
The wireless sensor network is one of the promising technologies in the agriculture field. Its actual usage in real agriculture fields is limited by its dependence on the small batteries which cannot make the network survive for long. Various protocols are being designed at the network and MAC layer to increase the lifetime of the nodes, but up to a certain extent only. Hence the energy harvesting to power up the WSN nodes is a promising technology to fulfill this ever energy demand, but the protocols need to be redesigned for this scenario. Solar energy harvesting based MAC protocol which is adaptive to the changing weather conditions is designed in this paper for the smart agriculture applications. It is based on the multilayer and receiver-initiated process to improve network quality. It has shown the remarkable performance over the other energy harvesting based protocols in terms of ENO ratio, energy consumption and collision rate.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodriguez de la Concepcion, A., Stefanelli, R., & Trinchero, D. (2014). A wireless sensor network platform optimized for assisted sustainable agriculture. In IEEE global humanitarian technology conference (GHTC 2014) (pp. 159–165).
Sakthipriya, N. (2014). An effective method for crop monitoring using wireless sensor network. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research,20(9), 1127–1132.
Kaur, P., Sohi, B. S., & Singh, P. (2019). Recent advances in MAC protocols for the energy harvesting based WSN: A comprehensive review. Wireless Personal Communications,104(1), 423–440.
Kaur, P., Singh, P., & Sohi, B. S. (2019). Traffic models for energy harvesting based wireless sensor networks. Recent Advances in Electrical and Electronic Engineering,12, 1–8.
Barker, S., Brennan, D., Wright, N. G., & Horsfall, A. B. (2011). Piezoelectric-powered wireless sensor system with regenerative transmit mode. IET Wireless Sensor Systems,1(1), 31–38.
Sharma, H., Haque, A., & Jaffery, Z. A. (2018). Solar energy harvesting wireless sensor network nodes: A survey. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy,10(2), 023704.
Galmés, S. (2018). Analytical model for the duty cycle in solar-based EH-WSN for environmental monitoring. Sensors,18(1), 1–32.
Kochhar, A., et al. (2018). Protocols for wireless sensor networks: A survey. Journal of Telecommunications and Information Technology,7, 18. https://doi.org/10.26636/jtit.2018.117417.
Hasenfratz, D., Meier, A., Moser, C., Chen, J.-J., & Thiele, L. (2010). Analysis, comparison, and optimization of routing protocols for energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. In IEEE international conference on sensor networks, ubiquitous, and trustworthy computing (pp. 19–26).
Zhang, P., Xiao, G., & Tan, H. P. (2013). Clustering algorithms for maximizing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks with energy-harvesting sensors. Computer Networks,57(14), 2689–2704.
Tan, L. T., & Le, L. B. (2016). Joint data compression and MAC protocol design for smartgrids with renewable energy. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing,16(16), 2590–2604.
Chen, Z., Peng, Y., & Yue, W. (2015). Modeling and analyzing CSMA/CA protocol for energy-harvesting wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,11, 257157.
Adu-manu, K. S., Adam, N., Tapparello, C., Ayatollahi, H., & Heinzelman, W. (2018). Energy-harvesting wireless sensor networks (EH-WSNs): A review. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks,14(2), 50.
Lin, E. A., Rabaey, J. M., & Wolisz, A. (2004). Power-efficient rendez-vous schemes for dense wireless sensor networks. In IEEE communications society (pp. 3769–3776).
Sun, Y., Gurewitz, O., & Johnson, D. B. (2008). RI-MAC : A receiver-initiated asynchronous duty cycle MAC protocol for dynamic traffic loads in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM conference on embedded network sensor systems (pp. 1–14). ACM.
Yong, Y., Chow, C., Kanesan, J., & Ishii, H. (2011). EE-RI-MAC: An energy-efficient receiver-initiated asynchronous duty cycle MAC protocol for dynamic traffic loads in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Physical Sciences,6(11), 2633–2643.
Eu, Z. A., Tan, H.-P., & Seah, W. K. G. (2011). Design and performance analysis of MAC schemes for wireless sensor networks powered by ambient energy harvesting. Ad Hoc Networks,9(3), 300–323.
Lohier, S., Rachedi, A., Livolant, E., & Salhi, I. (2011). Wireless sensor network simulators relevance compared to a real IEEE 802.15.4 testbed. In Wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC), IEEE 7th international (pp. 1347–1352).
Eu, Z. A., & Tan, H. P. (2012). Probabilistic polling for multi-hop energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. In 2012 IEEE international conference on communication (pp. 271–275).
Fujii, C., & Seah, W. K. G. (2011). Multi-tier probabilistic polling in Wireless Sensor Networks powered by energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2011 7th international conference on intelligent sensors, sensor networks and information processing ISSNIP 2011 (pp. 383–388).
Nguyen, K., Nguyen, V., Le, D., Ji, Y., Duong, D. A., & Yamada, S. (2014). ERI-MAC : An energy-harvested receiver-initiated MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,10, 514169.
Kaur, P., Singh, P., & Sohi, B. S. (2019). Hybrid multilayer receiver based MAC protocol for green wireless sensor networks. In 2019 IEEE international conference on electrical, computer and communication technologies (ICECCT). New York: IEEE.
Jha, M. K., Pandey, A. K., Pal, D., & Mohan, A. (2011). An energy-efficient multi-layer MAC (ML-MAC) protocol for wireless sensor networks. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 65(3), 209–216.
Fafoutis, X., & Dragoni, N. (2011). ODMAC : An on-demand MAC protocol for energy harvesting—Wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of 8th ACM symposium on performance evaluation of wireless ad hoc, sensor, ubiquitous networks (pp. 49–56).
Fafoutis, X., & Dragoni, N. (2012). Analytical comparison of MAC schemes for energy harvesting—Wireless sensor networks. In International conference on networked sensing (INSS) (pp. 1–6).
Ti. (2013). eZ430-RF2500-SEH user’s guide. No. 20/05/2014.
Nayyar, Anand, & Singh, Rajeshwar. (2015). A comprehensive review of simulation tools for wireless sensor networks (WSNs). Journal of Wireless Networking and Communications,5(1), 19–47.
Dall’Ora, R., Raza, U., Brunelli, D., & Pietro Picco, G. (2014). SensEH: From simulation to deployment of energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 39th annual IEEE conference on local computer networks work (pp. 566–573).
Kosunalp, S. (2016). A performance evaluation of solar energy prediction approaches for energy-harvesting wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Applied Mathematics, Electronics and Computers,4, 424–427.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, P., Singh, P. & Sohi, B.S. Adaptive MAC Protocol for Solar Energy Harvesting Based Wireless Sensor Networks in Agriculture. Wireless Pers Commun 111, 2263–2285 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06985-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06985-9