Abstract
The IEEE 802.15.6 slotted Aloha based protocol for wireless body area network includes contention based medium access control to accommodate heterogeneous body sensor nodes. Current protocol has been designed to handle incoming packets from sensors having different priorities but per class throughput degrades as the number of competing nodes increases. An improved algorithm is suggested to handle not only the throughput issue but also the starvation issue in saturated conditions. Simulation results validates the suggested algorithm.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
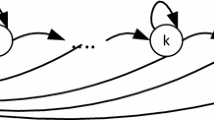
More precisely, it moves to \(k+1\) only if there were two consecutive failures. It stays in the current state if idle or if it has the first transmission failure.
Of course, the node moves back to state 0 if it succeeds in transmission
In this case we have only one node per class, so throughput sum becomes a throughput of a node
The CPmin values in Table 3 show slight changes among different priority classes, however these small changes in CPmin do not affect the resulting throughput since they are all sufficiently low and the changes among them are negligible. In fact, we could use the same low CPmin, such as \(10^{-6}\), for all classes and get the similar result.
We show \(smax+smin\) instead of smax to explicitly show the total throughput.
\(\beta\) = 1.0 means we don’t do occasional increment of CP.
References
Baek, Y. M, Lee, B. H., Li, J., Shu, Q., Han, J. H., & Han, K. J. (2009). An adaptive rate control for congestion avoidance in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Cyber-Enabled Distributed Computer Knowledge Discovery (pp. 1–4).
Chiti, F., Fantacci, R., & Lappoli, S. (2010). Contention delay minimization in wireless body sensor networks: A game theoretic perspective. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Telecommunication Conference (pp. 1–6).
Chowdhury, M. S., Ashrafuzzaman, K., & Kwak, K. S. (2014). Modeling IEEE 802.15.6 slotted Aloha in heterogeneous condition. Electronics Letters, 50(5), 415–416.
Fatehy, M., & Kohno, R. (2014). A novel contention probability dynamism for IEEE 802.15.6 standard. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2014, 92. doi:10.1186/1687-1499-2014-92.
Kahsay, L., Paso T., & Iinatti, J. (2013). Evaluation of IEEE 802.15.6 MAC user priorities with UWB PHY for medical application. In International Symposium in Medical Information and Communication Technology.
Kar, K., Sarkar, S., & Tassiulas, L. (2004). Achieving proportional fairness using local information in Aloha networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 49(10), 1858–1862.
Karim, L., Nasser, N., Taleb, T., & Alqallaf, A. (2012). An efficient priority packet scheduling algorithm for wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communication (pp. 334–338).
Kim, B., & Cho, J. (2012). A novel priority-based channel access algorithm for contention-based MAC Protocol in WBANs. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication, Kuala Lumpur, 20–22 Feb 2012.
Michopoulos, V., Guan, L., & Phillips, I. (2010). A new congestion control mechanism for WSNs. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Information Technology (pp. 709–714).
Misra, S., Oommen, B. J., Yanamandra, S., & Obaidat, M. S. (2010). Random early detection for congestion avoidance in wired networks: The discretized pursuit learning-automata-like solution. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B, 40(1), 66–76.
Misra, S., & Sarkar, S. (2015). Priority-based time-slot allocation in wireless body area networks during medical emergency situations: An evolutionary game-theoretic perspective. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 19, 541–548.
(2012). Part 15.6: Wireless body area networks. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks, IEEE Standard 802.15.6.
Rashwand, S., Misic, J., & Khazaei, H. (2011). Performance analysis of IEEE 802.15. 6 under saturation condition and error-prone channel. In IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Mexico (pp. 1167–1172).
Samanta, A., Bera, S., & Misra, S. (2015). Link-quality-aware resource allocation with load balance in wireless body area networks. IEEE Systems Journal, PP(99), 1–8. doi:10.1109/JSYST.2015.2458586.
Wang, D., Comaniciu, C., & Tureli, U. (2007). Cooperation and fairness for slotted aloha. Wireless Personal Communications, 43(1), 13–27.
Yi, C., Alfa, A. S., & Cai, J. (2015). An incentive-compatible mechanism for transmission scheduling of delay-sensitive medical packets in e-health networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 1–13.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Inha University Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, J., Kim, J. & Kim, K. Beta-Decrement of Contention Probability to Enhance Both Fairness and Throughput in IEEE 802.15.6 Slotted Aloha Algorithm. Wireless Pers Commun 97, 2053–2067 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4595-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4595-3