Abstract
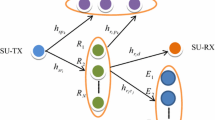
In this paper, we study the secure communication of dual-hop cognitive relaying networks. An eavesdropper can combine two received signals from two hops by using the maximum ratio combining technique. The data transmission from the secondary source to the secondary destination is assisted by the best decode-and-forward relay, which is selected from four relay selection schemes. The first scheme, MaSR, is based on the maximum channel gain from the source to the relays. In the second scheme, MaRD, the best relay is selected on the basis of the maximum channel gain from the relays to the destination. In the third scheme, MiRE, the gain to the eavesdroppers is instead minimized. Finally, optimal relay selection is considered as the fourth scheme. For these four schemes, we study the system security performance by deriving the exact analytical secrecy outage probability. These analytical expressions are then verified by comparing them with the results of Monte Carlo simulations. Herein, we evaluate and discuss the outage performance of the schemes while varying important system parameters: the number and locations of the relay nodes, primary user node, and eavesdropper; the transmit power threshold; and the target secure rate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shannon, C. E. (1949). Communication theory of secrecy systems. Bell System Technical Journal, 28(4), 646–715.
Silva, E. D., Santos, A. L. D., Albini, L. C. P., & Lima, M. N. (2008). Identity-based key management in mobile ad hoc networks: Schemes and applications. IEEE Wireless Communications, 15(5), 46–52.
Wyner, A. D. (1975). The wire-tap channel. The Bell System Technical Journal, 54(8), 1355–1387.
Leung-Yan-Cheong, S., & Hellman, M. (1978). The Gaussian wire-tap channel. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 24(4), 451–456.
Csiszar, I., & Korner, J. (1978). Broadcast channels with confidential messages. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 24(3), 339–348.
Liang, Y., Poor, H. V., & Shamai, S. (2008). Secure Communication Over Fading Channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(6), 2470–2492.
Barros, J., & Rodrigues, M. (2006). Secrecy capacity of wireless channels. In Proceedings of IEEE ISIT (pp. 356–360).
Bloch, M., Barros, J., Rodrigues, M. R. D., & McLaughlin, S. W. (2008). Wireless information-theoretic security. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(6), 2515–2534.
Nosratinia, A., Hunter, T. E., & Hedayat, A. (2004). Cooperative communication in wireless networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 42(10), 74–80.
Laneman, J. N., Tse, D. N. C., & Wornell, G. W. (2004). Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 50(12), 3062–3080.
Dong, L., Han, Z., Petropulu, A. P., & Poor, H. V. (2010). Improving wireless physical layer security via cooperating relays. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 58(3), 1875–1888.
Wang, L., Kim, K. J., Duong, T. Q., Elkashlan, M., & Poor, H. V. (2014). On the security of cooperative single carrier systems. In Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM (pp. 1956–1601).
Fan, L., Lei, X., Duong, T. Q., Elkashlan, M., & Karagiannidis, G. K. (2014). Secure multiuser communications in multiple amplify-and-forward relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 62(9), 3299–3310.
Lee, J.-H. (2015). Cooperative relaying protocol for improving physical layer security in wireless decode-and-forward relaying networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 83(4), 3033–3044.
Fan, L., Yang, N., Duong, T. Q., Elkashlan, M., & Karagiannidis, G. K. (2016). Exploiting direct links for physical layer security in multi-user multi-relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(6), 3856–3867.
Akyildiz, L. F., Lee, W. Y., Vuran, M. C., & Mohanty, S. (2008). A survey on spectrum management in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 46(4), 40–48.
Duong, T. Q., Costa, D. B., Tsiftsis, T. A., Zhong, C., & Nallanathan, A. (2012). Outage and diversity of cognitive relaying systems under spectrum sharing environments in Nakagami-m fading. IEEE Communications Letters, 16(12), 2075–2078.
Najafi, M., Ardebilipour, M., Nasab, E. S., & Vahidian, S. (2015). Multi-hop cooperative communication technique for cognitive DF and AF relay networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 83(4), 3209–3221.
Zhang, Q., Feng, Z., Yang, T., & Li, W. (2015). Optimal power allocation and relay selection in multi-hop cognitive relay networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 86(3), 1673–1692.
Duong, T. Q., Duy, T. T., Elkashlan, M., Tran, N. H., & Dobre, O. A. (2014). Secured cooperative cognitive radio networks with relay selection. In Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM (pp. 3074–3079).
Liu, Y., Wang, L., Duy, T. T., Elkashlan, M., & Duong, T. Q. (2015). Relay selection for security enhancement in cognitive relay networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 4(1), 46–49.
Gradshteyn, I. S., & Ryzhik, I. M. (2007). Table of integrals, series, and products (7th ed.). Waltham: Academic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1: Proof of Lemma 1
Appendix 1: Proof of Lemma 1
By setting \(u = {\lambda _2}\theta \frac{{{x_3}}}{{{x_5}}}\), the integral \({I_1}\) can be rewritten by:
Using equation 3.382.4 in [22] (\(\int _0^\infty {{{\left( {x + \beta } \right) }^v}{e^{ - \mu x}}dx} = {\mu ^{ - v - 1}}{e^{\beta \mu }}\Gamma \left( {v + 1,\beta \mu } \right)\)), we obtain:
This finishes the proof.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, S.Q., Kong, H.Y. Exact Outage Probability Analysis of a Dual-Hop Cognitive Relaying Network Under the Overhearing of an Active Eavesdropper. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 2271–2288 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4297-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4297-x