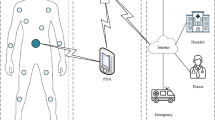
Abstract
Loss in communication due to lack of power is to be avoided in Wireless Body Sensor Network (WBSN). Fault tolerant strategy adapts scheduling of sensors and choosing a fault tolerant path caused by fault due to lack of energy in the network. The Fail Safe Fault Tolerant (FSFT) serves as a solution to HOT SPOT in the WBSN. The lifetime enhancement of FSFT is made possible by classifying the data packets based on the state of the subject, scheduling the sensors connected to Human body and based on the residual energy of the node. Markovian model helps in prediction the state of the subject and scheduling the wearable body sensors. Simulation results shows that the proposed algorithm increases the lifetime of the network approximately 40 % and increases the throughput of the network by 120 %. FSFT decreases the HOT SPOT and Energy Hole problem providing a fail safe mechanism to the system.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanagachidambaresan, G. R., SarmaDhulipala, V.R., Vanusha, D., & Udhaya, M. S. (2011). Matlab based modelling of body sensor network using ZigBee protocol. In CIIT 2011, CCIS 250 (pp. 773–776).
Akyildiz, I. F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., & Cayirci, E. (2002). Wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks. , 38, 393–422. doi:10.1016/S1389-1286(01)00302-4.
Kanagachidambaresan, G. R., SarmaDhulipala, V. R., & Udhayaa, M. S. (2012). Markovian model based trustworthy architecture ICCTSD 2012 procedia engineering.
SarmaDhulipala, V. R., Kanagachidambaresan, G. R., & Chandrasekaran, R. M. (2012). Lack of power avoidance: A fault classification based fault tolerant framework solution for lifetime enhancement and reliable communication in wireless sensor network. Information Technology Journal, 11(6), doi:10.3923/itj.2012.719.724.
Ameen, M. A., Nessa A., & Kwak, K. S. (2008). QoS issues with focus on wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of ICCIT08: the 2008 third international conference on convergence and hybrid information technology, Washington, DC, USA (pp. 801–807).
Razzaque, M. A., Hong, C. S., & Lee, S. (2011). Data-centric muliobjective Qos-aware routing protocol for body sensor networks. Sensors, 917–937. doi:10.3390/s110100917.
Otal, B., Alonso, L., & Verikoukis, C. (2008). Novel QoS scheduling and energy-saving MAC protocol for body sensor networks optimization. In Proceedings of the ICST 3rd international conference on body area networks, Tempe, AZ, USA (pp. 1–4).
Kuryloski, P., Giani, A., Giannantonio, R., Gilani, K., Gravina, R., Seppa, V. P., Seto, E., Shia, V., Wang, C., Yan, P., Yang, A. Y., Hyttinen, J., Sastry, S., Wicker, S., & Bajcsy, R. (2009). DexterNet: An open platform for heterogeneous body sensor networks and its applications. In International workshop on wearable and implantable body sensor networks, Berkeley, CA, USA (pp. 92–97).
Otal, B., Alonso, L., & Verikoukis, C. (2009). Highly reliable energy-saving MAC for wireless body sensor networks in healthcare systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 27, 553–565.
Zhou, G., Lu, J., Wan, C. Y., Yarvis, M., & Stankovic, J. (2008). BodyQoS: Adaptive and radio-agnostic QoS for body sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 27th conference on computer communications, Phoenix, AZ, USA (pp. 565–573).
Otal, B., Verikoukis, C., & Alonso, L. (2009). Fuzzy-logic scheduling for highly reliable and energy-efficient medical body sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications workshops, Dresden, Germany (pp. 1–5).
Natarajan, A., Motani, M., de Silva, B., Yap, K., & Chua, K. (2007). Investigating network architectures for body sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM SIGMOBILE international workshop on systems and networking support for healthcare and assisted living environments (HealthNet 2007), San Juan, Puerto Rico (pp. 19–24).
De Silva, B., Natarajan, A., & Motani, M. (2009). Inter-user interference in body sensor networks: Preliminary investigation and an infrastructure-based solution. In Proceedings of the sixth international workshop on wearable and implantable body sensor networks (BSN 2009), Berkeley, CA, USA (pp. 35–40).
Braem, B., Latre, B., Blondia, C., Moerman, I., & Demeester, P. (2008). Improving reliability in multi-hop body sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2008 second international conference on sensor technologies and applications, Cap Esterel, France (pp. 342–347).
Braem, B., Latre, B., Blondia, C., Moerman, I., & Demeester, P. (2009). Analyzing and improving reliability in multi-hop body sensor networks. International Journal on Advances in Internet Technology, 2, 152–161.
Qiao, Y., Yan, X., Matthews, A., Fallon, E., Hanley, A., Hay, G., & Kearney, K. (2007). Handover strategies in multi-homed body sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2007 information technology and telecommunications conference, Dublin, Ireland (pp. 183–189).
Linz, T., von Krshiwoblozki, M., & Walter, H. (2010). Novel packaging technology for body sensor networks based on adhesive bonding. In Proceedings of the 2010 international conference on body sensor networks, Biopolis, Singapore (pp. 308–314).
Ali, M. S., Dey, T. & Diswas, R. (2008). ALEACH: Advanced leach routing protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the IECE 2008 (Vols. 1 and 2, pp. 909–914). doi:10.1109/ICECE.2008.476934.
Chen, M., Gonzalez, S., Vasilakos, A., Cao, H., & Leung, C. C. M. (2011). Body area networks: A survey. Mobile Networks and Applications. doi:10.107/s11036-010-0260-8.
Custodio, V., Herrera, F. J., Lopez, G., & Moreno, J. I. (2012). A review on architectures and communication technologies for wearable health monitoring system. Sensors, 13907–13946. doi:10.3390/s121013907.
Hughes, L., Wang, X., & Chen, T. (2012). A review of protocol implementation and energy efficient cross layer design for wireless body area networks. Sensors, 14730–14773. doi:10.3390/s121114730.
Jiang, C. J., Shi, W. R., Xiang, M., & Tang, X. L. (2010). Energy balanced unequal clustering protocol for wireless sensor network. Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunication, 17, 94–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanagachidambaresan, G.R., Chitra, A. Fail Safe Fault Tolerant Mechanism for Wireless Body Sensor Network (WBSN) . Wireless Pers Commun 80, 247–260 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2006-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2006-6