Abstract
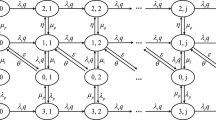
Cognitive radio networks (CRNs) offer a promising solution for improving spectrum utilization. However, ensuring quality of service (QoS) for heterogeneous secondary users (SUs) during spectrum handoff, particularly under high primary network traffic, poses challenges. This study develops a Markov-based analytical model to evaluate the gain of a non-switching spectrum handoff technique using a hybrid interweave-underlay spectrum access strategy, considering sensing errors. The proposed model assesses the effects of the hybrid spectrum access method for prioritized traffic across multiple SU classes, aiming to meet QoS requirements for delay-sensitive traffic. The study examines the CRN’s short-term behavior and realistic queueing scenarios by analyzing the system’s transient dynamics. Different spectrum access methods are compared for evaluation purposes. The analysis focuses on evaluating the effectiveness of the enhanced hybrid spectrum access scheme compared to individual interweave and hybrid interweave-underlay spectrum access strategies in terms of QoS provisioning for heterogeneous SUs. The results demonstrate increased throughput and improved spectrum utilization with the suggested scheme, affirming its suitability for satisfying QoS requirements for both delay-sensitive and delay-tolerant users.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 April 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-024-03746-w
References
Amjad, M., Rehmani, M. H., & Mao, S. (2018). Wireless multimedia cognitive radio networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 20(2), 1056–1103.
Paramita, S., Bebartta, H.N.D., & Pattanayak, P. (2021). IoT based healthcare monitoring system using 5G communication and machine learning models. In: Patgiri, R. Biswas, A. Roy, P. (eds) Health informatics: A computational perspective in healthcare (Vol. 932, pp. 159–182), Springer.
Aijaz, A., & Aghvami, A. H. (2015). Cognitive machine-to-machine communications for internet-of-things: A protocol stack perspective. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2(2), 103–112.
Somov, A., Dupont, C., & Giaffreda, R. (2013). Supporting smart-city mobility with cognitive Internet of Things. In 2013 Future Network & Mobile Summit, pp. 1–10.
Khasawneh, M., Azab, A., Alrabaee, S., Sakkal, H., & Bakhit, H. H. (2023). Convergence of IoT and cognitive radio networks: A survey of applications, techniques, and challenges. IEEE Access, 11, 71097–71112.
Liang, Y.-C., Zeng, Y., Peh, E. C. Y., & Hoang, A. T. (2008). Sensing-throughput tradeoff for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(4), 1326–1337.
El Tanab, M., & Hamouda, W. (2017). Resource allocation for underlay cognitive radio networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 19(2), 1249–1276.
Zheng, K., Jia, X., Chi, K., & Liu, X. (2023). DDPG-based joint time and energy management in ambient backscatter-assisted hybrid underlay CRNs. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 71(1), 441–456.
Shakeel, A., Hussain, R., Iqbal, A., Khan, I. L., Hasan, Q. U., & Malik, S. A. (2019). Analysis of efficient spectrum handoff in a multi-class hybrid spectrum access cognitive radio network using Markov modelling. Sensors, 19(19), 4120.
Iqbal, A., Hussain, R., Shakeel, A., Khan, I. L., Javed, M. A., Hasan, Q. U., Lee, B. M., & Malik, S. A. (2021). Enhanced spectrum access for QoS provisioning in multi-class cognitive D2D communication system. IEEE Access, 9, 33608–33624.
Thakur, P., Kumar, A., Pandit, S., Singh, G., & Satashia, S. N. (2018). Performance analysis of high-traffic cognitive radio communication system using hybrid spectrum access, prediction and monitoring techniques. Wireless Networks, 24(6), 2005–2015.
Chu, T. M. C., & Zepernick, H.-J. (2018). Optimal power allocation for hybrid cognitive cooperative radio networks with imperfect spectrum sensing. IEEE Access, 6, 10365–10380.
Balapuwaduge, I. A. M., Li, F. Y., & Pla, V. (2018). Dynamic spectrum reservation for CR networks in the presence of channel Failures: Channel allocation and reliability analysis. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 17(2), 882–898.
Khan, A. U., Abbas, G., Abbas, Z. H., Baker, T., Waqas, M. (2020). Spectrum efficiency in CRNs using hybrid dynamic channel reservation and enhanced dynamic spectrum access. Ad Hoc Networks, 107, 102246.
Khan, A. U., Abbas, G., Abbas, Z. H., Khan, W. U., Waqas, M. (2021). Spectrum utilization efficiency in CRNs with hybrid spectrum access and channel reservation: A comprehensive analysis under prioritized traffic. Future Generation Computer Systems, 125, 726–742.
Goel, S., & Kulshrestha, R. (2020). Channel allocation and ultra-reliable communication in CRNs with heterogeneous traffic and retrials: A dependability theory-based analysis. Computer Communications, 158, 51–63.
Balapuwaduge, I.A.M., & Li, F.Y. (2018). A joint time-space domain analysis for ultra-reliable communication in 5G networks. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 1–6
Bayrakdar, M. E., & Çalhan, A. (2017). Improving spectrum handoff utilization for prioritized cognitive radio users by exploiting channel bonding with starvation mitigation. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 71, 181–191.
Zhang, L., Song, T., Wu, M., Bao, X., Guo, J., & Hu, J. (2015). Traffic-adaptive proactive spectrum handoff strategy for graded secondary users in cognitive radio networks. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 24(4), 844–851.
Wu, Y., Hu, F., Kumar, S., Guo, M., & Bao, K. (2013). Spectrum handoffs with mixed-priority queueing model over cognitive radio networks. In 2013 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing, pp. 1194–1197.
El Azaly, N. M., Badran, E. F., Kheirallah, H. N., & Farag, H. H. (2021). Performance analysis of centralized dynamic spectrum access via channel reservation mechanism in cognitive radio networks. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 60(1), 1677–1688.
Chu, T. M. C., Phan, H., & Zepernick, H.-J. (2014). Hybrid interweave-underlay spectrum access for cognitive cooperative radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 62(7), 2183–2197.
Biagi, M., & Cuomo, F. (2012). Primary and secondary nodes coexistence through opportunistic MIMO cognitive radio. In 2012 IEEE Globecom Workshops, pp. 925–930. IEEE
Biagi, M., & Cuomo, F. (2013). An opportunistic access scheme through distributed interference control for MIMO cognitive nodes. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(12), 6500–6513.
Tang, S., & Mark, B. L. (2009). Modeling and analysis of opportunistic spectrum sharing with unreliable spectrum sensing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(4), 1934–1943.
El-Sherif, A. A., & Liu, K. J. R. (2011). Joint design of spectrum sensing and channel access in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(6), 1743–1753.
Salameh, O., De Turck, K., Fiems, D., Bruneel, H., & Wittevrongel, S. (2018). Performance analysis of a cognitive radio network with imperfect spectrum sensing. IEICE Transactions on Communications, E101(B1), 213–222.
Agrawal, S. K., Samant, A., & Yadav, S. K. (2022). Spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks and metacognition for dynamic spectrum sharing between radar and communication system: A review. Physical Communication, 52, 101673.
Arjoune, Y., & Kaabouch, N. (2019). A comprehensive survey on spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks: Recent advances, new challenges, and future research directions. Sensors, 19(1), 126.
Alqahtani, A. S., Changalasetty, S. B., Parthasarathy, P., Thota, L. S., & Mubarakali, A. (2023). Effective spectrum sensing using cognitive radios in 5G and wireless body area networks. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 105, 108493.
Zhang, L., & Duan, L. (2022). Modeling and analysis of opportunistic spectrum access schemes in cognitive cellular networks under imperfect sensing. In ITM Web of Conferences, vol. 47 . EDP Sciences
Kulshrestha, R. (2022). Analysis of spectrum sensing and spectrum access in cognitive radio networks with heterogeneous traffic and p-retry buffering. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 21(7), 2318–2331.
Kalil, M. A., Al-Mahdi, H., Hammam, H., & Saroit, I. A. (2017). A buffering and switching scheme for admission control in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 6(3), 358–361.
Falcão, M. R. M., Balieiro, A. M., & Dias, K. L. (2018). A flexible-bandwidth model with channel reservation and channel aggregation for three-layered cognitive radio networks. Computer Networks, 135, 213–225.
Chu, T.M.C., Zepernick, H.-J., & Phan, H. (2015). Channel reservation for dynamic spectrum access of cognitive radio networks with prioritized traffic. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communication Workshop (ICCW), pp. 883–888. IEEE
Goel, S., & Kulshrestha, R. (2022). Queueing based spectrum management in cognitive radio networks with retrial and heterogeneous service classes. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 13(5), 2429–2437.
Goel, S., & Kulshrestha, R. (2022). Dependability-based analysis for ultra-reliable communication in heterogeneous traffic cognitive radio networks with spectrum reservation. Wireless Personal Communications, 127(4), 3015–3039.
Stevenson, C.R., Chouinard, G., Lei, Z., Hu, W., Shellhammer, S.J., & Caldwell, W. (2009). IEEE 802.22: The first cognitive radio wireless regional area network standard. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(1), 130–138
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the referees and chief editor for their insightful remarks for the improvement of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kulshrestha, R., Goel, S. & Balhara, P. Transient analysis of enhanced hybrid spectrum access for QoS provisioning in multi-class cognitive radio networks. Wireless Netw (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-024-03715-3
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-024-03715-3