Abstract
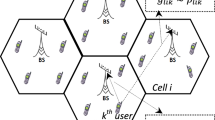
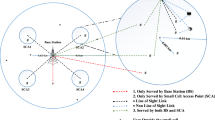
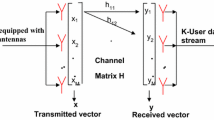
Modern 5G wireless cellular networks use massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology. This concept entails using an antenna array at a base station to concurrently service many mobile devices that have several antennas on their side. In this field, a significant role is played by the precoding (beamforming) problem. During downlink, an important part of precoding is the power allocation problem that distributes power between transmitted symbols. In this paper, we consider the power allocation problem for a class of precodings that asymptotically work as regularized zero-forcing. Under some realistic assumptions, we simplify the spectral efficiency functional and obtain tractable expressions for it. We prove that equal power allocation provides optimum for the simplified functional with total power constraint (TPC). We propose low-complexity Intersection methods (IM) that improve equal power allocation in the case of per-antenna power constraints (PAPC). On simulations using Quadriga, the proposed IM method in combination with widely-studied water filling (WF) shows a significant gain in spectral efficiency while using a similar computing time as the reference equal power (EP) solution.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availibility
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available in the GitHub repository, https://github.com/eugenbobrov/Power-Allocation-Algorithms-for-Massive-MIMO-Systems-with-Multi-Antenna-Users
Abbreviations
- ARZF:
-
Adaptive regularized zero-forcing
- BP:
-
Baseline power
- CD:
-
Conjugate detection
- CDF:
-
Cumulative density function
- CSI:
-
Channel state information
- EESM:
-
Exponential effective SINR mapping
- EP:
-
Equal power
- ESM:
-
Effective SINR mapping
- IM:
-
Intersection method
- IRC:
-
Interference rejection combiner
- LOS:
-
Line-of-sight
- MCS:
-
Modulation and coding scheme
- MIMO:
-
Multiple-input multiple-output
- MMSE:
-
Minimum mean squared error
- MRT:
-
Maximum ratio transmission
- MSE:
-
Mean squared error
- NLOS:
-
Non-line-of-sight
- OFDM:
-
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
- PA:
-
Power allocation
- PAPC:
-
Per-antenna power constraints
- PHY:
-
Physical layer
- RZF:
-
Regularized zero-forcing
- SE:
-
Spectral efficiency
- SINR:
-
Signal-to-interference-and-noise
- SVD:
-
Singular-value-decomposition
- TDD:
-
Time division duplex
- TPC:
-
Total power constraints
- UE:
-
User equipment
- WF:
-
Water filling
- ZF:
-
Zero-forcing
References
Andrews, Jeffrey G., Buzzi, Stefano, Choi, Wan, Hanly, Stephen V., Lozano, Angel, Soong, Anthony CK., & Zhang, Jianzhong Charlie. (2014). What will 5G be? IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(6), 1065–1082.
Marzetta, Thomas L. (2010). Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 9(11), 3590–3600.
Ge, Xiaohu, Zi, Ran, Wang, Haichao, Zhang, Jing, & Jo, Minho. (2016). Multi-user massive MIMO communication systems based on irregular antenna arrays. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(8), 5287–5301.
Le, Long, & Hossain, Ekram. (2007). Multihop cellular networks: Potential gains, research challenges, and a resource allocation framework. IEEE Communications Magazine, 45(9), 66–73.
Phan, Khoa T., Le-Ngoc, Tho, Vorobyov, Sergiy A., & Tellambura, Chintha. (2009). Power allocation in wireless multi-user relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(5), 2535–2545.
Ngo, Hien Quoc, Larsson, Erik G., & Marzetta, Thomas L. (2013). Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(4), 1436–1449.
Parfait, Tebe., Kuang, Yujun., & Jerry, Kponyo. (2014). Performance analysis and comparison of ZF and MRT based downlink massive MIMO systems. In 2014 sixth international conference on ubiquitous and future networks (ICUFN), pages 383–388. IEEE.
Zhang, Jiankang, Chen, Sheng, Maunder, Robert G., Zhang, Rong, & Hanzo, Lajos. (2018). Regularized zero-forcing precoding-aided adaptive coding and modulation for large-scale antenna array-based air-to-air communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 36(9), 2087–210.
Fatema, Nusrat, Hua, Guang, Xiang, Yong, Peng, Dezhong, & Natgunanathan, Iynkaran. (2017). Massive MIMO linear precoding: A survey. IEEE Systems journal, 12(4), 3920–3931.
Zheng, Kan, Zhao, Long, Mei, Jie, Shao, Bin, Xiang, Wei, & Hanzo, Lajos. (2015). Survey of large-scale MIMO systems. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 17(3), 1738–1760.
Dhakal, Sunil. (2019). High rate signal processing schemes for correlated channels in 5G networks.
Björnson, Emil, Hoydis, Jakob, & Sanguinetti, Luca. (2017). Massive MIMO networks: Spectral, energy, and hardware efficiency. Foundations and Trends in Signal Processing, 11(3–4), 154–655.
Tse, David., & Viswanath, Pramod. (2005).Fundamentals of wireless communication. Cambridge university press.
Wei, Yu. (2006). Uplink-downlink duality via minimax duality. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52(2), 361–374.
Björnson, Emil., & Jorswieck, Eduard. (2013). Optimal resource allocation in coordinated multi-cell systems. Now Publishers Inc.
Boccardi, Federico., Huang, Howard. (2006). Optimum power allocation for the MIMO-BC zero-forcing precoder with per-antenna power constraints. In 2006 40th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, pages 504–504. IEEE.
Deng, Xitirnin, & Haimovich, Alexander M. (2005). Power allocation for cooperative relaying in wireless networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 9(11), 994–996.
Host-Madsen, Anders, & Zhang, Junshan. (2005). Capacity bounds and power allocation for wireless relay channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(6), 2020–2040.
Liang, Yingbin, & Veeravalli, Venugopal V. (2005). Gaussian orthogonal relay channels: Optimal resource allocation and capacity. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(9), 3284–3289.
Zhao, Yi., Adve, Raviraj., & Lim, Teng Joon. (2006). Improving amplify-and-forward relay networks: optimal power allocation versus selection. In 2006 ieee international symposium on information theory, pages 1234–1238. IEEE.
Nguyen, Duy HN., & Nguyen, Ha. H. (2011). Power allocation in wireless multiuser multi-relay networks with distributed beamforming. IET Communications, 5(14), 2040–2051.
Sanguinetti, Luca., Zappone, Alessio., & Debbah, Merouane. (2018). Deep learning power allocation in massive MIMO. In 2018 52nd Asilomar conference on signals, systems, and computers, pages 1257–1261. IEEE.
Van Chien, Trinh, Björnson, Emil, & Larsson, Erik G. (2020). Joint power allocation and load balancing optimization for energy-efficient cell-free massive MIMO networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 19(10), 6798–6812.
Björnson, Emil, Jorswieck, Eduard, & Ottersten, Bjorn. (2010). Impact of spatial correlation and precoding design in OSTBC MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 9(11), 3578–3589.
Sun, Liang, & McKay, Matthew R. (2010). Eigen-based transceivers for the MIMO broadcast channel with semi-orthogonal user selection. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 58(10), 5246–5261.
Hanzaz, Zakaria., Schotten, Hans Dieter. (2013). Analysis of effective SINR mapping models for MIMO OFDM in LTE system. pages 1509–1515.
Mohajer, Amin. (2022). Mahya Sam Daliri, A Mirzaei, A Ziaeddini, M Nabipour, and Maryam Bavaghar. Heterogeneous computational resource allocation for noma: Toward green mobile edge-computing systems. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing.
Nikjoo, Faramarz, Mirzaei, Abbas, & Mohajer, Amin. (2018). A novel approach to efficient resource allocation in noma heterogeneous networks: Multi-criteria green resource management. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 32(7–8), 583–612.
Amin Mohajer, F., Sorouri, A Mirzaei, Ziaeddini, A., Jalali Rad, K., & Bavaghar, Maryam. (2022). Energy-aware hierarchical resource management and backhaul traffic optimization in heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Systems Journal, 16(4), 5188–5199.
Jaeckel, Stephan, Raschkowski, Leszek, Börner, Kai, & Thiele, Lars. (2014). QuaDRiGa: A 3-D multi-cell channel model with time evolution for enabling virtual field trials. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 62(6), 3242–3256.
Aitken, Alexander C. (1936). IV.-On least squares and linear combination of observations. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 55, 42–48.
Zaidi, Ali., Athley, Fredrik., Medbo, Jonas., Gustavsson, Ulf., Durisi, Giuseppe., & Chen, Xiaoming. (2018). 5G Physical Layer: principles, models and technology components. Academic Press.
Bobrov, Evgeny., Chinyaev, Boris., Kuznetsov, Viktor., Lu, Hao., Minenkov, Dmitrii., Troshin, Sergey., Yudakov, Daniil., & Zaev, Danila. (2021). Adaptive regularized zero-forcing beamforming in Massive MIMO with multi-antenna users. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.00853.
Mahmood, Nurul H., Berardinelli, Gilberto., Tavares, Fernando ML., Lauridsen, Mads., Mogensen, Preben., & Pajukoski, Kari. (2014). An efficient rank adaptation algorithm for cellular MIMO systems with IRC receivers. In 2014 IEEE 79th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Bobrov, Evgeny., Markov, Alexander., & Vetrov, Dmitry. (2021). Variational autoencoders for studying the manifold of precoding matrices with high spectral efficiency. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.15626.
Joham, Michael, Utschick, Wolfgang, & Nossek, Josef A. (2005). Linear transmit processing in MIMO communications systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 53(8), 2700–2712.
Nguyen, Duy HN., & Le-Ngoc, Tho. (2014). Mmse precoding for multiuser miso downlink transmission with non-homogeneous user snr conditions. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 1–12, 2014.
Shi, Shuying, Schubert, Martin, & Boche, Holger. (2007). Downlink MMSE transceiver optimization for multiuser MIMO systems: Duality and sum-MSE minimization. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(11), 5436–5446.
Hesham Mehana, A., & Nosratinia, A. (2012). Diversity of MMSE MIMO receivers. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 58(11), 6788–6805.
Wubben, Dirk., Bohnke, Ronald., Kuhn, Volker., & Kammeyer, K-D. (2004). Near-maximum-likelihood detection of MIMO systems using MMSE-based lattice-reduction. In 2004 IEEE International Conference on Communications (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37577), volume 2, pages 798–802. IEEE.
Ren, Bin, Wang, Yingmin, Sun, Shaohui, Zhang, Yawen, Dai, Xiaoming, & Niu, Kai. (2017). Low-complexity MMSE-IRC algorithm for uplink massive MIMO systems. Electronics Letters, 53(14), 972–974.
Wang, Bin, Chang, Yongyu, & Yang, Dacheng. (2014). On the SINR in massive MIMO networks with MMSE receivers. IEEE Communications Letters, 18(11), 1979–1982.
Verdú, Sergio. (2002). Spectral efficiency in the wideband regime. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 48(6), 1319–1343.
Björnson, Emil, Bengtsson, Mats, & Ottersten, Björn. (2014). Optimal multiuser transmit beamforming: A difficult problem with a simple solution structure [lecture notes]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 31(4), 142–148.
Lagen, Sandra., Wanuga, Kevin., Elkotby, Hussain., Goyal, Sanjay., Patriciello, Natale., & Giupponi, Lorenza. (2020). New radio physical layer abstraction for system-level simulations of 5G networks. In ICC 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pages 1–7. IEEE.
Brueninghaus, Karsten., Astely, David., Salzer, Thomas., Visuri, Samuli., Alexiou, Angeliki., Karger, Stephan., Seraji, G-A. (2005). Link performance models for system level simulations of broadband radio access systems. In 2005 IEEE 16th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, volume 4, pages 2306–2311. IEEE.
Francis, Jobin, & Mehta, Neelesh B. (2014). Eesm-based link adaptation in point-to-point and multi-cell ofdm systems: Modeling and analysis. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(1), 407–417.
Bobrov, Evgeny., Kropotov, Dmitry., Troshin, Sergey., & Zaev, Danila. (2021). L-BFGS precoding optimization algorithm for massive MIMO systems with multi-antenna users.
Bohagen, Frode., Orten, Pål., & Oien, GE. (2005). Construction and capacity analysis of high-rank line-of-sight MIMO channels. In IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, 2005, volume 1, pages 432–437. IEEE.
Wei, Yu., Rhee, Wonjong, Boyd, Stephen, & Cioffi, John M. (2004). Iterative water-filling for gaussian vector multiple-access channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 50(1), 145–152.
Hoydis, Jakob., Cammerer, Sebastian., Aoudia, Fayçal Ait., Vem, Avinash., Binder, Nikolaus., Marcus, Guillermo., & Keller, Alexander. (2022). Sionna: An open-source library for next-generation physical layer research. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.11854.
Bobrov, Evgeny., Kropotov, Dmitry., & Lu, Hao. (2021). Massive MIMO adaptive modulation and coding using online deep learning algorithm. IEEE Communications Letters.
TSG RAN; NR;. Physical layer procedures for data (release 16) v16.0.0. 3GPP TS 38.214, 2019.
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Irina Basieva, Lu Hao, Dmitri Shmelkin and Yue Zongdi for discussions and support. Also authors appreciate valuable and constructive comments from unknown reviewers.
Funding
The research was supported by Huawei Technologies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Search of MCS-\(\beta\) Effective SINR
The values of \(\beta\) for Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS) [52] are taken from Table 4. There are different \(\beta\) values for different MCSes [45]. The Table 4 shows \(\beta\) values, which corresponds to Tables 5.1.3.1-1 to 5.1.3.1-2 in [53]. The MCS value depends on the radio quality and therefore on \(\text {SINR}^{eff}_\beta\).
Thus, \(\text {SINR}^{eff}_\beta\) can be found by simple iteration method on the equation (12), initializing \(\text {SINR}^{eff}_\beta\) by geometrical average using (33) and then taking \(\beta = \beta (\text {MCS})\) from Table 4 and \(\text {MCS} = \text {MCS}(\text {SINR}^{eff}_\beta )\) from Table 5.
Also note that low values of \(\text {SINR}^{eff}_\beta\) (up to -5 dB) indicate that the user is almost out of service, and high values of \(\text {SINR}^{eff}_\beta\) (after 23 dB) do not make much sense.
1.2 Derivation of the eq. (47)
From the identity (45) \({\mathcal {L}}^{'}_{{p}_l}=0\):
Taking average of (62):
From (63):
From (64) and (65) we can derive:
Also, we know that \(x_l=\exp \left( -\frac{{p}_l}{\beta _l\sigma ^2 s_l^{-2}}\right)\).
So we know \(p_l=-\beta _l\sigma ^2 s_l^{-2}\ln \left( x_l\right)\) and can substitute (66) in the \(p_l\) expression.
Taking into account \(\sum \limits _{l=1}^{L}(\Vert {{\varvec{w}'}}_{l}\Vert ^2{p}_l)=P\) we obtain:
Substituting (68) into (65) and (65) into (64) we get the required expressions for \(x_l\) and then for \(p_l\).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bobrov, E., Chinyaev, B., Kuznetsov, V. et al. Power allocation algorithms for massive MIMO systems with multi-antenna users. Wireless Netw 29, 3747–3768 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03442-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03442-1