Abstract
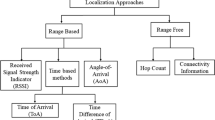
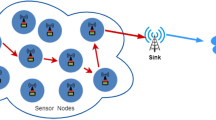
The ongoing ubiquitous computing era with the internet of things (IoT) and wireless sensor networks (WSN) is desperate to realize near-to-truth information by collecting and processing every significant data. It needs precise localization of unknown sensors that are communicating field-sensed data. The significance of location attracts security threats also, like wormhole attacks (WA). The WA compromises network security more simply; however it ruins the localization terribly. Most of the existing WA-combat localization algorithms instead of finding nodes by defining infeasibility, try to identify inappropriate nodes with too narrowly defined parameters to apply to the global visibility of network states. Therefore, the infeasibility defined by Farkas’ lemma is implemented in the proposed algorithm i.e. secure localization algorithm using Farkas’ lemma (SLAF). SLAF has two steps: WA detection and elimination (WDE), and localization of unknown node (LoU). In WDE, it detects nodes that are inconsistent in terms of distance equations defined between sensor pairs. Subsequently, in LoU, distance is approximated as suggested by DV-Hop. However, distance values are further improved by defining elastic variables. Finally, these distance values are passed to linear optimization for localization. The simulation validates SLAF as consistent, reliable, scalable, and precise in comparison with other recent time contenders.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing does not apply to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Change history
16 March 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03316-6
References
Zhang, N. (2022). Moore’s Law is dead, long live Moore’s Law!https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2205.15011.
Almurisi, N., & Tadisetty, S. (2022). Cloud-based virtualization environment for IoT-based WSN: Solutions, approaches and challenges. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 1, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12652-021-03515-Z/TABLES/5
Fascista, A. (2022). Toward integrated large-scale environmental monitoring using WSN/UAV/Crowdsensing: A review of applications, signal processing, and future perspectives. Sensors, 22(5), 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/S22051824
Xiao, Z., & Zeng, Y. (2021). An overview on integrated localization and communication towards 6G. Sci. China Inf. Sci., 65(3), 1–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11432-020-3218-8
Niculescu, B., & Nath, D. (2001). Ad-Hoc positioning systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2001.965964.
Kumar, S., Kumar, S., & Batra, N. (2021). Optimized distance range free localization algorithm for WSN. Wireless Personal Communications, 117(3), 1879–1907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07950-7
Kumar, S., Batra, N., & Kumar, S. (2021). Range-independent localization for GPS dead zone in MWSN. Wirel. Networks, 27(7), 4807–4823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02773-1
Kumar, S., Kumar, S., & Lobiyal, D. K. (2022). MWLP-DP: Mobile war-fighters location prediction for dark phase in Internet of Battlefield Things. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 33(4), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.4397
Sujihelen, L., & Jayakumar, C. (2018). Inclusive elliptical curve cryptography (IECC) for wireless sensor network efficient operations. Wireless Personal Communications, 99(2), 893–914. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11277-017-5157-4
Li, J., & Wang, D. (2019). The security DV-Hop algorithm against multiple-wormhole-node-link in WSN. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 13(4), 2223–2242. https://doi.org/10.3837/TIIS.2019.04.027
Yadav, K., Jain, A., Osman Sid Ahmed, N. M., Saad-Hamad, S. A., Dhiman, G., & Alotaibi, S. D. (2022). Internet of thing based koch fractal curve fractal antennas for wireless applications. IETE Journal of Research. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2022.2058631
Aliady, W. A., & Al-Ahmadi, S. A. (2019). Energy preserving secure measure against wormhole attack in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 7, 84132–84141. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2924283
Dutta, N., & Singh, M. M. (2019). Wormhole attack in wireless sensor networks: A critical review. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 702, 147–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0680-8_14/COVER/
Lenzen, C., Locher, T., Sommer, P., & Wattenhofer, R. (2010). Clock synchronization: open problems in theory and practice. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), Vol. 5901 LNCS, pp. 61–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11266-9_5/COVER.
Teng, Z., Du, C., Li, M., Zhang, H., & Zhu, W. (2022). A wormhole attack detection algorithm integrated with the node trust optimization model in WSNs. IEEE Sensors Journal, 22(7), 7361–7370. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2022.3152841
Han, D., et al. (2022). A novel secure DV-Hop localization algorithm against wormhole attacks. Telecommunication Systems, 80(3), 413–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11235-022-00914-1
Maier, K., Helwig, A., & Müller, G. (2017). Room-temperature dosimeter-type gas sensors with periodic reset. Sensors Actuators B Chem., 244, 701–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2016.12.119
Wang, M., Jin, W., Liu, X., Sun, W., Zhang, C., & Bi, W. (2022). Design and research of magnetic field sensor based on grapefruit optical fiber filled with magnetic fluid. Optoelectronics Letters, 18(5), 269–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11801-022-1135-5
Lin, S., et al. (2022). An ultralight, flexible, and biocompatible all-fiber motion sensor for artificial intelligence wearable electronics. NPJ Flex Electro., 6(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-022-00158-8
Thomson, C., Wadhaj, I., Tan, Z., & Al-Dubai, A. (2021). A mobility aware duty cycling and preambling solution for wireless sensor network with mobile sink node. Wirel. Networks, 27(5), 3423–3439. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11276-021-02580-8/FIGURES/17
Singh, S., & Singh, H. (2022). Intelligent Ad–Hoc–On demand multipath distance vector for wormhole attack in clustered WSN. Wireless Personal Communications, 122(1), 1305–1327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08950-x
Shahid, H., Ashraf, H., Javed, H., Humayun, M., Jhanjhi, N., & AlZain, M. A. (2021). Energy optimised security against wormhole attack in IoT-based wireless sensor networks. Comput. Mater. Contin., 68(2), 1967. https://doi.org/10.32604/CMC.2021.015259
Dani, V., Bhonde, R., & Mandloi, A. (2022). “iWAD: An improved wormhole attack detection system for wireless sensor network. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 418, 1002–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96308-8_93/COVER/
Sun, Y., & Chen, Y. (2022). Detection of wormhole attacks in wireless sensor networks based on anomaly detection algorithms. In: 2022 2nd international conference on consumer electronics and computer engineering (ICCECE), pp. 777–782, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCECE54139.2022.9712659
Bhosale, S. A., & Sonavane, S. S. (2022). Wormhole attack detection system for IoT network: A hybrid approach. Wireless Personal Communications, 124(2), 1081–1108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09395-y
Kaur, A., Gupta, G. P., & Mittal, S. (2021). Comparative study of the different variants of the DV—hop based node localization algorithms for wireless sensor, Vol. 123, no. 0123456789. Springer, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09206-4
Liouane, H., Messous, S., Cheikhrouhou, O., Baz, M., & Hamam, H. (2021). Regularized least square multi-hops localization algorithm for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 9, 136406–136418. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3116767
Kumar, S., Batra, N., & Kumar, S. (2022) Range-free localization by optimization in anisotropic WSN, pp. 157–168, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5747-4_14.
Kumar, S., Kumar, S., & Garg, R. (2022). Range–free localization for GWSN using k-NN algorithm with local linear Gaussian kernel regression ( KGR ). Evolving Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-022-09436-2
Farkas, J. (1902). Theorie der Einfachen Ungleichungen. J. für die reine und Angew Math., 479, 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1515/crll.1902.124.1
Kouvelas, N., Prasad, R. V., Yazdani, N., & Lucani, D. E. (2021). Np-CECADA: Enhancing ubiquitous connectivity of LoRa networks. In: Proceedings of 2021 IEEE 18th international conference mobile ad hoc smart system MASS 2021, pp. 374–382. https://doi.org/10.1109/MASS52906.2021.00054.
Coppersmith, D., & Winograd, S. (1990). Matrix multiplication via arithmetic progressions. Journal of Symbolic Computation, 9(3), 251–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0747-7171(08)80013-2
Karmarkar, N. (1984). A new polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming. In: Proceedings of the annual ACM symposium on Theory Computer, pp. 302–311. https://doi.org/10.1145/800057.808695.
Kumar, G., Rai, M. K., & Saha, R. (2017). Securing range free localization against wormhole attack using distance estimation and maximum likelihood estimation in Wireless Sensor Networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 99, 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JNCA.2017.10.006
Rivest, R. L., Shamir, A., & Adleman, L. (1978). A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Communications of the ACM, 21(2), 120–126. https://doi.org/10.1145/359340.359342
Hill, J., Szewczyk, R., Woo, A., Hollar, S., Culler, D., & Pister, K. (2000). System architecture directions for networked sensors. ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review, 34(5), 93–104. https://doi.org/10.1145/384264.379006
Kaushik, A., Lobiyal, D. K., & Kumar, S. (2021). Improved 3-dimensional DV-hop localization algorithm based on information of nearby nodes. Wirel. Networks, 27(3), 1801–1819. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11276-020-02533-7
Shen, S., Yang, B., Qian, K., She, Y., & Wang, W. (2019). On improved DV-hop localization algorithm for accurate node localization in wireless sensor networks. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 28(3), 658–666. https://doi.org/10.1049/cje.2019.03.013
Funding
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The affiliation of author Tarun Gulati error has been corrected.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, R., Gulati, T. & Kumar, S. Range free localization in WSN against wormhole attack using Farkas’ Lemma. Wireless Netw 29, 2029–2043 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03279-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03279-8