Abstract
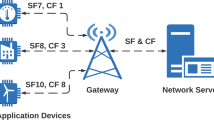
LoRaWAN is a promising LPWAN technology for IoT connectivity. It offers long-range and wide-area communication at low-power, low cost and low data rate. LoRaWAN performance has been evaluated according to many features such as coverage, scalability, physical layer parameters, communication reliability and latency. Existing studies assume that the LoRaWAN end-devices are already connected to the LoRa NetServer. Therefore, the performance of LoRaWAN activation procedure has not been well investigated. In this work, we study the performance of LoRaWAN during the Over-The-Air activation procedure. This process enables a large number of end-devices to join the network before being able to exchange any kind of packets. Thus, we analyze the average activation delay and the average energy consumption for an end-device in a large scale LoRaWAN. To achieve this goal, we first implement the Over-The-Air activation procedure in ns-3, especially in the ’lorawan’ module and conduct extensive simulations. Then, we elaborate a mathematical model using Markov-chain to evaluate both the delay and the energy consumption analytically. Our study shows that in a LoRaWAN cell composed of 1000 end-devices, the average activation delay for an end-device is about 35 minutes and this activation requires an average of three join-packet transmissions and an average energy consumption of 0.0887J.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
LoRaWAN Specification v1.1, LoRa Alliance
Sigfox, ‘Sigfox-The Global Communications Service Provider for the Internet of Things (IoT’). [online]. Available:https://www.sigfox.com/en
ROHDE, D. et SCHWARZ, J. Narrowband internet of things. (2016). Available: www.rohde-schwarz.com/us/applications/narrowband-internet-of-things-application-note.html
Mekki, K., Bajic, E., Chaxel, F., & Meyer, F. (2019). A comparative study of LPWAN technologies for large-scale IoT deployment. ICT Express, 5(1), 1–7.
Springer, A., Gugler, W., Huemer, M., Reindl, L., Ruppel, C. C. W., & Weigel, R. (2000). Spread spectrum communications using chirp signals. In IEEE/AFCEA EUROCOMM 2000. Information Systems for Enhanced Public Safety and Security (Cat. No. 00EX405) (pp. 166–170). IEEE.
Phung, K. H., Tran, H., Nguyen, Q., Huong, T. T., & Nguyen, T. L. (2018). Analysis and assessment of LoRaWAN. In 2018 2nd International Conference on Recent Advances in Signal Processing, Telecommunications and Computing (SigTelCom) (pp. 241–246). IEEE
de Carvalho Silva, J., Rodrigues, J. J., Alberti, A. M., Solic, P., & Aquino, A. L. (2017). LoRaWAN-A low power WAN protocol for Internet of Things: A review and opportunities. In 2017 2nd International Multidisciplinary Conference on Computer and Energy Science (SpliTech) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Lavric, A., & Petrariu, A. I. (2018). LoRaWAN communication protocol: The new era of IoT. In 2018 International Conference on Development and Application Systems (DAS) (pp. 74–77). IEEE.
Basford, P. J., Bulot, F. M. J., Apetroaie-Cristea, M., Cox, S. J., & Ossont, S. J. (2020). LoRaWAN for smart city IoT deployments: A long term evaluation. Sensors, 20, 648.
Ali, Z., Henna, S., Akhunzada, A., Raza, M., & Kim, S. W. (2019). Performance evaluation of LoRaWAN for green Internet of Things. IEEE Access, 7, 164102–164112.
Fernandes, C. D., Depari, A., Sisinni, E., Ferrari, P., Flammini, A., Rinaldi, S., & Pasetti, M. (2020). Hybrid indoor and outdoor localization for elderly care applications with LoRaWAN. In 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Froiz-Miguez, I., Fraga-Lamas, P., Varela-Barbeito, J., & Fernández-Caramés, T.M. (2020).LoRaWAN and Blockchain based Safety and Health Monitoring System for Industry 4.0 Operators. Proceedings, 42, 77.
Mason, F., Chiariotti, F., Capuzzo, M., Magrin, D., Zanella, A., & Zorzi, M. (2020). Combining LoRaWAN and a New 3D Motion Model for Remote UAV Tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.04849.
El Chall, R., Lahoud, S., & El Helou, M. (2019). LoRaWAN network: Radio propagation models and performance evaluation in various environments in Lebanon. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(2), 2366–2378.
Alves, H. B., Lima, V. S., Silva, D. R., Nogueira, M. B., Rodrigues, M. C., Cunha, R. N., & Ferrari, P. (2020). Introducing a survey methodology for assessing LoRaWAN coverage in Smart Campus scenarios. In 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT (pp. 708–712). IEEE.
Santos Filho, F. H. C. D., Dester, P. S., Stancanelli, E. M., Cardieri, P., Nardelli, P. H., Carrillo, D., & Alves, H. (2020). Performance of LoRaWAN for handling telemetry and alarm messages in industrial applications. Sensors, 20(11), 3061.
Muzammir, M. I., Abidin, H. Z., Abdullah, S. A. C., & Zaman, F. H. K. (2019). Performance analysis of LoRaWAN for indoor application. In 2019 IEEE 9th Symposium on Computer Applications & Industrial Electronics (ISCAIE) (pp. 156–159). IEEE.
YAYE, S. A. R. R., GUEYE, Bamba, et CHEIKH, S. A. R. R. (2019). Performance analysis of a smart street lighting application using LoRa Wan. In 2019 International Conference on Advanced Communication Technologies and Networking (CommNet). IEEE, p. 1–6.
Wadatkar, P. V., Chaudhari, B. S., & Zennaro, M. (2019). Impact of interference on LoRaWAN link performance. In 2019 5th International Conference On Computing, Communication, Control And Automation (ICCUBEA) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Croce, D., Gucciardo, M., Mangione, S., Santaromita, G., & Tinnirello, I. (2018). Impact of LoRa imperfect orthogonality: Analysis of link-level performance. IEEE Communications Letters, 22(4), 796–799.
Abdelfadeel, K. Q., Zorbas, D., Cionca, V., & Pesch, D. (2019). \(FREE\)–fine-grained scheduling for reliable and energy-efficient data collection in LoRaWAN. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(1), 669–683.
Zorbas, D., Abdelfadeel, K., Kotzanikolaou, P., & Pesch, D. (2020). TS-LoRa: Time-slotted LoRaWAN for the Industrial Internet of Things. Computer Communications, 153, 1–10.
Mroue, H., Parrein, B., Hamrioui, S., Bakowski, P., Nasser, A., Cruz, E. M., & Vince, W. (2020). LoRa+: An extension of LoRaWAN protocol to reduce infrastructure costs by improving the Quality of Service. Internet of Things, 9, 100176.
Dönmez, T. C., & Nigussie, E. (2018). Security of join procedure and its delegation in lorawan v1. 1. Procedia Computer Science, 134, 204–211.
Santamaria, M., & Marchiori, A. (2019). Demystifying LoRa WAN Security and Capacity. In 2019 29th International Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ITNAC) (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Noura, H., Hatoum, T., Salman, O., et al. (2020). LoRaWAN security survey: Issues, threats and possible mitigation techniques. Internet of Things, p. 100303.
Eldefrawy, M., Butun, I., Pereira, N., & Gidlund, M. (2019). Formal security analysis of LoRaWAN. Computer Networks, 148, 328–339.
Sanchez-Iborra, R., Sánchez-Gómez, J., Pérez, S., et al. (2018). Enhancing Lorawan security through a lightweight and authenticated key management approach. Sensors, 18(6), 1833.
Naoui, S., Elhdhili, M. E., & et Saidane, L. A. (2020). Novel enhanced LoRaWAN framework for smart home remote control security. Wireless Personal Communications, 110(4), 2109–2130.
Danish, S. M., Lestas, M., Asif, W., Qureshi, H. K., & Rajarajan, M. (2019). A lightweight blockchain based two factor authentication mechanism for lorawan join procedure. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Toussaint, J., El Rachkidy, N., & Guitton, A. (2016). Performance analysis of the on-the-air activation in LoRaWAN. In 2016 IEEE 7th annual information technology, electronics and mobile communication conference (IEMCON) (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Pham, C., Bounceur, A., Clavier, L., Noreen, U., & Ehsan, M. (2019). Investigating and experimenting interference mitigation by capture effect in LoRa networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Future Networks and Distributed Systems (pp. 1–6).
El Fehri, Chékra, et al. (2021). Experimental analysis of the Over-The-Air activation procedure in LoRaWAN. In 2021 17th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob). IEEE.
Carvalho, D. F., Depari, A., Ferrari, P., Flammini, A., Rinaldi, S., & Sisinni, E. (2019). On the evaluation of application level delays in public LoRaWAN networks. In 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Measurements & Networking (M&N) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Pötsch, A., & Hammer, F. (2019). Towards end-to-end latency of LoRaWAN: Experimental analysis and IIoT applicability. In 2019 15th IEEE international workshop on factory communication systems (WFCS) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
Carvalho, D. F., Ferrari, P., Sisinni, E., Depari, A., Rinaldi, S., Pasetti, M., & Silva, D. (2019). A test methodology for evaluating architectural delays of LoRaWAN implementations. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 56, 1–17.
Khan, F. H., Jurdak, R., & Portmann, M. (2019). A model for reliable uplink transmissions in LoRaWAN. In 2019 15th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (DCOSS) (pp. 147–156). IEEE.
Delobel, F., El Rachkidy, N., & Guitton, A. (2017). Analysis of the delay of confirmed downlink frames in Class B of LoRaWAN. In 2017 IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Ron, D., Lee, C. J., Lee, K., Choi, H. H., & Lee, J. R. (2020). Performance analysis and optimization of downlink transmission in LoRaWAN class B mode. IEEE Internet of Things Journal.
LoRaWAN Regional parameters v1.1, LoRa Alliance.
Devices, E. S. R. (2017). operating in the frequency range 25 MHz to 1 000 MHz. ETSI EN, 300, 220.
MARKKULA, J., MIKHAYLOV, K., et HAAPOLA, J. (2019). Simulating LoRaWAN: On importance of inter spreading factor interference and collision effect. In ICC 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC). IEEE, 2019. p. 1–7.
Magrin, D., Capuzzo, M., & Zanella, A. (2019). A thorough study of LoRaWAN performance under different parameter settings. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(1), 116–127.
IEEE Standards Association. (2018). Guidelines for Use of Extended Unique Identifier (EUI), Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), and Company ID (CID).
https://lora-developers.semtech.com/library/tech-papers-and-guides/the-book/joining-and-rejoining/
Oliver C. (2013). Ibe, 4 - Discrete-Time Markov Chains, Editor(s): Oliver C. Ibe, Markov processes for stochastic modeling (Second Edition),Elsevier, pp. 59–84, ISBN 9780124077959, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407795-9.00004-9.
Sornin, N., Luis, M., Eirich, T., Kramp, T., & Hersent, O. (2015). LoRa specification 1.0 LoRa alliance standard specification. LoRa Alliance., 87.
LoRa SX1301 datasheet Version 2.4, Semtech (2017)
Sorensen, R. B., Razmi, N., Nielsen, J. J., & Popovski, P. (2019). Analysis of LoRaWAN uplink with multiple demodulating paths and capture effect. In ICC 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
3GPP, Radio Frequency (RF) system scenarios, Tech. Rep., 36.942 V13.0.0, (2016)
Available : https://www.rfsolutions.co.uk/downloads/1462271988SX1272_SEMTECH.pdf
Casals, L., Mir, B., Vidal, R., et al. (2017). Modeling the energy performance of LoRaWAN. Sensors, 17(10), 2364.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical support from Davide Magrin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fehri, C.E., Baccour, N. & Kammoun, I. Performance evaluation of the Over-The-Air activation procedure in a large scale LoRaWAN. Wireless Netw 28, 2455–2470 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-02952-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-02952-8