Abstract
This review elucidates different bioremediation approaches used for degradation of HCH from contaminated sites. It highlights the significance of degradative pathways, microbial diversity and impact of different environmental factors for developing viable bioremediation strategies. The application of innovative biotechnological approaches and a thorough understanding of HCH biodegradation pathways show great promise for the creation of long-term solutions to HCH pollution and the restoration of polluted soil ecosystems. Bioremediation technologies viz. biostimulation, bioaugmentation, phytoremediation have been considered till date for treating HCH-contaminated sites. Different bacterial and fungal strains have been reported for degradation of HCH residues. However, these methods are limited to γ-HCH degradation, at laboratory scale and achieving lower success rate for large scale demonstration trials. This review presents a theoretical background for degradation of different HCH isomers in soil through plants, microbes and through their cooperative interactions. This work briefly overviews the substantial contamination of the environment by HCH residues, along with spontaneous evolution of degradation pathways through various HCH degrading microbes. Bioremediation mechanism and pathways of HCH degradation through plants and microbes have been discussed thoroughly. Through molecular and genetic investigations, the complex metabolic pathways used by these microbes, including reductive dechlorination, hydrolysis, and ring cleavage, has been clarified. This study seeks to give a thorough summary of recent discoveries and developments in bioremediation methods for soil HCH degradation. Numerous microbial consortia, including fungi, plants, and bacteria have been recognised as important participants in the transformation of HCH.
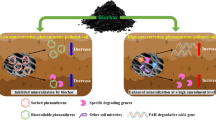
Graphical Abstract




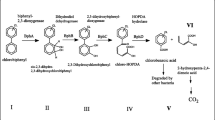
(Source: van Doesburg et al. 2005)

(Source: Lal et al. 2010)

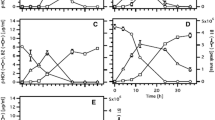
(Source: Zhang et al. 2020)

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting the findings of this review are available in the references cited within this article.
References
Abhilash PC, Singh N (2010a) Withania somnifera Dunal-mediated dissipation of lindane from simulated soil: implications for rhizoremediation of contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 10:272–282
Abhilash PC, Singh N (2010b) Effect of growing Sesamum indicum L. on enhanced dissipation of lindane (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6-hexachlorocyclohexane) from soil. Int J Phytoremediation 12(5):440–453
Abhilash PC, Jamil S, Singh V, Singh A, Singh N, Srivastava SC (2008) Occurrence and distribution of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in vegetation samples from a contaminated area. Chemosphere 72(1):79–86
Abhilash PC, Singh B, Srivastava P, Schaeffer A, Singh N (2013) Remediation of lindane by Jatropha curcas L: utilization of multipurpose species for rhizoremediation. Biomass Bioenergy 51:189–193
Alvarez A, Yañez ML, Benimeli CS, Amoroso MJ (2012) Maize plants (Zea mays) root exudates enhance lindane removal by native Streptomyces strains. Int Biodeterior &Biodegradation 66(1):14–18
Anand S, Malhotra J, Niharika N, Lal D, Jindal S, Kaur J, …, Sangwan N (2013) Bioremediation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) pollution at HCH dumpsites. Knowledge Systems of Societies for Adaptation and Mitigation of Impacts of Climate Change. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 387–404
Badea SL, Stegarus DI, Niculescu VC, Enache S, Soare A, Ionete RE, …, Höhener P (2021) Dehalogenation of α-hexachlorocyclohexane by iron sulfide nanoparticles: study of reaction mechanism with stable carbon isotopes and pH variations. Sci Total Environ 801:149672
Bajaj S, Sagar S, Khare S, Singh DK (2017) Biodegradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (lindane) by halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter sp. LD2 isolated from HCH dumpsite. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 122:23–28
Balazs HE, Schmid CA, Cruzeiro C, Podar D, Szatmari PM, Buegger F, …, Schroeder P (2021) Post-reclamation microbial diversity and functions in hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) contaminated soil in relation to spontaneous HCH tolerant vegetation. Sci Total Environ 767:144653
Becerra-Castro C, Prieto-Fernández Á, Kidd PS, Weyens N, Rodríguez-Garrido B, Touceda-González M, …, Vangronsveld J (2013) Improving performance of Cytisus striatus on substrates contaminated with hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) isomers using bacterial inoculants: developing a phytoremediation strategy. Plant Soil 362:247–260
Benimeli CS, González AJ, Chaile AP, Amoroso MJ (2007) Temperature and pH effect on lindane removal by Streptomyces sp. M7 in soil extract. J Basic Microbiol 47:468–473
Bescós A, Herrerías CI, Hormigón Z, Mayoral JA, Salvatella L (2021) Theoretical insight on the treatment of β-hexachlorocyclohexane waste through alkaline dehydrochlorination. Sci Rep 11(1):8777
Beyer A, Matthies M (2001) Long-range transport potential of semi-volatile organic chemicals in coupled air-water systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 8:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987382
Camacho-Pérez B, Ríos-Leal E, Rinderknecht-Seijas N, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2012) Enzymes involved in the biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane: a mini review. J Environ Manage 95:S306–S318
Chakraborty J, Das S (2016) Molecular perspectives and recent advances in microbial remediation of persistent organic pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:16883–16903
Chaudhary P, Kumar M, Khangarot BS, Kumar A (2006) Degradation and detoxification of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ITRC-5. Int Biodeterior &Biodegradation 57(2):107–113
Chen H, Gao B, Wang S, Fang J (2015) Microbial Degradation of Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) Pesticides. Advances in Biodegradation and Bioremediation of Industrial Waste, 195–224
Cuozzo SA, Sineli PE, Costa D, J., Tortella G (2018) Streptomyces sp. is a powerful biotechnological tool for the biodegradation of HCH isomers: biochemical and molecular basis. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38(5):719–728
Dadhwal M, Singh A, Prakash O, Gupta SK, Kumari K, Sharma P, …, Lal R (2009) Proposal of biostimulation for hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-decontamination and characterization of culturable bacterial community from high‐dose point HCH‐contaminated soils. J Appl Microbiol 106(2):381–392
De Paolis MR, Lippi D, Guerriero E, Polcaro CM, Donati E (2013) Biodegradation of α-, β-and γ-hexachlorocyclohexane by Arthrobacter fluorescens and Arthrobacter giacomelloi. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:514–524
Dominguez CM, Romero A, Checa-Fernandez A, Santos A (2021) Remediation of HCHs-contaminated sediments by chemical oxidation treatments. Sci Total Environ 751:141754
Dritsa V, Rigas F (2013) The ligninolytic and biodegradation potential on lindane of Pleurotus ostreatus spp. J Min World Express 2(1):23–30
Dubey RK, Tripathi V, Singh N, Abhilash PC (2014) Phytoextraction and dissipation of lindane by Spinacia oleracea L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 109:22–26
Egorova DO, Buzmakov SA, Nazarova EA, Andreev DN, Demakov VA, Plotnikova EG (2017) Bioremediation of hexachlorocyclohexane-contaminated soil by the new Rhodococcus wratislaviensis strain Ch628. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:1–16
Elcey CD, Kunhi AAM (2010) Substantially enhanced degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by a microbial consortium on acclimation. J Agric Food Chem 58:1046–1054
Endo R, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Nagata Y (2007) Identification and characterization of genes encoding a putative ABC-type transporter essential for utilization of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingobium japonicum UT26. J Bacteriol 189(10):3712–3720
Garg N, Lata P, Jit S, Sangwan N, Singh AK, Dwivedi V, …, Lal R (2016) Laboratory and field scale bioremediation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) contaminated soils by means of bioaugmentation and biostimulation. Biodegradation 27:179–193
Geueke B, Garg N, Ghosh S, Fleischmann T, Holliger C, Lal R, Kohler HPE (2013) Metabolomics of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) transformation: ratio of LinA to LinB determines metabolic fate of HCH isomers. Environ Microbiol 15(4):1040–1049
Guillén-Jiménez FDM, Cristiani-Urbina E, Cancino-Díaz JC, Flores-Moreno JL, Barragán-Huerta BE (2012) Lindane biodegradation by the Fusarium verticillioides AT-100 strain, isolated from Agave tequilana leaves: kinetic study and identification of metabolites. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 74:36–47
Haddaoui I, Mahjoub O, Mahjoub B, Boujelben A, Di Bella G (2016) Occurrence and distribution of PAHs, PCBs, and chlorinated pesticides in tunisian soil irrigated with treated wastewater. Chemosphere 146:195–205
Jaiswal S, Singh DK, Shukla P (2022) Lindane bioremediation by Paenibacillus dendritiformis SJPS-4, its metabolic pathway analysis and functional gene annotation, vol 27. Environmental Technology & Innovation, p 102433
Jaiswal S, Singh DK, Shukla P (2023) Degradation effectiveness of hexachlorohexane (ϒ-HCH) by bacterial isolate Bacillus cereus SJPS-2, its gene annotation for bioremediation and comparison with Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ Pollut 318:120867
Jit S, Dadhwal M, Kumari H, Jindal S, Kaur J, Lata P, …, Lal R (2011) Evaluation of hexachlorocyclohexane contamination from the last lindane production plant operating in India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:586–597
Kaur H, Kapoor S, Kaur G (2016) Application of ligninolytic potentials of a white-rot fungus Ganoderma lucidum for degradation of lindane. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–10
Kumar D, Pannu R (2018) Perspectives of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) biodegradation from the environment: a review. Bioresources and Bioprocessing 5(1):29
Kumar D, Kumar A, Sharma J (2016) Degradation study of lindane by novel strains Kocuria sp. DAB-1Y and Staphylococcus sp. DAB-1 W. Bioresources and Bioprocessing 3:1–16
Lal R, Pandey G, Sharma P, Kumari K, Malhotra S, Pandey R, …, Oakeshott JG (2010) Biochemistry of microbial degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane and prospects for bioremediation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 74(1):58–80
Li YF, Macdonald RW, Jantunen LMM, Harner T, Bidleman TF, Strachan WMJ (2002) The transport of β-hexachlorocyclohexane to the western Arctic Ocean: a contrast to α-HCH. Sci Total Environ 291(1–3):229–246
Liu X, Bonhomme J, Merbach I, Kümmel S, Richnow HH (2021) Uptake of α-HCH by wheat from the gas phase and translocation to soil analysed by a stable carbon isotope labelling experiment. Chemosphere 264:128489
Ma Y, Yun X, Ruan Z, Lu C, Shi Y, Qin Q, …, Xie Y (2020) Review of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) contamination in chinese soils. Sci Total Environ 749:141212
Manickam N, Mau M, Schlömann M (2006) Characterization of the novel HCH-degrading strain, Microbacterium sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol ITRC1:69, 580–588
Manickam N, Misra R, Mayilraj S (2007) A novel pathway for the biodegradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane by a Xanthomonas sp. strain ICH12. J Appl Microbiol 102(6):1468–1478
Manickam N, Reddy MK, Saini HS, Shanker R (2008) Isolation of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas sp. by dehalogenase assay and characterization of genes involved in γ‐HCH degradation. J Appl Microbiol 104(4):952–960
Manickam N, Bajaj A, Saini HS, Shanker R (2012) Surfactant mediated enhanced biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) isomers by Sphingomonas sp. NM05. Biodegradation 23(5):673–682
Mortazavi N, Asadikaram G, Ebadzadeh MR, Kamalati A, Pakmanesh H, Dadgar R et al (2019) Organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides and bladder cancer: a case-control study. J Cell Biochem 120:14847–14859. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28746
Nagata Y, Prokop Z, Sato Y, Jerabek P, Kumar A, Ohtsubo Y…, Damborský J (2005) Degradation of β-hexachlorocyclohexane by haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(4):2183–2185
Nagata Y, Endo R, Ito M, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M (2007) Aerobic degradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) in bacteria and its biochemical and molecular basis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(4):741
Nagpal V, Paknikar KM (2006) Integrated biological approach for the enhanced degradation of lindane
Nagpal V, Srinivasan MC, Paknikar KM (2008) Biodegradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (lindane) by a non-white rot fungus Conidiobolus 03-1-56 isolated from litter. Indian J Microbiol 48:134–141
Odewale GO, Sosan MB, Oyekunle JAO, Adeleye AO (2021) Human health risk assessment of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables in Nigeria, vol 28. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, pp 33133–33145
Okeke BC, Siddique T, Arbestain MC, Frankenberger WT (2002) Biodegradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (lindane) and a-hexachlorocyclohexane in water and a soil slurry by a Pandoraea species. J Agric Food Chem 50:2548–2555
Quintero JC, Moreira MT, Feijoo G, Lema JM (2005) Effect of surfactants on the soil desorption of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) isomers and their anaerobic biodegradation. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology: International Research in Process, Environmental & Clean Technology, 80(9), 1005–1015
Quintero JC, Lu-Chau TA, Moreira MT, Feijoo G, Lema JM (2007) Bioremediation of HCH present in soil by the white-rot fungus bjerkandera adusta in a slurry batch bioreactor. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 60(4):319–326
Raina V, Suar M, Singh A, Prakash O, Dadhwal M, Gupta SK, …, Lal R (2008) Enhanced biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) in contaminated soils via inoculation with Sphingobium indicum B90A. Biodegradation 19:27–40
Rajan S, Parween M, Raju NJ (2023) Pesticides in the hydrogeo-environment: a review of contaminant prevalence, source and mobilisation in India. Environ Geochem Health, 1–33
Rigas F, Papadopoulou K, Philippoussis A, Papadopoulou M, Chatzipavlidis J (2009) Bioremediation of lindane contaminated soil by Pleurotus ostreatus in non-sterile conditions using multilevel factorial design. Water Air and Soil Pollution 197:121–129
Saez JM, Alvarez A, Fuentes MS, Amoroso MJ, Benimeli CS (2017) An overview on microbial degradation of lindane. Microbe-Induced Degradation of Pesticides. Springer, Cham, pp 191–212
Sagar V, Singh DP (2011) Biodegradation of lindane pesticide by non-white-rots soil fungus Fusarium sp. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:1747–1754
Sahoo B, Ningthoujam R, Chaudhuri S (2019) Isolation and characterization of a lindane degrading bacteria paracoccus sp. NITDBR1 and evaluation of its plant growth promoting traits. Int Microbiol 22:155–167
Salam JA, Das N (2013) Enhanced biodegradation of lindane using oil-in-water bio-microemulsion stabilized by biosurfactant produced by a new yeast strain, Pseudozyma VITJzN01. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(11):1598–1609
Salam JA, Das N (2014) Lindane degradation by Candida VITJzN04, a newly isolated yeast strain from contaminated soil: kinetic study, enzyme analysis and biodegradation pathway. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30(4):1301–1313
Salam JA, Lakshmi V, Das D, Das N (2013) Biodegradation of lindane using a novel yeast strain, Rhodotorula sp. VITJzN03 isolated from agricultural soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(3):475–487
Salam JA, Hatha MA, Das N (2017) Microbial-enhanced lindane removal by sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) in doped soil-applications in phytoremediation and bioaugmentation. J Environ Manage 193:394–399
Shrivastava N, Prokop Z, Kumar A (2015) Novel LinA type 3 δ-hexachlorocyclohexane dehydrochlorinase. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(21):7553–7559
Sineli PE, Tortella G, Dávila Costa JS, Benimeli CS, Cuozzo SA (2016) Evidence of α-, β-and γ-HCH mixture aerobic degradation by the native actinobacteria Streptomyces sp. M7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:1–9
Singh T, Singh DK (2019) Lindane degradation by root epiphytic bacterium Achromobacter sp. strain A3 from Acorus calamus and characterization of associated proteins. Int J Phytoremediation 21:419–424. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1524835
Singh AK, Chaudhary P, Macwan AS, Diwedi UN, Kumar A (2007) Selective loss of lin genes from hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa ITRC-5 under different growth conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:895–901
Singh S, Sherkhane PD, Kale SP, Eapen S (2011) Expression of a human cytochrome P4502E1 in Nicotiana tabacum enhances tolerance and remediation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane. New Biotechnol 28(4):423–429
Srivastava V, Srivastava T, Kumar MS (2019) Fate of the persistent organic pollutant (POP) hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and remediation challenges. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 140:43–56
Suar M, Hauser A, Poiger T, Buser HR, Müller MD, Dogra C, …, Kohler HP (2005) Enantioselective transformation of α-HCH by dehydrochlorinasesLinA1 and LinA2 from soil bacterium Sphingomonas paucimobilis B90A. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8514–8518
Tripathi V, Edrisi SA, Chaurasia R, Pandey KK, Dinesh D, Srivastava R, …, Abhilash PC (2019) Restoring HCHs polluted land as one of the priority activities during the UN-International decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021–2030): a call for global action. Sci Total Environ 689:1304–1315
Usman M, Tascone O, Rybnikova V, Faure P, Hanna K (2017) Application of chemical oxidation to remediate HCH-contaminated soil under batch and flow through conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(17):14748–14757
van Doesburg W, van Eekert MH, Middeldorp PJ, Balk M, Schraa G, Stams AJ (2005) Reductive dechlorination of β-hexachlorocyclohexane (β-HCH) by a Dehalobacter species in coculture with a Sedimentibacter sp. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54(1):87–95
Vijgen J, Abhilash PC, Li YF, Lal R, Forter M, Torres J, …, Weber R (2011) Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) as new Stockholm Convention POPs—a global perspective on the management of lindane and its waste isomers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:152–162
Wu J, Hong Q, Sun Y, Hong Y, Yan Q, Li S (2007) Analysis of the role of LinA and LinB in biodegradation of δ-hexachlorocyclohexane. Environ Microbiol 9(9):2331–2340
Yang PF, Macdonald RW, Hung H, Muir DC, Kallenborn R, Nikolaev AN, …, Li YF (2023) Modeling historical budget for β-Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) in the Arctic Ocean: a contrast to α-HCH. Environ Sci Ecotechnology 14:100229
Zhang W, Lin Z, Pang S, Bhatt P, Chen S (2020) Insights into the biodegradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) using a microbial system. Front Microbiol 11:522
Zheng G, Selvam A, Wong JW (2011) Rapid degradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) at low temperature by Sphingobium strains. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65(4):612–618
Acknowledgements
The work was partly supported by GAP-3429 and institutional project of CSIR- National Botanical Research Institute. AR is thankful to Indian Council of Medical Research for awarding fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aditi Roy: Conceptualization, Writing- original draft, Writing - review &editing. Poornima Vajpayee: Writing - review & editing, Visualization, Supervision. Suchi Srivastava: Conceptualization, Writing- original draft, Writing - review & editing, Visualization, Supervision. Pankaj Kumar Srivastava: Resources, Writing - review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, A., Vajpayee, P., Srivastava, S. et al. Revelation of bioremediation approaches for hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 243 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03692-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03692-3