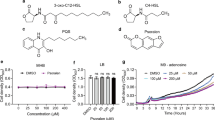
Abstract
Serious infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa are usually related to quorum sensing (QS)-dependent virulence factors. Hence, QS inhibition is a promising approach to overcoming P. aeruginosa infections. This study aimed to investigate the effect of naproxen on biofilm formation and QS-related virulence traits of P. aeruginosa. Furthermore, the anti-QS potential of naproxen was evaluated using real-time PCR and molecular docking analysis. Our findings supported the anti-QS activity of naproxen, as evidenced by down-regulation of the lasI and rhlI genes expression as well as the attenuation of bacterial protease, hemolysin, pyocyanin, biofilm, and motility. Additionally, the high binding affinity of naproxen with QS regulatory proteins was determined in the molecular docking simulation. Altogether, these findings suggest that naproxen has a promising potential in inhibiting QS-associated traits of P. aeruginosa.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The majority of the data used to support the findings of this study were included in the manuscript. In addition, the additional data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abbas HA (2015) Inhibition of virulence factors of pseudomonas aeruginosa by diclofenac sodium. Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol 74:79–85
Abbas HA, Serry FM, El-Masry EM (2012) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and sodium ascorbate potentiate the antibiotic activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Res J Pharm Technol 8:1124–1129
Alatraktchi FA, Svendsen WE, Molin S (2020) Electrochemical detection of pyocyanin as a biomarker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a focused review. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185218
Askoura M, Saleh M, Abbas H (2020) An innovative role for tenoxicam as a quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01771-4
Chang CY, Krishnan T, Wang H, Chen Y, Yin WF, Chong YM, Tan LY, Chong TM, Chan KG (2014) Non-antibiotic quorum sensing inhibitors acting against N-acyl homoserine lactone synthase as druggable target. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07245
Chmiel JF, Konstan MW, Elborn JS (2013) Antibiotic and anti-inflammatory therapies for cystic fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009779
Crofford LJ (2013) Use of NSAIDs in treating patients with arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4174
Dai L, Wu TQ, Xiong YS, Ni HB, Ding Y, Zhang WC, Chu SP, Ju SQ, Yu J (2019) Ibuprofen-mediated potential inhibition of biofilm development and quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116947
Das S, Dash HR (2014) Microbial biotechnology—a laboratory manual for bacterial systems. Springer, New Delhi
Das T, Sehar S, Manefield M (2013) The roles of extracellular DNA in the structural integrity of EPS and bacterial biofilm. Environ Microbiol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12085
Deka N (2014) Comparison of tissue culture plate method, tube method and Congo-red agar method for the detection of biofilm formation by coagulase negative Staphylococcus isolated from non-clinical isolates. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3:810–815
El-Mowafy SA, Abd El Galil KH, El-Messery SM, Shaaban MI (2014) Aspirin is an efficient inhibitor of quorum sensing, virulence and toxins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb Pathog. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2014.07.008
Engel LS, Hill JM, Caballero AR, Green LC, O’Callaghan RJ (1998) Protease IV, a unique extracellular protease and virulence factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.27.16792
Filloux A, Ramos JL (eds) (2014) Pseudomonas methods and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa
Gellatly SL, Hancock REW (2013) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: new insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathog Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/2049-632x.12033
Jurado-Martín I, Sainz-Mejías M, McClean S (2021) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an audacious pathogen with an adaptable arsenal of virulence factors. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063128
Kariminik A, Baseri-Salehi M, Kheirkhah B (2017) Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing modulates immune responses: an updated review article. Immunol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2017.07.002
Khan F, Pham DTN, Oloketuyi SF, Kim YM (2019) Regulation and controlling the motility properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10201-w
Khodaparast S, Ghanbari F, Zamani H (2022) Evaluation of the effect of ibuprofen in combination with ciprofloxacin on the virulence-associated traits, and efflux pump genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03316-2
Lee J, Zhang L (2015) The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-014-0100-x
Lee J-H, Kim Y-G, Cho MH, Kim J-A, Lee J (2012) 7-fluoroindole as an antivirulence compound against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 329:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02500.x
Marshall J (2013) Quorum sensing. PANS. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1301432110
Mohsen A, Gomaa A, Mohamed F, Ragab R, Eid mennatallah, Ahmed AH, Khalaf A, Kamal M, Mokhtar S, Mohamed H, Salah I, Abbas R, Ali S, Mahmoud Abd El-Baky R (2015) Antibacterial, anti-biofilm activity of some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and N-acetyl cysteine against some biofilm producing uropathogens. Am J Epidemiol Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajeid-3-1-1
Olivares E, Badel-Berchoux S, Provot C, Prévost G, Bernardi T, Jehl F (2020) Clinical impact of antibiotics for the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02894
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Prithiviraj B, Bais HP, Weir T, Suresh B, Najarro EH, Dayakar BV, Schweizer HP, Vivanco JM (2005) Down regulation of virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by salicylic acid attenuates its virulence on Arabidopsis thaliana and Caenorhabditis elegans. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.73.9.5319-5328.2005
Rasamiravaka T, Labtani Q, Duez P, El Jaziri M (2015) The formation of biofilms by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a review of the natural and synthetic compounds interfering with control mechanisms. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/759348
Rastgar MG, Rasti B, Zamani H (2022) Ibuprofen involves with the reduced expression of pelD and pelF in pathogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02930-w
Rutherford ST, Bassler BL (2012) Bacterial quorum sensing: its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a012427
Saghalli M, Bidoki SK, Jamali A, Bagheri H, Ghaemi EA (2016) Subminimum inhibitory concentrations of zinc oxide nanoparticles reduce the expression of the Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin. Indian J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000181
Schuster M, Greenberg EPA (2006) network of networks: quorum-sensing gene regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Med Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.036
She P, Wang Y, Luo Z, Chen L, Tan R, Wang Y, Wu Y (2018) Meloxicam inhibits biofilm formation and enhances antimicrobial agents efficacy by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiologyopen. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.545
Shrout JD, Chopp DL, Just CL, Hentzer M, Givskov M, Parsek MR (2006) The impact of quorum sensing and swarming motility on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation is nutritionally conditional. Mol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05421.x
Sun E, Liu S, Hancock REW (2018) Surfing motility: a conserved yet diverse adaptation among motile bacteria. J Bacteriol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00394-18
Tacconelli E, Carrara E, Savoldi A, Harbarth S, Mendelson M, Monnet DL, et al (2018) Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30753-3
Thees AV, Pietrosimone KM, Melchiorre CK, Marden JN, Graf J, Lynes MA, Maltz-Matyschsyk M (2021) PmtA regulates pyocyanin expression and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.789765
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Zahmatkesh H, Mirpour M, Zamani H et al (2022) Effect of samarium oxide nanoparticles on virulence factors and motility of multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38:209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03384-4
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FE, DR, and Hossein Zahmatkesh: study design, lab experiments, computational analysis, data analysis, writing-original draft, writing & editing. Hojjatolah Zamani: supervision, study design, technical assistance, writing, verification, review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Esnaashari, F., Rostamnejad, D., Zahmatkesh, H. et al. In vitro and in silico assessment of anti-quorum sensing activity of Naproxen against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 244 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03690-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03690-5