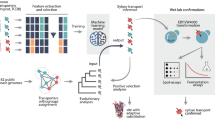
Abstract
The modification of gene expression is being researched in the production of useful chemicals by metabolic engineering of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. When the expression levels of many metabolic enzyme genes are modified simultaneously, the expression ratio of these genes becomes diverse; the relationship between the gene expression ratio and chemical productivity remains unclear. In other words, it is challenging to predict phenotypes from genotypes. However, the productivity of useful chemicals can be improved if this relationship is clarified. In this study, we aimed to construct a machine-learning model that can be used to clarify the relationship between gene expression levels and d-lactic acid productivity and predict the optimal gene expression level for efficient d-lactic acid production in yeast. A machine-learning model was constructed using data on d-lactate dehydrogenase and glycolytic genes expression (13 dimensions) and d-lactic acid productivity. The coefficient of determination of the completed machine-learning model was 0.6932 when using the training data and 0.6628 when using the test data. Using the constructed machine-learning model, we predicted the optimal gene expression level for high d-lactic acid production. We successfully constructed a machine-learning model to predict both d-lactic acid productivity and the suitable gene expression ratio for the production of d-lactic acid. The technique established in this study could be key for predicting phenotypes from genotypes, a problem faced by recent metabolic engineering strategies.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ali M (2020) PyCaret: an open source, low-code machine learning library in Python. PyCaret version 2. https://www.pycaret.org.
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Bhushan N, Mekhilef S, Tey KS et al (2022) Overview of model- and non-model-based online battery management systems for electric vehicle applications: a comprehensive review of experimental and simulation studies. Sustainability 14:15912. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315912
Caldeira AT, Arteiro JM, Roseiro JC et al (2011) An artificial intelligence approach to Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CCMI 1051 cultures: application to the production of anti-fungal compounds. Bioresour Technol 102:1469–1502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.07.080
Chen DC, Yang BC, Kuo TT (1992) One-step transformation of yeast in stationary phase. Curr Genet 21:83–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318659
Culley C, Vijayakumar S, Zampieri G, Angione C (2020) A mechanism-aware and multiomic machine-learning pipeline characterizes yeast cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:18869–18879. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2002959117
Gibson DG, Benders GA, Andrews-Pfannkoch C et al (2008) Complete chemical synthesis, assembly, and cloning of a Mycoplasma genitalium genome. Science 319(5867):1215–1220. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1151721
Guo Y, Dong J, Zhou T et al (2015) YeastFab: the design and construction of standard biological parts for metabolic engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e88. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv464
Hallborn J, Walfridsson M, Airaksinen U et al (1991) Xylitol production by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nat Biotechnol 9:1090–1095. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1191-1090
Hofvendahl K, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Factors affecting the fermentative lactic acid production from renewable resources. Enzyme Microb Technol 26:87–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(99)00155-6
Hong KK, Nielsen J (2012) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a key cell factory platform for future biorefineries. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:2671–2690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-0945-1
Ishida N, Suzuki T, Tokuhiro K et al (2006) D-Lactic acid production by metabolically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng 101:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.101.172
Jullesson D, David F, Pfleger B, Nielsen J (2015) Impact of synthetic biology and metabolic engineering on industrial production of fine chemicals. Biotechnol Adv 33:1395–1402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.02.011
Kaneko H (2018) Automatic outlier sample detection based on regression analysis and repeated ensemble learning. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 177:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2018.04.015
Kim SJ, Seo SO, Jin YS, Seo JH (2013) Production of 2, 3-butanediol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 146:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.081
Konishi M (2020) Bioethanol production estimated from volatile compositions in hydrolysates of lignocellulosic biomass by deep learning. J Biosci Bioeng 129:723–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2020.01.006
Lennen RM, Pfleger BF (2012) Engineering Escherichia coli to synthesize free fatty acids. Trends Biotechnol 30:659–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.09.006
Lian J, Zhao H (2017) Recent advances in biosynthesis of fatty acids derived products in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via enhanced supply of precursor metabolites. J Ind Microb Biotechnol 42:437–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1518-0
Matsuda F, Ishii J, Kondo T et al (2013) Increased isobutanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by eliminating competing pathways and resolving cofactor imbalance. Microb Cell Fact 12:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-12-119
Mitsui R, Yamada R, Ogino H (2019) CRISPR system in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its application in the bioproduction of useful chemicals. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2688-8
Mitsui R, Nishikawa R, Yamada R et al (2020) Construction of yeast producing patchoulol by global metabolic engineering strategy. Biotechnol Bioeng 117:1348–1356. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27284
Mitsui R, Yamada R, Matsumoto T, Ogino H (2022) Bioengineering for the industrial production of 2,3-butanediol by the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38:38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03224-x
Quinlan JR (1986) Induction of decision trees. Mach Learn 1:81–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116251
Rossi G, Sauer M, Porro D, Branduardi P (2010) Effect of HXT1 and HXT7 hexose transporter overexpression on wild-type and lactic acid producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Microb Cell Fact 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-9-15
Sakai A, Shimizu Y, Hishinuma F (1990) Integration of heterologous genes into the chromosome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a delta sequence of yeast retrotransposon Ty. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33:302–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164526
Schaaff I, Heinisch J, Zimmermann FK (1989) Overproduction of glycolytic enzymes in yeast. Yeast 5:285–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.320050408
Silva R, Ferreira S, Bonifácio MJ et al (2012) Optimization of fermentation conditions for the production of human soluble catechol-O-methyltransferase by Escherichia coli using artificial neural network. J Biotechnol 160:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.03.025
Tanino T, Ito T, Ogino C et al (2012) Sugar consumption and ethanol fermentation by transporter-overexpressed xylose-metabolizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae harboring a xyloseisomerase pathway. J Biosci Bioeng 114:209–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.03.004
Tsai ER, Demirtas D, Hoogendijk N et al (2022) Turnaround time prediction for clinical chemistry samples using machine learning. Clin Chem Lab Med 60:1902–1910. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2022-0668
Wang G, Björk SM, Huang M et al (2019) RNAi expression tuning, microfluidic screening, and genome recombineering for improved protein production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:9324–9332. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820561116
Yamada R, Taniguchi N, Tanaka T (2010) Cocktail δ-integration: a novel method to construct cellulolytic enzyme expression ratio-optimized yeast strains. Microb Cell Fact 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-9-32
Yamada R, Wakita K, Mitsui R, Ogino H (2017a) Enhanced d-lactic acid production by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae following optimization of the global metabolic pathway. Biotechnol Bioeng 114:2075–2084. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26330
Yamada R, Wakita K, Mitsui R et al (2017b) Efficient production of 2,3-butanediol by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae through modulation of gene expression by cocktail δ-integration. Bioresour Technol 245:1558–1566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.034
Yamada R, Wakita K, Ogino H (2017c) Global metabolic engineering of glycolytic pathway via multicopy integration in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. ACS Synth Biol 6:659–666. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.6b00281
Yamada R, Yamauchi A, Ando Y et al (2018) Modulation of gene expression by cocktail δ-integration to improve carotenoid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 268:616–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.044
Yeo IK, Richard AJ (2000) A new family of power transformations to improve normality or symmetry. Biometrika 87:954–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/87.4.954
Zhou Y, Li G, Dong J et al (2018) MiYA, an efficient machine-learning workflow in conjunction with the YeastFab assembly strategy for combinatorial optimization of heterologous metabolic pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 47:294–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.03.020
Funding
This study was partly supported by JST PRESTO (JPMJPR20KB) and JSPS KAKENHI (JP22H03803). We would like to thank Editage for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Y.: Investigation and writing the original draft. R.Y.: conceptualization, investigation, writing the original draft, supervision, and funding acquisition. T.M.: supervision. H.O.: supervision. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, Y., Yamada, R., Matsumoto, T. et al. Construction of a machine-learning model to predict the optimal gene expression level for efficient production of d-lactic acid in yeast. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 69 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03515-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03515-x