Abstract
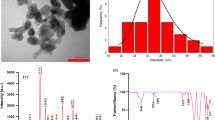
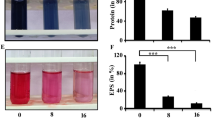
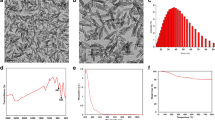
Biofilm formation and quorum sensing (QS) dependent virulence factors are considered the major causes of the emergence of drug resistance, therapeutic failure and development of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. This study aimed to investigate the effects of samarium oxide nanoparticles (Sm2O3NPs) on biofilm, virulence factors, and motility of multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. Sm2O3NPs were synthesized using curcumin and characterized by Transmission Electron Microscopy, X-ray diffractometer, Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy, and Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was determined using broth microdilution method. The antibiofilm potential of Sm2O3NPs was also evaluated by crystal violet staining and light microscopy examination. Then, the effect of sub-MICs concentrations of Sm2O3NPs on the proteolytic and hemolytic activities of P. aeruginosa was investigated. Finally, the effect of Sm2O3NPs on various types of motility including swarming, swimming, and twitching was studied. Our results showed that Sm2O3NPs significantly inhibited biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa by 49–61%. Additionally, sub-MICs concentrations of Sm2O3NPs effectively decreased virulence factors including pyocyanin (33–55%), protease (24–45%), and hemolytic activity (22–41%). Moreover, swarming, swimming, and twitching motility remarkably was reduced after exposure to the NPs. The findings of this work showed that Sm2O3NPs have a high potential in inhibiting QS-dependent virulence of P. aeruginosa, which could be considered for antibacterial chemotherapy after further characterization.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The majority of the data used to support the findings of this study were included in the manuscript. In addition, the additional data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aderibigbe B (2017) Metal-based nanoparticles for the treatment of infectious diseases. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081370
Alatraktchi FA, Svendsen WE, Molin S (2020) Electrochemical detection of pyocyanin as a biomarker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a focused review. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185218
Ali SG, Ansari MA, Alzohairy MA, Alomary MN, Jalal M, AlYahya S, Asiri SMM, Khan HM (2020) Effect of biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles on multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050260
Ansari MA, Khan HM, Khan AA, Cameotra SS, Pal R (2013) Antibiofilm efficacy of silver nanoparticles against biofilm of extended spectrum β-lactamase isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-013-0266-1
Antunes LCM, Ferreira RBR, Buckner MMC, Finlay BB (2010) Quorum sensing in bacterial virulence. Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.038794-0
Asmi H, Bentayeb F, Bouzekraoui Y, Bonutti F (2020) Optimization of scatter correction method in samarium-153 single-photon emission computed tomography using triple-energy window: a Monte Carlo simulation study. Indian J Nucl Med. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_11_20
Axelrad I, Safrin M, Cahan R, Suh SJ, Ohman DE, Kessler E (2021) Extracellular proteolytic activation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa aminopeptidase (PaAP) and insight into the role of its non-catalytic N-terminal domain. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252970
Boles BR, Thoendel M, Singh PK (2005) Rhamnolipids mediate detachment of Pseudomonas aeruginosafrom biofilms. Mol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04743.x
Bradshaw JL, Caballero AR, Bierdeman MA, Adams KV, Pipkins HR, Tang A, O’Callaghan RJ, McDaniel LS (2018) Pseudomonas aeruginosa protease IV exacerbates pneumococcal pneumonia and systemic disease. mSphere. https://doi.org/10.1128/msphere.00212-18
Burrows LL (2012) Pseudomonas aeruginosa twitching motility: type IV pili in action. Annu Rev Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150055
Chang CY, Krishnan T, Wang H, Chen Y, Yin WF, Chong YM, Tan LY, Chong TM, Chan KG (2014) Non-antibiotic quorum sensing inhibitors acting against N-acyl homoserine lactone synthase as druggable target. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07245
Choi O, Deng KK, Kim NJ, Ross L Jr, Surampalli RY, Hu Z (2008) The inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles, silver ions, and silver chloride colloids on microbial growth. Water Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.02.021
Ciofu O, Tolker-Nielsen T (2019) Tolerance and resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to antimicrobial agents—how P. aeruginosa can escape antibiotics. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00913
CLSI (2018) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; CLSI supplement M100, 28th edn. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Colvin KM, Gordon VD, Murakami K, Borlee BR, Wozniak DJ, Wong GCL, Parsek MR (2011) The Pel polysaccharide can serve a structural and protective role in the biofilm matrix of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001264
Crompton R, Williams H, Ansell D, Campbell L, Holden K, Cruickshank S, Hardman MJ (2016) Oestrogen promotes healing in a bacterial LPS model of delayed cutaneous wound repair. Lab Investig. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2015.160
Das S, Dash HR (2014) Microbial biotechnology—a laboratory manual for bacterial systems. Springer, New Delhi
Defoirdt T, Boon N, Bossier P (2010) Can bacteria evolve resistance to quorum sensing disruption? PLoS Pathog. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000989
Diggle SP, Stacey RE, Dodd C, Camara M, Williams P, Winzer K (2006) The galactophilic lectin, LecA, contributes to biofilm development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.001001.x
Dusane DH, Zinjarde SS, Venugopalan VP, Mclean RJ, Weber MM, Rahman PKSM (2010) Quorum sensing: implications on Rhamnolipid biosurfactant production. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/02648725.2010.10648149
Engel LS, Hill JM, Caballero AR, Green LC, O’Callaghan RJ (1998) Protease IV, a unique extracellular protease and virulence factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.27.16792
Filloux A, Ramos JL (eds) (2014) Pseudomonas methods and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa
Fischbach MA, Walsh CT (2009) Antibiotics for emerging pathogens. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1176667
Ghafoor A, Hay ID, Rehm BHA (2011) Role of exopolysaccharides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and architecture. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00637-11
Guilger-Casagrande M, de Lima R (2019) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by fungi: a review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00287
Haiko J, Westerlund-Wikström B (2013) The role of the bacterial flagellum in adhesion and virulence. Biology. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2041242
Husain FM, Ahmad I, Al-thubiani AS, Abulreesh HH, AlHazza IM, Aqil F (2017) Leaf extracts of Mangifera indica L. inhibit quorum sensing—regulated production of virulence factors and biofilm in test bacteria. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00727
Ibáñez de Aldecoa AL, Zafra O, González-Pastor JE (2017) Mechanisms and regulation of extracellular DNA release and its biological roles in microbial communities. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01390
Iravani S, Varma RS (2020) Sustainable synthesis of cobalt and cobalt oxide nanoparticles and their catalytic and biomedical applications. Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0gc00885k
Kazmierczak BI, Schniederberend M, Jain R (2015) Cross-regulation of Pseudomonas motility systems: the intimate relationship between flagella, pili and virulence. Curr Opin Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2015.07.017
Kearns DB (2010) A field guide to bacterial swarming motility. Nat Rev Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2405
Khan F, Pham DTN, Oloketuyi SF, Kim YM (2019a) Regulation and controlling the motility properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10201-w
Khan F, Manivasagan P, Lee JW, Pham D, Oh J, Kim YM (2019b) Fucoidan-stabilized gold nanoparticle-mediated biofilm inhibition, attenuation of virulence and motility properties in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mar Drugs. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040208
Khan F, Kang MG, Jo DM, Chandika P, Jung WK, Kang HW, Kim YM (2021) Phloroglucinol-gold and -zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibiofilm and antivirulence activities towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mar Drugs. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110601
Lee K, Yoon SS (2017) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm, a programmed bacterial life for fitness. J Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1611.11056
Ma L, Wang J, Wang S, Anderson EM, Lam JS, Parsek MR, Wozniak DJ (2012) Synthesis of multiple Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix exopolysaccharides is post-transcriptionally regulated. Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02753.x
Marshall J (2013) Quorum sensing. PANS. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1301432110
Mattick JS (2002) Type IV pili and twitching motility. Annu Rev Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160938
Mulcahy H, Charron-Mazenod L, Lewenza S (2010) Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces an extracellular deoxyribonuclease that is required for utilization of DNA as a nutrient source. Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02208.x
Nabeel AI (2020) Samarium enriches antitumor activity of ZnO nanoparticles via downregulation of CXCR4 receptor and cytochrome P450. Tumour Biol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428320909999
Nallathamby PD, Lee KJ, Desai T, Xu XHN (2010) Study of the multidrug membrane transporter of single living Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells using size-dependent plasmonic nanoparticle optical probes. Biochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi100268k
Olivares E, Badel-Berchoux S, Provot C, Prévost G, Bernardi T, Jehl F (2020) Clinical impact of antibiotics for the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02894
Otton LM, Campos MS, Meneghetti KL, Corção G (2017) Influence of twitching and swarming motilities on biofilm formation in Pseudomonas strains. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1344-7
Padwal P, Bandyopadhyaya R, Mehra S (2014) Polyacrylic acid-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for targeting drug resistance in mycobacteria. Langmuir. https://doi.org/10.1021/la503808d
Pang Z, Raudonis R, Glick BR, Lin TJ, Cheng Z (2019) Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol Adv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.013
Prithiviraj B, Bais HP, Weir T, Suresh B, Najarro EH, Dayakar BV, Schweizer HP, Vivanco JM (2005) Down regulation of virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by salicylic acid attenuates its virulence on Arabidopsis thaliana and Caenorhabditis elegans. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.73.9.5319-5328.2005
Qais FA, Ahmad I, Altaf M, Manoharadas S, Al-Rayes BF, Ali Abuhasil MS, Almaroai YA (2021) Biofabricated silver nanoparticles exhibit broad-spectrum antibiofilm and antiquorum sensing activity against Gram-negative bacteria. RSC Adv. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra00488c
Rasamiravaka T, Labtani Q, Duez P, El Jaziri M (2015) The formation of biofilms by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a review of the natural and synthetic compounds interfering with control mechanisms. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/759348
Sadikot RT, Blackwell TS, Christman JW, Prince AS (2005) Pathogen–host interactions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200408-1044so
Saeki EK, Yamada AY, de Araujo LA, Anversa L, Garcia D de O, de Souza RLB, Martins HM, Kobayashi RKT, Nakazato G (2021) Subinhibitory concentrations of biogenic silver nanoparticles affect motility and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.656984
Saghalli M, Bidoki SK, Jamali A, Bagheri H, Ghaemi EA (2016) Sub-minimum inhibitory concentrations of zinc oxide nanoparticles reduce the expression of the Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin. Indian J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000181
Schuster M, Peter Greenberg E (2006) A network of networks: quorum-sensing gene regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Med Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.036
Shkodenko L, Kassirov I, Koshel E (2020) Metal oxide nanoparticles against bacterial biofilms: perspectives and limitations. Microorganisms. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101545
Shrout JD, Chopp DL, Just CL, Hentzer M, Givskov M, Parsek MR (2006) The impact of quorum sensing and swarming motility on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation is nutritionally conditional. Mol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05421.x
Sun E, Liu S, Hancock REW (2018) Surfing motility: a conserved yet diverse adaptation among motile bacteria. J Bacteriol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00394-18
Tan RM, Kuang Z, Hao Y, Lau GW (2014) Type IV pilus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa confers resistance to antimicrobial activities of the pulmonary surfactant protein-A. J Innate Immun. https://doi.org/10.1159/000354304
Thi MTT, Wibowo D, Rehm BHA (2020) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228671
Tielker D, Hacker S, Loris R, Strathmann M, Wingender J, Wilhelm S, Rosenau F, Jaeger KE (2005) Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectin LecB is located in the outer membrane and is involved in biofilm formation. Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27701-0
Tredget EE, Shankowsky HA, Rennie R, Burrell RE, Logsetty S (2004) Pseudomonas infections in the thermally injured patient. Burns. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2003.08.007
Velsankar K, Sudhahar S, Parvathy G, Kaliammal R (2020) Effect of cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of biosynthesis of ZnO hexagonal shaped nanoparticles by Echinochloa frumentacea grains extract as a reducing agent. Mater Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121976
Wilson R, Pitt T, Taylor G, Watson D, MacDermot J, Sykes D, Roberts D, Cole P (1987) Pyocyanin and 1-hydroxyphenazine produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibit the beating of human respiratory cilia in vitro. J Clin Investig. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci112787
Yang L, Nilsson M, Gjermansen M, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T (2009) Pyoverdine and PQS mediated subpopulation interactions involved in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Mol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06934.x
Zahmatkesh H, Mirpour M, Zamani H, Rasti B (2022) Effect of samarium oxide nanoparticles fabricated by curcumin on efflux pump and virulence genes expression in MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. J Clust Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02274-x
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hossein Zahmatkesh: Study design, Lab experiments, Data analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing & editing; Hojjatolah Zamani: Experimental design, Supervision, Technical assistance, Writing, Verification, Review & Editing; MM & BR: Study design, Supervision; FAR: Preparation of Blood Agar, NP: Drafted part of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zahmatkesh, H., Mirpour, M., Zamani, H. et al. Effect of samarium oxide nanoparticles on virulence factors and motility of multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 209 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03384-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03384-4