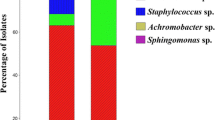
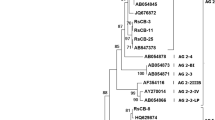
Abstract
The effect of rhizobacterium Burkholderia sp. strain R456 on the inhibition of Rhizoctonia solani, sheath blight of rice was examined. Results from this study indicated that strain R456 not only suppressed the in vitro mycelial growth of R. solani, but also reduced the incidence and severity of rice sheath blight under greenhouse conditions. However, similar to plant pathogenic strain LMG 1222T of Burkholderia cepacia, the type species of the genus, infiltration of tobacco leaves with cell suspension of strain R456 resulted in typical hypersensitivity reactions while the two bacterial strains were unable to cause disease symptoms on rice seedlings. The fatty acid methyl ester profile, sole carbon source utilization, and biochemical tests confirmed that the antagonistic rhizobacterium R456 is a member of the genus Burkholderia. Furthermore, strain R456 was differentiated from B. cepacia LMG 1222T and was identified as Burkholderia seminalis based on recA gene sequence analysis and multilocus sequence typing. In addition, this rhizobacterium had a lower proteolytic activity compared with that of the pathogenic B. cepacia LMG 1222T while no cblA and esmR marker genes were detected for the two bacterial strains. Overall, this is the first characterization of rhizobacterium B. seminalis that protected rice seedlings from infection by R. solani.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin A, Mahenthiralingam E, Thickett KM, Honeybourne D, Maiden MCJ, Govan JR, Speert DP, LiPuma JJ, Vandamme P, Dowson CG (2005) Multilocus sequence typing scheme that provides both species and strain differentiation for the Burkholderia cepacia complex. J Clin Microbiol 43:4665–4673. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.9.4665-4673.2005
Chumthong A, Kanjanamaneesathian M, Pengnoo A, Wiwattanapatapee R (2008) Water-soluble granules containing Bacillus megaterium for biological control of rice sheath blight: formulation, bacterial viability and efficacy testing. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:2499–2507. doi:10.1007/s11274-008-9774-7
Coenye T, Vandamme P (2003) Diversity and significance of Burkholderia species occupying diverse ecological niches. Environ Microbiol 5:719–729. doi:10.1046/j.1462-2920.2003.00471.x
De Costa DM, Samarasinghe SST, Dias HRD, Dissanayake DMN (2008) Control of rice sheath blight by phyllosphere epiphytic microbial antagonists. Phytoparasitica 36:52–65
Fain MG, Haddock JD (2001) Phenotypic and phylogenetic characterization of Burkholderia (Pseudomonas) sp. strain LB400. Curr Microbiol 42:269–275. doi:10.1007/s002840110216
Fang Y, Zhang LX, Xie GL (2007) Internal bacterial rot of onion bulbs caused by Burkholderia cepacia in China. J Plant Pathol 89:304
Fang Y, Li B, Wang F, Liu BP, Wu ZY, Qiu W, Xie GL (2009) Bacterial fruit rot of apricot caused by Burkholderia cepacia in China. Plant Pathol J 25:429–432
Fang Y, Lou MM, Li B, Xie GL, Wang F, Zhang LX, Luo YC (2010) Characterization of Burkholderia cepacia complex from cystic fibrosis patients in China and their chitosan susceptibility. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:443–450. doi:10.1007/s11274-009-0187-z
Gingues S, Kooi C, Visser MB, Subsin B, Sokol PA (2005) Distribution and expression of the ZmpA metalloprotease in the Burkholderia cepacia complex. J Bacteriol 187:8247–8255
Henry DA, Mahenthiralingam E, Vandamme P, Coenye T, Speert DP (2001) Phenotypic methods for determining genomovar status of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. J Clin Microbiol 39:1073–1078. doi:10.1128/JCM.39.3.1073-1078.2001
Jacobs JL, Fasi AC, Ramette A, Smith JJ, Hammerschmidt R, Sundin GW (2008) Identification and onion pathogenicity of Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates from the onion rhizosphere and onion field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3121–3129. doi:10.1128/AEM.01941-07
Jolley KA, Chan MS, Maiden MC (2004) mlstdbNet–distributed multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) databases. BMC Bioinformatics 5:86. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-5-86
Lawongsa P, Boonkerd N, Wongkaew S, O’Gara F, Teaumroong N (2008) Molecular and phenotypic characterization of potential plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas from rice and maize rhizospheres. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1877–1884. doi:10.1007/s11274-008-9685-7
Li B, Xie GL, Zhang JZ, Janssens D, Swings J (2006) Identification of the bacterial leaf spot pathogen of poinsettia in China. J Phytopathol 154:711–715. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0434.2006.01178.x
Li B, Xu LH, Lou MM, Li F, Zhang YD, Xie GL (2008) Isolation and characterization of antagonistic bacteria against bacterial leaf spot of Euphorbia pulcherrima. Lett Appl Microbiol 46:450–455. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2008.02337.x
Li B, Yu RR, Yu SH, Qiu W, Fang Y, Xie GL (2009) First report on bacterial heart rot of garlic caused by Pseudomonas fluorescens in China. Plant Pathol J 25:91–94
Li B, Fang Y, Zhang GQ, Yu RR, Lou MM, Xie GL, Wang YL, Sun GC (2010) Molecular characterization of Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates causing bacterial fruit rot of apricot. Plant Pathol J 26:223–230
Ludovic V, Groleau MC, Dekimpe V, Deziel E (2007) Burkholderia diversity and versatility: an inventory of the extracellular products. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:1407–1429
Mahenthiralingam E, Bischof J, Byrne SK, Radomski C, Davies JE, Av-Gay Y, Vandamme P (2000) DNA-based diagnostic approaches for identification of Burkholderia cepacia complex, Burkholderia vietnamiensis, Burkholderia multivorans, Burkholderia stabilis, and Burkholderia cepacia genomovars I and III. J Clin Microbiol 38:3165–3173
Mahenthiralingam E, Baldwin A, Dowson CG (2008) Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria: opportunistic pathogens with important natural biology. J Appl Microbiol 104:1539–1551. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03706.x
Padaria JC, Singh A (2009) Molecular characterization of soil bacteria antagonistic to Rhizoctonia solani, sheath blight of rice. J Environ Sci Heal B 44:397–402
Payne GW, Vandamme P, Morgan SH, LiPuma JJ, Coenye T, Weightman AJ, Hefin Jones T, Mahenthiralingam E (2005) Development of a recA gene-based identification approach for the entire Burkholderia genus. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3917–3927. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.7.3917-3927.2005
Pengnoo A, Wiwattanapattapee R, Chumthong A, Kanjanamaneesathian M (2006) Bacterial antagonist as seed treatment to control leaf blight disease of bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:9–14. doi:10.1007/s11274-005-2820-9
Perin L, Martínez-Aguilar L, Castro-González R, Estrada-de los Santos P, Cabellos-Avelar T, Guedes HV, Reis VM, Caballero-Mellado J (2006) Diazotrophic Burkholderia species associated with field-grown maize and sugarcane. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3103–3110. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.5.3103-3110.2006
Ren HY, Gu GY, Long JY, Yin Q, Wu TQ, Song T, Zhang SJ, Chen ZY, Dong HS (2006) Combinative effects of a bacterial type-III effector and a biocontrol bacterium on rice growth and disease resistance. J Biosci 31:617–627
Saikia R, Kumar R, Arora DK, Gogoi DK, Azad P (2006) Pseudomonas aeruginosa inducing rice resistance against Rhizoctonia solani: production of salicylic acid and peroxidases. Folia Microbiol 51:375–380
Schaad NW, Jones JB, Chun W (2001) Laboratory guide for identification of plant pathogenic bacteria, 3rd edn. American Phytopathological Society, Minnesota
Sexton MM, Jones AL, Chaowagul W, Woods DE (1994) Purification and characterization of a protease from Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Can J Microbiol 40:903–910
Sokol PA, Ohman DE, Iglewski BH (1979) A more sensitive plate assay for detection of protease production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol 9:538–540
Stanier RY, Palleroni NJ, Doudoroff M (1966) The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol 43:159–271. doi:10.1099/00221287-43-2-159
Stead DE (1992) Grouping of plant-pathogenic bacteria and some other Pseudornonas spp. by using cellular fatty acid profiles. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:281–295
Vanlaere E, LiPuma JJ, Baldwin A, Henry D, Brandt ED, Mahenthiralingam E, Speert DP, Dowson C, Vandamme P (2008) Burkholderia latens sp. nov., Burkholderia diffusa sp. nov., Burkholderia arboris sp. nov., Burkholderia seminalis sp. nov. and Burkholderia metallica sp. nov., novel species within the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1580–1590. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65634-0
Vanlaere E, Baldwin A, Gevers D, Henry D, Brandt ED, LiPuma JJ, Mahenthiralingam E, Speert DP, Dowson C, Vandamme P (2009) Taxon K, a complex within the Burkholderia cepacia complex, comprises at least two novel species: Burkholderia contaminans sp. Nov. and Burkholderia lata sp. Nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:102–111. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.001123-0
Vermis K, Coenye T, Mahenthiralingam E, Nelis HJ, Vandamme P (2002) Evaluation of species-specific recA-based PCR tests for genomovar level identification within the Burkholderia cepacia complex. J Med Microbiol 51:937–940
Wiwattanapatapee R, Chumthong A, Pengnoo A, Kanjanamaneesathian A (2007) Effervescent fast-disintegrating bacterial fortnulation for biological control of rice sheath blight. J Control Release 119:229–235. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.01.015
Yabuuchi E, Kosako Y, Oyaizu H, Yano I, Hotta H, Hashimoto Y, Ezaki T, Arakawa M (1992) Proposal of Burkholderia gen. nov. and transfer of seven species of the genus Pseudomonas homology group II to the new genus, with the type species Burkholderia cepacia (Palleroni and Holmes 1981) comb. nov. Microbiol Immunol 36:1251–1275
Yang DJ, Wang B, Wang JX, Chen Y, Zhou MG (2009) Activity and efficacy of Bacillus subtilis strain NJ-18 against rice sheath blight and Sclerotinia stem rot of rape. Biol Control 51:61–65. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2009.05.021
Yu YM, Zhao BP, Gao HR, Wu HT, Yu M (2010) Restraining effect of biological controlling strain R13 on rice sheath blight. Heilongjiang Agricult Sci 1:3–4
Zhang LX, Xie GL (2007) Diversity and distribution of Burkholderia cepacia complex in the rhizosphere of rice and maize. FEMS Microbiol Lett 266:231–235. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00530.x
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Y3090150), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYJD09022), Zhejiang Provincial Project (2010R10091), the Agricultural Ministry of China (nyhyzx07-056; nyhyzx200803010) and Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20090101120083).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Liu, BP., Yu, RR. et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of rhizobacterium Burkholderia sp. strain R456 antagonistic to Rhizoctonia solani, sheath blight of rice. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 2305–2313 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0696-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0696-4