Abstract
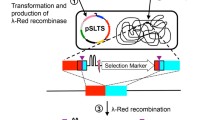
A simple and general method for disrupting chromosomal genes and introducing insertions is described. This procedure involves eliminating wild-type bacterial genes and introducing mutant alleles or other insertions at the original locus of the wild-type gene. To demonstrate the utility of this approach, the tig gene of Escherichia coli was replaced by homologous recombination with a cassette containing the chloramphenicol resistance gene and the sacB gene. The cassette was then removed and the tig mutant alleles were moved into the native tig location. Sequencing and Western blotting results demonstrated that insertions or deletions can be introduced precisely in E. coli using our approach. Our system does not require extra in vitro manipulations such as restriction digestion or ligation, and does not require use of specific plasmids or strains which are used to prevent false positive transformants caused by template plasmid transformation. This technique can be used widely in bacterial genome analysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba T, Ara T, Hasegawa M, Takai Y, Okumura Y, Baba M, Datsenko KA, Tomita M, Wanner BL, Mori H (2006) Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol Syst Biol 2:8
Baram D, Pyetan E, Sittner A, Auerbach-Nevo T, Bashan A, Yonath A (2005) Structure of trigger factor binding domain in biologically homologous complex with eubacterial ribosome reveals its chaperone action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:12017–12022
Court DL, Sawitzke JA, Thomason LC (2002) Genetic engineering using homologous recombination. Annu Rev Genet 36:361–388
Dabert P, Smith GR (1997) Gene replacement with linear DNA fragments in wild-type Escherichia coli: enhancement by Chi sites. Genetics 145:877–889
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645
Doublet B, Douard G, Targant H, Meunier D, Madec JY, Cloeckaert A (2008) Antibiotic marker modifications of lambda Red and FLP helper plasmids, pKD46 and pCP20, for inactivation of chromosomal genes using PCR products in multidrug-resistant strains. J Microbiol Methods 75:359–361
El Karoui M, Amundsen SK, Dabert P, Gruss A (1999) Gene replacement with linear DNA in electroporated wild-type Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 27:1296–1299
Ellermeier CD, Janakiraman A, Slauch JM (2002) Construction of targeted single copy lac fusions using lambda Red and FLP-mediated site-specific recombination in bacteria. Gene 290:153–161
Fan DJ, Ding YW, Pan XM, Zhou JM (2008) Thermal unfolding of Escherichia coli trigger factor studied by ultra-sensitive differential scanning calorimetry. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:1728–1734
Fan DJ, Ding YW, Zhou JM (2009) Structural rearrangements and the unfolding mechanism of a Trigger Factor mutant studied by multiple structural probes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794:944–952
Hamilton CM, Aldea M, Washburn BK, Babitzke P, Kushner SR (1989) New method for generating deletions and gene replacements in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 171:4617–4622
Hesterkamp T, Deuerling E, Bukau B (1997) The amino-terminal 118 amino acids of Escherichia coli trigger factor constitute a domain that is necessary and sufficient for binding to ribosomes. J Biol Chem 272:21865–21871
Imam AM, Patrinos GP, de Krom M, Bottardi S, Janssens RJ, Katsantoni E, Wai AW, Sherratt DJ, Grosveld FG (2000) Modification of human beta-globin locus PAC clones by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 28:E65
Kao KC, Tran LM, Liao JC (2005) A global regulatory role of gluconeogenic genes in Escherichia coli revealed by transcriptome network analysis. J Biol Chem 280:36079–36087
Lalioti M, Heath J (2001) A new method for generating point mutations in bacterial artificial chromosomes by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 29:E14
Link AJ, Phillips D, Church GM (1997) Methods for generating precise deletions and insertions in the genome of wild-type Escherichia coli: application to open reading frame characterization. J Bacteriol 179:6228–6237
Liu CP, Zhou JM (2004) Trigger factor-assisted folding of bovine carbonic anhydrase II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:509–515
Merz F, Hoffmann A, Rutkowska A, Zachmann-Brand B, Bukau B, Deuerling E (2006) The C-terminal domain of Escherichia coli trigger factor represents the central module of its chaperone activity. J Biol Chem 281:31963–31971
Muyrers JP, Zhang Y, Testa G, Stewart AF (1999) Rapid modification of bacterial artificial chromosomes by ET-recombination. Nucleic Acids Res 27:1555–1557
Oswald W, Tonpitak W, Ohrt G, Gerlach G (1999) A single-step transconjugation system for the introduction of unmarked deletions into Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 7 using a sucrose sensitivity marker. FEMS Microbiol Lett 179:153–160
Posfai G, Kolisnychenko V, Bereczki Z, Blattner FR (1999) Markerless gene replacement in Escherichia coli stimulated by a double-strand break in the chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res 27:4409–4415
Quandt J, Hynes MF (1993) Versatile suicide vectors which allow direct selection for gene replacement in gram-negative bacteria. Gene 127:15–21
Stoller G, Tradler T, Rucknagel KP, Rahfeld JU, Fischer G (1996) An 11.8 kDa proteolytic fragment of the E. coli trigger factor represents the domain carrying the peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase activity. FEBS Lett 384:117–122
Sun W, Wang S, Curtiss R III (2008) Highly efficient method for introducing successive multiple scarless gene deletions and markerless gene insertions into the Yersinia pestis chromosome. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:4241–4245
Uzzau S, Figueroa-Bossi N, Rubino S, Bossi L (2001) Epitope tagging of chromosomal genes in Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:15264–15269
Yu D, Ellis HM, Lee EC, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Court DL (2000) An efficient recombination system for chromosome engineering in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5978–5983
Zarnt T, Tradler T, Stoller G, Scholz C, Schmid FX, Fischer G (1997) Modular structure of the trigger factor required for high activity in protein folding. J Mol Biol 271:827–837
Zhang XM, Huang JD (2003) Combination of overlapping bacterial artificial chromosomes by a two-step recombinogenic engineering method. Nucleic Acids Res 31:e81
Zhang Y, Buchholz F, Muyrers JP, Stewart AF (1998) A new logic for DNA engineering using recombination in Escherichia coli. Nat Genet 20:123–128
Zhang Y, Muyrers JP, Testa G, Stewart AF (2000) DNA cloning by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 18:1314–1317
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Professor B. Wanner and the Coli Genetics Stock Center (CGSC) for the gift of plasmids and strains. This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30800548), a CAS Knowledge Innovation Grant (KSCX2-SW214-3) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (MOST, No.2007AA021405). The authors would like to thank Dr. Joy Fleming for her critical reading of this paper and helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Qi-Ming Zhou, Dong-Jie Fan have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, QM., Fan, DJ., Xie, JB. et al. A method for generating precise gene deletions and insertions in Escherichia coli . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 1323–1329 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0305-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0305-y