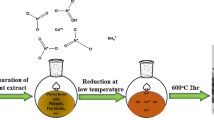
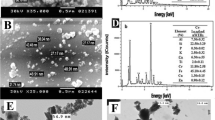
Abstract
Despite several technological advances and breakthroughs wastewater treatment continue to be a major problem on a world basis. Here, in this work we synthesised cerium oxide nanoparticles for the removal of chromium, lead and cadmium ions from water. Cerium oxide nanoparticles have been synthesized from Pisum sativum pods extract by the green synthesis route and characterized by various instrumental techniques like double beam UV-Visible spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer. Further, the effects of several factors, like adsorbent dose, ion concentration, pH, contact time are also studied through batch adsorption experiments. We also studied pseudo second order and pseudo first order kinetics model. The qmax values for the elimination of Pb(II), Cr(VI), and Cd(II) was calculated to be 100, 125 and 100mg/g respectively. The maximum elimination of lead and cadmium ions were observed at pH 6 and the maximum removal percentage of chromium was observed at pH 3. Based on our results, it concluded that, the synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticles could be used to treat water for better adsorbent.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated during this study are included in this manuscript.
References
Al-Rashdi, B. A. M., Johnson, D. J., & Hilal, N. (2013). Removal of heavy metal ions by nano filtration. Desalination, 315, 2–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.05.022
Altaf, M., Manoharadas, S., & Zeyad, M. T. (2021). Green synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Acorus calamus extract and their antibiofilm activity against bacterial pathogens. Microscopy Research and Technique, 84(8), 1638–1648.
Alvand, M., & Shemirani, F. (2016). Fabrication of Fe 3 O 4@ graphene oxide core-shell nanospheres for ferrofluid-based dispersive solid phase extraction as exemplified for Cd (II) as a model analyte. Microchimica Acta, 183, 1749–1757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-18058
Amarendra, D. D. (2010). Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Chenopodium album leaf extracts. Colloids Surf., A, 369(3), 27–33.
Arumugam, A., Karthikeyan, C., Hameed, A. S. H., Gopinath, K., Gowri, S., & Karthika, V. (2015). Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. leaf extract and their structural, optical and antibacterial properties. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 49, 408–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.042
Boeykens, S. P., Piol, M. N., Legal, L. S., Saralegui, A. B., & Vázquez, C. (2017). Eutrophication decrease: phosphate adsorption processes in presence of nitrates. Journal of Environmental Management, 203, 888–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.026
Ekka, B., Rout, L., Kumar, M. K. S. A., Patel, R. K., & Dash, P. (2015). Removal efficiency of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ionic liquid mediated mesoporous silica. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3(2), 1356–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.12.004
Espinoza-Sanchez, M. A., Arevalo-Nino, K., Quintero-Zapata, I., Castro-Gonzalez, I., & Almaguer-Cantu, V. (2019). Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solution by fungal bioremediation based using Rhizopus sp. Journal of Environmental Management, 251, 109595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109595
Gong, R., Zhu, S., Zhang, D., Chen, J., Ni, S., & Guan, R. (2008). Adsorption behavior of cationic dyes on citric acid esterifying wheat straw: kinetic and thermodynamic profile. Desalination, 230(1-3), 220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.12.002
Guo, X., Du, B., Wei, Q., Yang, J., Hu, L., Yan, L., & Xu, W. (2014). Synthesis of amino functionalized magnetic graphenes composite material and its application to remove Cr (VI), Pb (II), Hg (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) from contaminated water. Journal of hazardous materials, 278, 211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.075
Hashemzadeh, M., Nilchi, A., & Hassani, A. H. (2019). Synthesis of novel surface-modified hematite nanoparticles for lead ions removal from aqueous solution. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 227, 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.02.025
Hua, M., Zhang, S., Pan, B., Zhang, W., Lv, L., & Zhang, Q. (2012). Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: a review. Journal of hazardous materials, 211, 317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.016
Ibrahim, H. S., Jamil, T. S., & Hegazy, E. Z. (2010). Application of zeolite prepared from Egyptian kaolin for the removal of heavy metals: II. Isotherm models. Journal of Hazardous materials, 182(1-3), 842–847.
Janaki, N. J. S., Jebakumar, D. I., & Premkumar, P. S. (2022). Studies on the physical properties of green synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticles using Melia Dubia leaf extract. Materials Today: Proceedings, 58, 850–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.10.035
Kannan, S. K., & Sundrarajan, M. (2014). A green approach for the synthesis of a cerium oxide nanoparticle: characterization and antibacterial activity. International Journal of Nanoscience, 13(03), 1450018.
Kashyap, K., Khan, F., Verma, D. K., & Agrawal, S. (2022). Effective removal of uranium from aqueous solution by using cerium oxide nanoparticles derived from citrus limon peel extract. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08138-4
Kumar, S., Nair, R. R., Pillai, P. B., Gupta, S. N., Iyengar, M. A. R., & Sood, A. K. (2014). Graphene oxide–MnFe2O4 magnetic nanohybrids for efficient removal of lead and arsenic from water. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 6(20), 17426–17436. https://doi.org/10.1021/am504826q
Lagashetty, A. N. (2015). Green Synthesis and characterization of Silver nanoparticles using Piper betle leaf extract. Bulletin of Advanced Scientific Research, 1(5), 136–138.
Liu, T., Han, X., Wang, Y., Yan, L., Du, B., Wei, Q., & Wei, D. (2017). Magnetic chitosan/anaerobic granular sludge composite: synthesis, characterization and application in heavy metal ions removal. Journal of colloid and interface science, 508, 405–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.067
Liu, X., Huang, Y., Duan, S., Wang, Y., Li, J., Chen, Y., Hayat, T., & Wang, X. (2016). Graphene oxides with different oxidation degrees for Co (II) ion pollution management. Chemical Engineering Journal, 302, 763–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.107
Liu, Z., Wang, H., Liu, C., Jiang, Y., Yu, G., Mu, X., & Wang, X. (2012). Magnetic cellulose- chitosan hydrogels prepared from ionic liquids as reusable adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions. Chemical Communications, 48(59), 7350–7352. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC17795A
Luo, X., Zeng, J., Liu, S., & Zhang, L. (2015). An effective and recyclable adsorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system: magnetic chitosan/cellulosemicrospheres. Bioresource technology, 194, 403–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.044
Mahmud, H. N. M. E., Haq, A. K. O., & Yahya, R. B. (2015). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater aqueous solution by polypyrrole-based adsorbent. Royal Society of Chemistry, 6, 1–13.
Maleki, P., Nemati, F., Gholoobi, A., Hashemzadeh, A., Sabouri, Z., & Darroudi, M. (2021). Green facile synthesis of silver-doped cerium oxide nanoparticles and investigation of their cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 131, 108762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108762
Maqbool, Q., Nazar, M., Naz, S., Hussain, T., Jabeen, N., Kausar, R., Anwaar, S., Abbas, F., & Jan, T. (2016). Antimicrobial potential of green synthesized CeO2 nanoparticles from Olea europaea leaf extract. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 11, 5015. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S113508
Meepho, M., Sirimongkol, W., & Ayawanna, J. (2018). Samaria-doped ceria nanopowders for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 214, 56–65.
Miri, A., Beiki, H., Najafidoust, A., Khatami, M., & Sarani, M. (2021). Cerium oxide nanoparticles: green synthesis using Banana peel, cytotoxic effect, UV protection and their photocatalytic activity. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 44(9), 1891–1899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-021-02569-9
Mishra, S. R., & Ahmaruzzaman, M. (2021). Cerium oxide and its nanocomposites: Structure, synthesis, and wastewater treatment applications. Materials Today Communications, 28, 102562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102562
Phuengprasop, T., Sittiwong, J., & Unob, F. (2011). Removal of heavy metal ions by iron oxide coated sewage sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(1), 502–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.065
Ren, Y., Abbood, H. A., He, F., Peng, H., & Huang, K. (2013). Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbent: preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 226, 300–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.059
Sebastiammal, S., Sonia, S., Henry, J., & Fathima, A. L. (2021). Green synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using aloevera leaf extract and its optical properties. Songklanakarin Journal of Science & Technology, 43(2).
Sitko, R., Musielak, M., Zawisza, B., Talik, E., & Gagor, A. (2016). Graphene oxide/cellulose membranes in adsorption of divalent metal ions. RSC Advances, 6(99), 96595–96605. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA21432K
Vidu, R., Matei, E., Predescu, A. M., Alhalaili, B., Pantilimon, C., Tarcea, C., & Predescu, C. (2020). Removal of heavy metals from wastewaters: A challenge from current treatment methods to nanotechnology applications. Toxics, 8(4), 101.
Yiling, W., Murakonda, G. K., & Jarubula, R. (2021). Application of green-synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticles to treat spinal cord injury and cytotoxicity evaluation on paediatric leukaemia cells. Materials Research Express, 8(7), 075006. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ac0fad
Zhao, G., Li, C., Wu, X., Yu, J., Jiang, X., Hu, W., & Jiao, F. (2018). Reduced graphene oxide modified NiFe-calcinated layered double hydroxides for enhanced photocatalytic removal of methylene blue. Applied Surface Science, 434, 252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.181
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful the Department of Chemistry at the National Institute of Technology Raipur, India for providing the research facilities. One of the authors, Komal Kashyap, expresses gratitude to the CSIR-UGC NET for the fellowship (File number 09/1116(0007)/2018-EMR-I).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No conflicts of interest have been disclosed by the authors of this research.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kashyap, K., Moharana, M., Pattanayak, S.K. et al. Effective Removal of Pb(II), Cr(VI), and Cd(II) Ions from Water Using Environmentally Friendly Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized from Pods of Pisum sativum. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 276 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07092-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07092-7